Unveiling the World from a New Perspective: Exploring the Vertical World Map
Related Articles: Unveiling the World from a New Perspective: Exploring the Vertical World Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the World from a New Perspective: Exploring the Vertical World Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the World from a New Perspective: Exploring the Vertical World Map
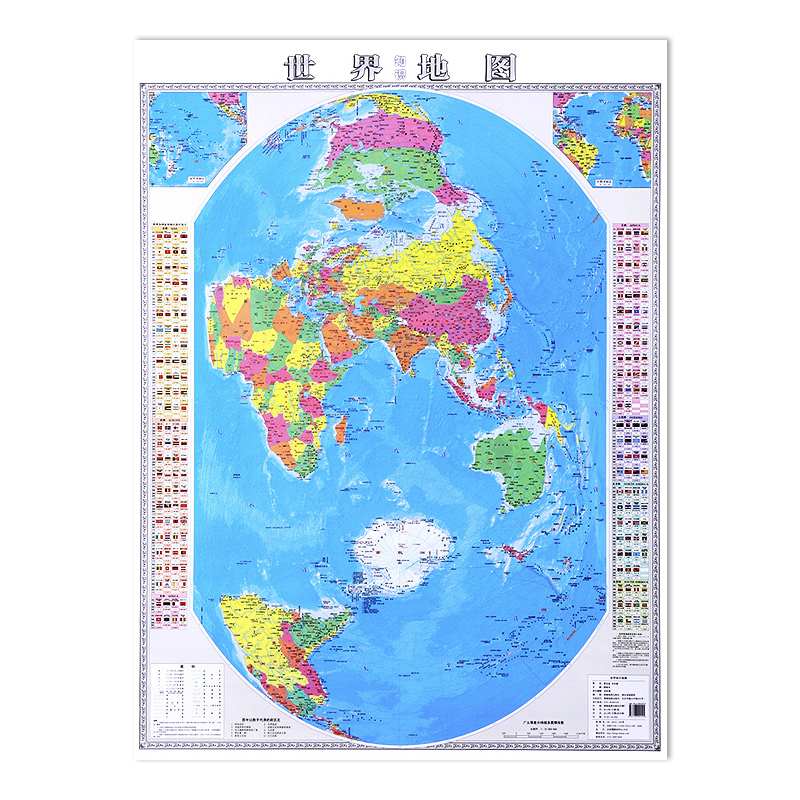
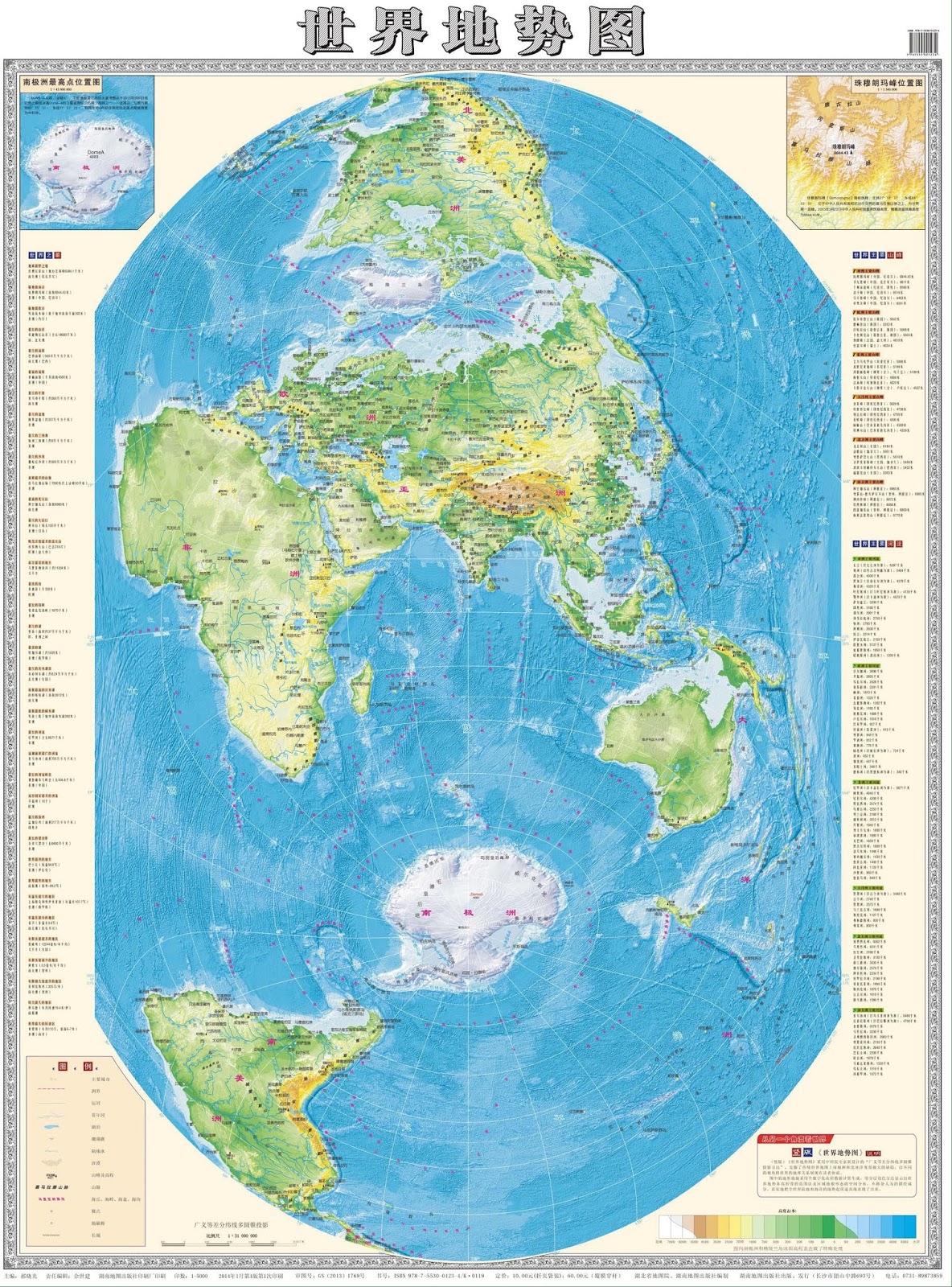
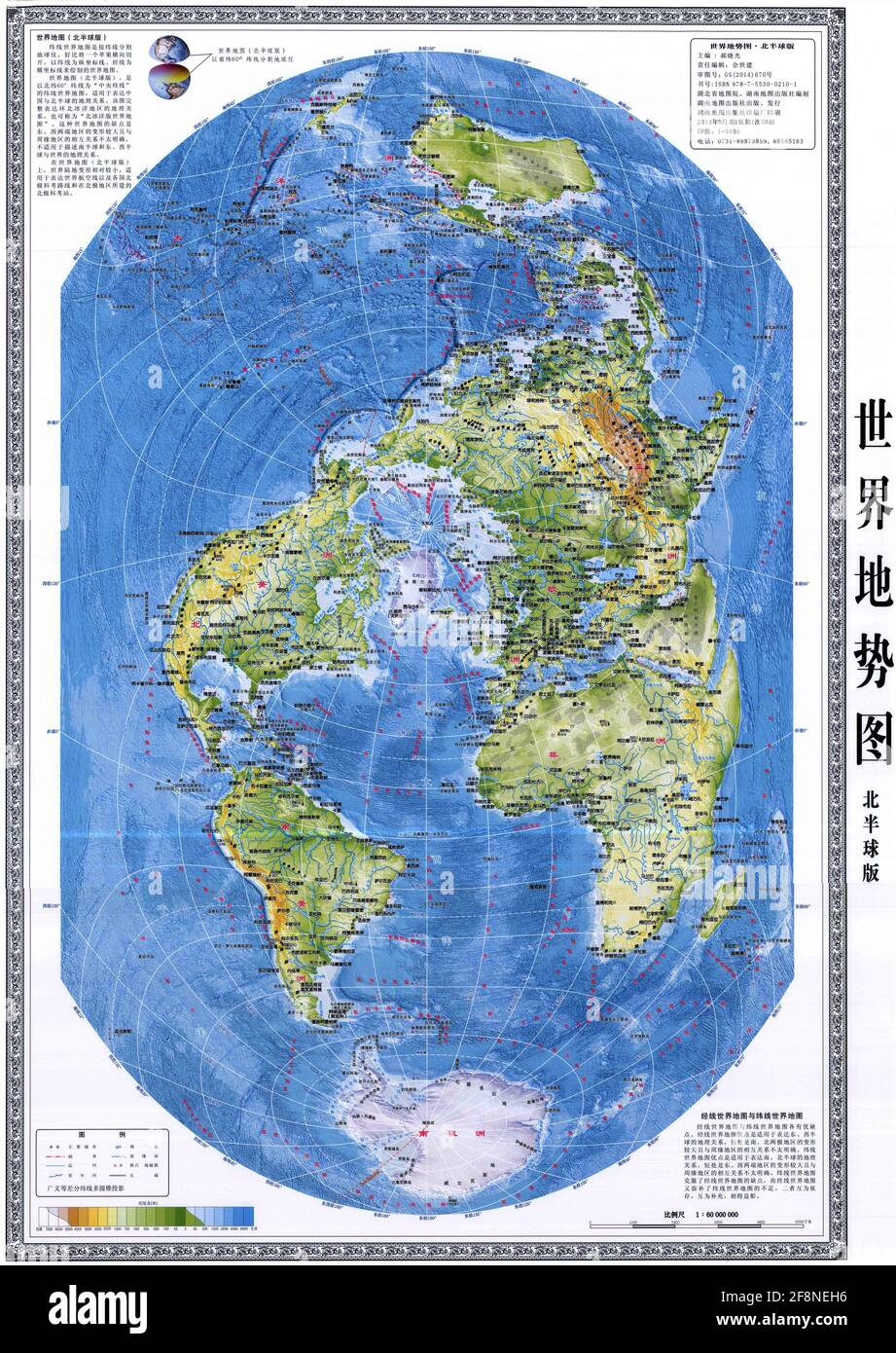
The world map, a ubiquitous tool for understanding our planet’s geography, is typically presented in a horizontal orientation. However, a lesser-known yet equally valuable perspective exists: the vertical world map. This unconventional representation, with the North Pole at the top and the South Pole at the bottom, offers a unique and insightful view of the world, challenging traditional perceptions and revealing hidden connections.
Breaking Free from the Horizontal: The Advantages of a Vertical World Map
The horizontal world map, with its familiar depiction of continents sprawling east to west, has become ingrained in our collective consciousness. Yet, this representation can inadvertently distort our understanding of global relationships and geographic realities. The vertical world map, by contrast, offers several distinct advantages:
-
A More Accurate Representation of Geographic Proportions: The horizontal world map, due to its projection method, often distorts the size and shape of continents, particularly those closer to the poles. The vertical world map, by preserving relative distances and shapes, provides a more accurate visual representation of the Earth’s landmasses.
-
A Fresh Perspective on Global Connectivity: By aligning the North and South Poles vertically, the vertical world map emphasizes the interconnectedness of continents, particularly those in the Northern Hemisphere. This perspective highlights the crucial role of the Arctic region in global climate and geopolitical dynamics.
-
Enhanced Understanding of Climate Patterns: The vertical orientation allows for a clearer visualization of global climate zones and patterns. The vertical arrangement of continents reveals how latitude directly influences temperature and precipitation, leading to a better understanding of climate variability.
-
A More Inclusive and Equitable View of the World: The horizontal world map, with its focus on the Northern Hemisphere, often inadvertently marginalizes countries in the Southern Hemisphere. The vertical world map, by positioning the equator at the center, provides a more balanced and inclusive representation of all regions.
Delving Deeper: The History and Evolution of the Vertical World Map
The concept of a vertical world map has been explored by cartographers and geographers for centuries. Early iterations often relied on cylindrical projections, which, while preserving the shapes of landmasses, could distort their relative sizes.
The advent of modern cartographic techniques, particularly the development of the Mercator projection, led to the widespread adoption of the horizontal world map. However, the vertical world map has continued to garner interest, particularly in academic circles, as a tool for promoting a more accurate and balanced understanding of the world.
Beyond the Traditional: Exploring Different Vertical World Map Variations
The vertical world map is not a singular concept but rather a family of projections, each with its own unique characteristics and advantages. Some notable variations include:
-
The Gall-Peters Projection: This projection preserves the relative areas of continents but distorts their shapes, making it ideal for visualizing global population distribution and resource allocation.
-
The Winkel Tripel Projection: This projection balances area distortion and shape distortion, providing a relatively accurate and aesthetically pleasing representation of the world.
-
The Goode Homolosine Projection: This projection, known for its distinctive "interrupted" appearance, minimizes area distortion and accurately portrays the shapes of continents, making it suitable for visualizing global climate patterns and oceanic currents.
Understanding the Vertical World Map: FAQs
1. What is the purpose of a vertical world map?
The primary purpose of a vertical world map is to provide a more accurate and inclusive representation of the world, challenging the distortions inherent in traditional horizontal maps. It offers a fresh perspective on global relationships, climate patterns, and geographic proportions.
2. How does a vertical world map differ from a horizontal world map?
The most significant difference lies in the orientation. A vertical world map aligns the North Pole at the top and the South Pole at the bottom, while a horizontal world map positions them at the edges. This change in orientation alters the perception of continents and their relative positions.
3. Are vertical world maps more accurate than horizontal world maps?
While no map projection can perfectly represent the spherical Earth on a flat surface, vertical world maps, particularly those based on equal-area projections, minimize area distortion and provide a more accurate representation of global proportions.
4. Why is the vertical world map not as widely used as the horizontal world map?
The horizontal world map, due to its familiarity and historical dominance, remains the dominant representation of the world. However, the vertical world map is gaining traction in academic and educational contexts as a tool for fostering a more balanced and accurate understanding of global relationships.
5. Can I use a vertical world map for navigation?
Vertical world maps, while useful for visualizing global relationships and proportions, are not typically used for navigation. Navigation tools rely on specific projections designed for accurate distance and direction calculations.
Tips for Using a Vertical World Map
-
Embrace the Unfamiliar: Approach the vertical world map with an open mind, recognizing that its unconventional orientation may challenge your preconceived notions about global geography.
-
Focus on Global Connections: Utilize the vertical perspective to explore the interconnectedness of continents, particularly in the Northern Hemisphere, and the role of the Arctic region in global dynamics.
-
Visualize Climate Patterns: Use the vertical arrangement of continents to understand how latitude influences temperature and precipitation, leading to a deeper understanding of climate variability.
-
Consider Different Projections: Explore various vertical world map projections, such as the Gall-Peters or the Winkel Tripel, to find the best representation for your specific needs and interests.
-
Engage in Critical Thinking: Use the vertical world map as a tool for critical analysis, questioning the assumptions and biases inherent in traditional representations of the world.
Conclusion: A New Lens for Understanding Our World
The vertical world map, though often overlooked, offers a valuable and insightful perspective on our planet. By challenging conventional representations and highlighting the interconnectedness of continents, it encourages a more accurate, balanced, and inclusive understanding of global relationships, climate patterns, and geographic proportions. As we strive to navigate a complex and interconnected world, embracing new perspectives, such as those offered by the vertical world map, is essential for fostering a deeper and more nuanced understanding of our planet and its inhabitants.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the World from a New Perspective: Exploring the Vertical World Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
