Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Latitudinal Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Latitudinal Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Latitudinal Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Latitudinal Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Latitudinal Maps
- 3.1 Understanding Latitudinal Maps: A Visual Representation of Latitude
- 3.2 The Mechanics of Latitudinal Projections: A Deep Dive
- 3.3 Advantages and Limitations: A Balanced Perspective
- 3.4 Beyond the Basics: Exploring Variations and Applications
- 3.5 Frequently Asked Questions: Addressing Common Concerns
- 3.6 Tips for Effective Use of Latitudinal Maps
- 3.7 Conclusion: A Powerful Tool for Visualizing the World
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Latitudinal Maps

The Earth, a vast and intricate sphere, holds countless wonders and diverse landscapes. To navigate and understand this complex globe, cartographers have devised numerous map projections, each with its unique strengths and limitations. Among these, latitudinal maps stand out as powerful tools for visualizing and analyzing the world’s spatial patterns, particularly those influenced by latitude.
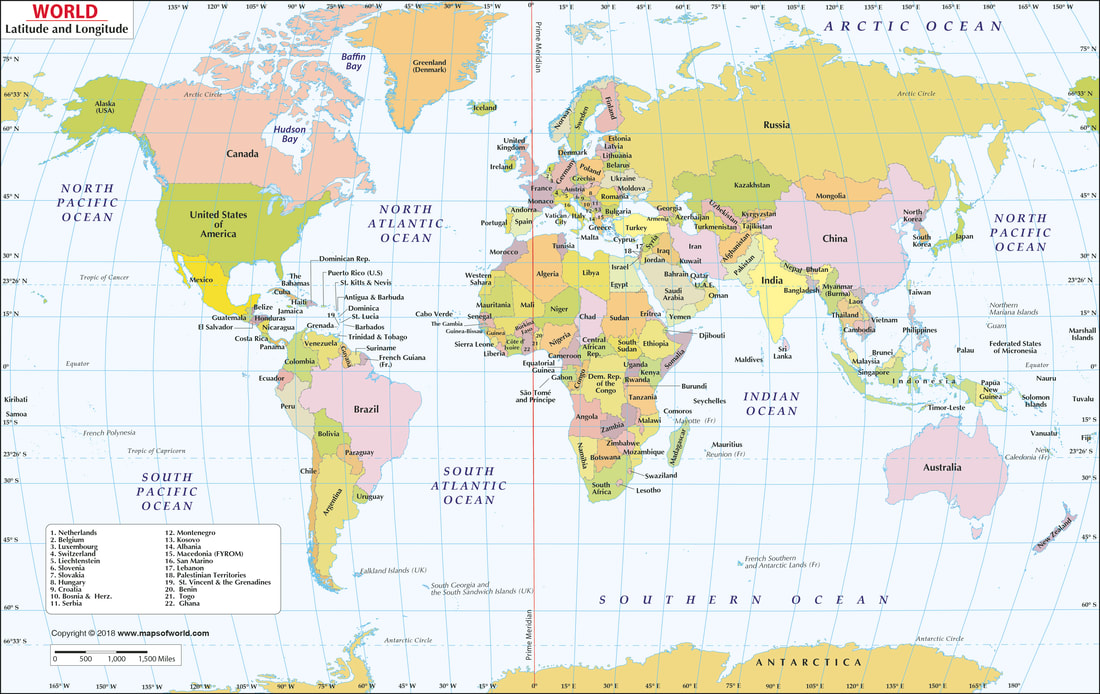
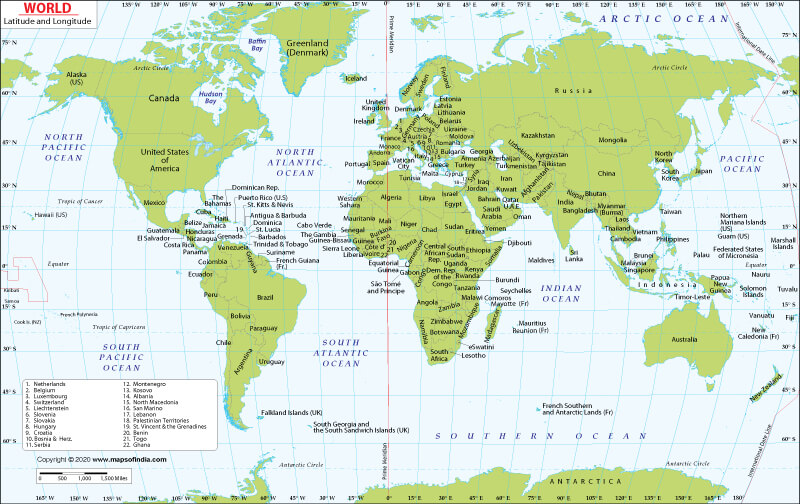
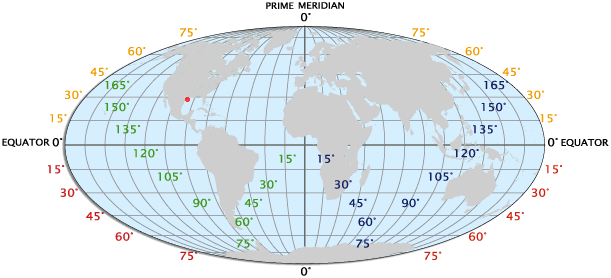
Understanding Latitudinal Maps: A Visual Representation of Latitude
Latitudinal maps, also known as equirectangular projections, are a specific type of map projection that prioritizes the accurate depiction of latitude. They achieve this by preserving the true distance along the equator and the meridians (lines of longitude). This characteristic makes them particularly useful for visualizing and analyzing phenomena that exhibit a strong latitudinal dependence, such as:
- Climate Zones: Latitudinal maps effectively display the Earth’s major climate zones, which are largely determined by the angle of the sun’s rays at different latitudes. This visual representation highlights the distinct climatic characteristics of equatorial, tropical, temperate, and polar regions.
- Biogeographic Regions: The distribution of plant and animal life often follows latitudinal patterns, influenced by factors like temperature, rainfall, and sunlight. Latitudinal maps provide a clear visual representation of these biogeographic regions, showcasing the distinct ecosystems found at different latitudes.
- Global Trade Routes: Historically, trade routes have often followed latitudinal lines, facilitating the exchange of goods and ideas across continents. Latitudinal maps effectively illustrate these historical pathways, connecting different regions and cultures.
The Mechanics of Latitudinal Projections: A Deep Dive
Latitudinal maps employ a specific projection method known as the equirectangular projection. This projection unfolds the Earth’s surface onto a flat plane, with the equator serving as the central line. The meridians are then projected as parallel lines, creating a grid system where distances along the equator are accurately represented. However, this projection distorts the size and shape of landmasses as they move further away from the equator.
The distortion inherent in latitudinal maps is a crucial aspect to understand. While they excel at preserving distances along the equator and meridians, they inevitably exaggerate the size of landmasses at higher latitudes. This distortion can lead to misinterpretations if not accounted for, especially when comparing the size of countries or continents at different latitudes.
Advantages and Limitations: A Balanced Perspective
Latitudinal maps offer several advantages:
- Simplicity and Clarity: Their straightforward grid system makes them easy to understand and interpret, particularly for visualizing latitudinal trends and patterns.
- Accurate Representation of Latitude: The preservation of distances along the equator and meridians ensures an accurate depiction of latitude, making them ideal for analyzing phenomena influenced by this factor.
- Versatility: Latitudinal maps can be used for various purposes, from displaying climate zones and biogeographic regions to illustrating historical trade routes and global population distribution.
However, their limitations should also be considered:
- Distortion at Higher Latitudes: The increasing distortion of landmasses as they move away from the equator can lead to misinterpretations regarding size and shape.
- Limited Use for Specific Applications: Their focus on latitude makes them less suitable for applications requiring accurate representations of areas near the poles or for displaying local features.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Variations and Applications
While the basic equirectangular projection forms the foundation of latitudinal maps, variations exist to address specific needs. For example, cylindrical projections offer a more accurate representation of the Earth’s surface, while conical projections are particularly useful for mapping specific regions.
Furthermore, the application of latitudinal maps extends beyond traditional cartography. They are increasingly employed in fields like:
- Environmental Science: Analyzing climate change patterns, tracking deforestation, and understanding biodiversity distribution.
- Social Sciences: Studying population density, migration patterns, and the impact of globalization.
- Economics: Visualizing trade routes, global commodity flows, and economic development trends.
Frequently Asked Questions: Addressing Common Concerns
Q: Are latitudinal maps accurate?
A: Latitudinal maps are accurate in their representation of latitude, preserving distances along the equator and meridians. However, they distort the size and shape of landmasses as they move away from the equator.
Q: What are the advantages of using latitudinal maps?
A: Latitudinal maps offer simplicity, clarity, and accurate representation of latitude, making them ideal for visualizing and analyzing phenomena influenced by this factor.
Q: What are the limitations of latitudinal maps?
A: The major limitation is the distortion of landmasses at higher latitudes, which can lead to misinterpretations regarding size and shape.
Q: What are some alternative map projections?
A: Cylindrical projections, conical projections, and azimuthal projections offer different advantages and limitations, depending on the specific application.
Q: How can I use latitudinal maps in my work or studies?
A: Latitudinal maps are valuable tools for various applications, from analyzing climate patterns to understanding population distribution. Choose the appropriate variation and consider the limitations to ensure accurate interpretation.
Tips for Effective Use of Latitudinal Maps
- Understand the Projection: Be aware of the inherent distortion of landmasses at higher latitudes to avoid misinterpretations.
- Consider the Application: Choose the appropriate variation of latitudinal maps based on the specific purpose and data being visualized.
- Compare with Other Projections: Use different projections to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the data and identify potential biases.
- Consult Expert Resources: Utilize cartographic resources and professional guidance for advanced applications and interpretation.
Conclusion: A Powerful Tool for Visualizing the World
Latitudinal maps, despite their inherent limitations, offer a valuable tool for understanding and visualizing the world’s spatial patterns. Their accurate representation of latitude and straightforward grid system make them ideal for analyzing phenomena influenced by this factor, from climate zones to global trade routes. By understanding their strengths and limitations, users can effectively utilize these maps to gain insights into the complex and interconnected world we inhabit.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Latitudinal Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
