Unveiling the Tapestry of Trade: A Journey Through the Ancient Silk Road
Related Articles: Unveiling the Tapestry of Trade: A Journey Through the Ancient Silk Road
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Tapestry of Trade: A Journey Through the Ancient Silk Road. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Tapestry of Trade: A Journey Through the Ancient Silk Road

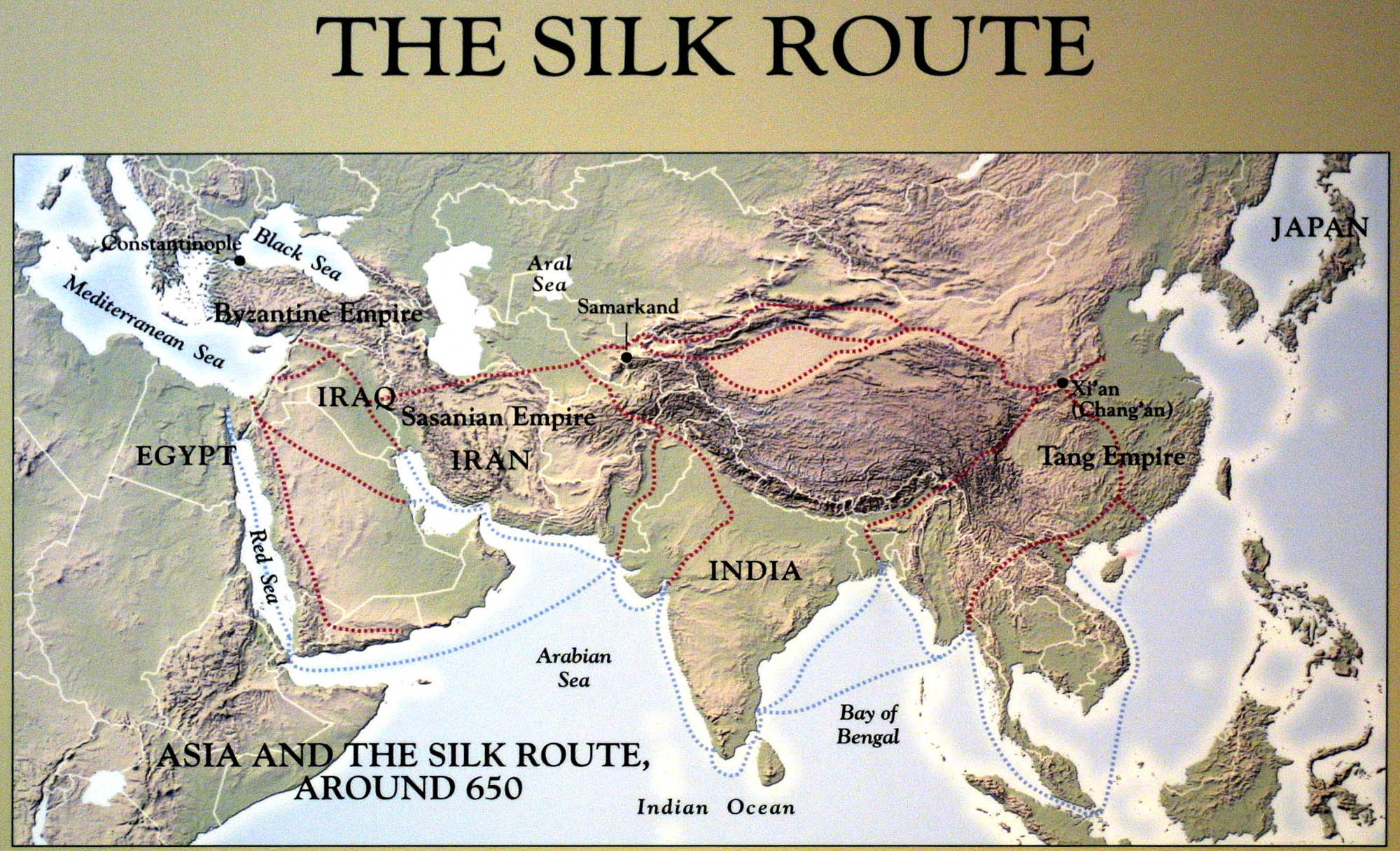
The Silk Road, a network of trade routes stretching across Eurasia for over 1,500 years, stands as a testament to the interconnectedness of ancient civilizations. Its legacy extends far beyond the physical path, encompassing cultural exchange, technological advancements, and the very fabric of global trade. This article delves into the map of the ancient Silk Road, exploring its intricate routes, pivotal cities, and the enduring impact it left on the world.
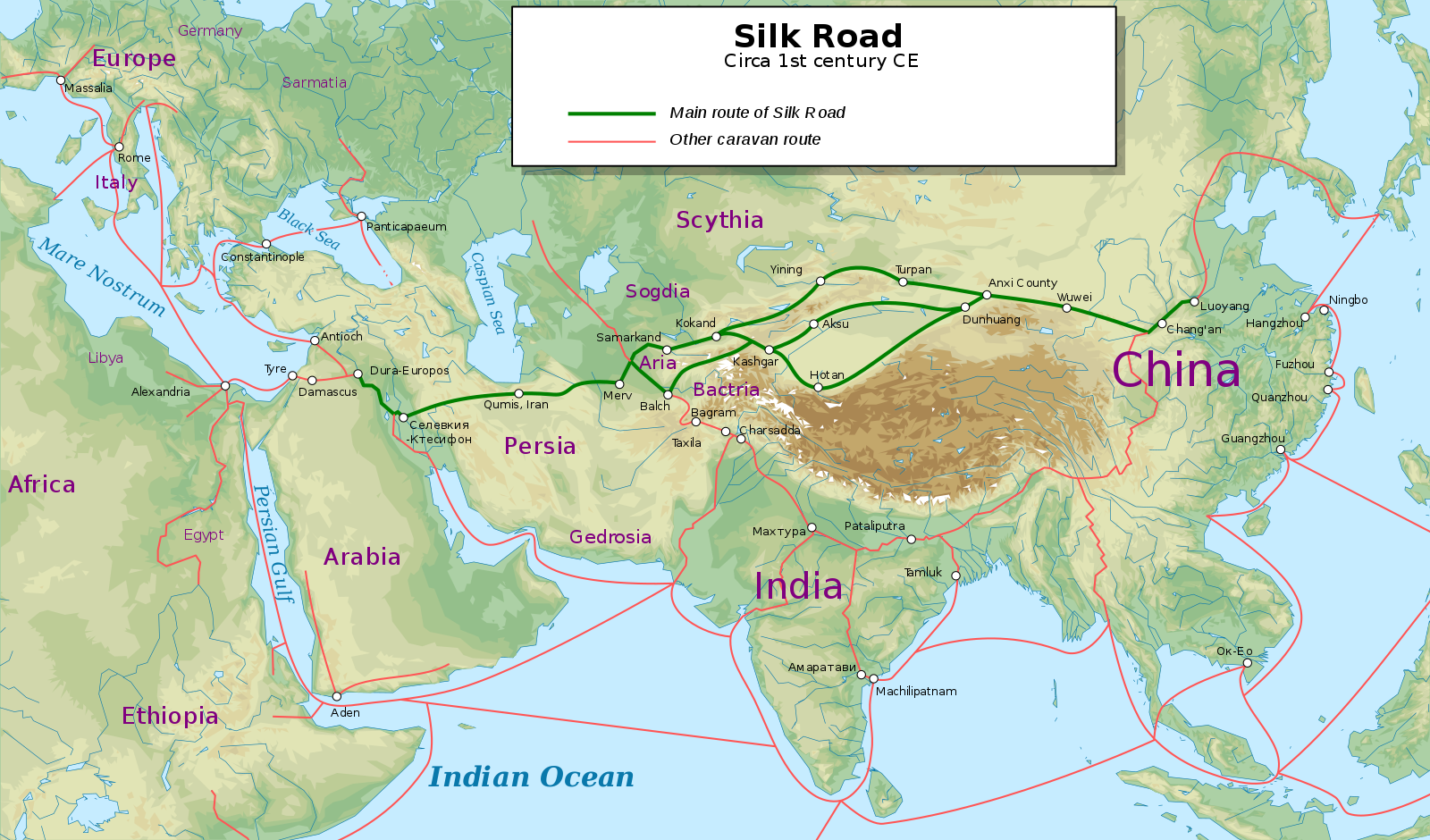
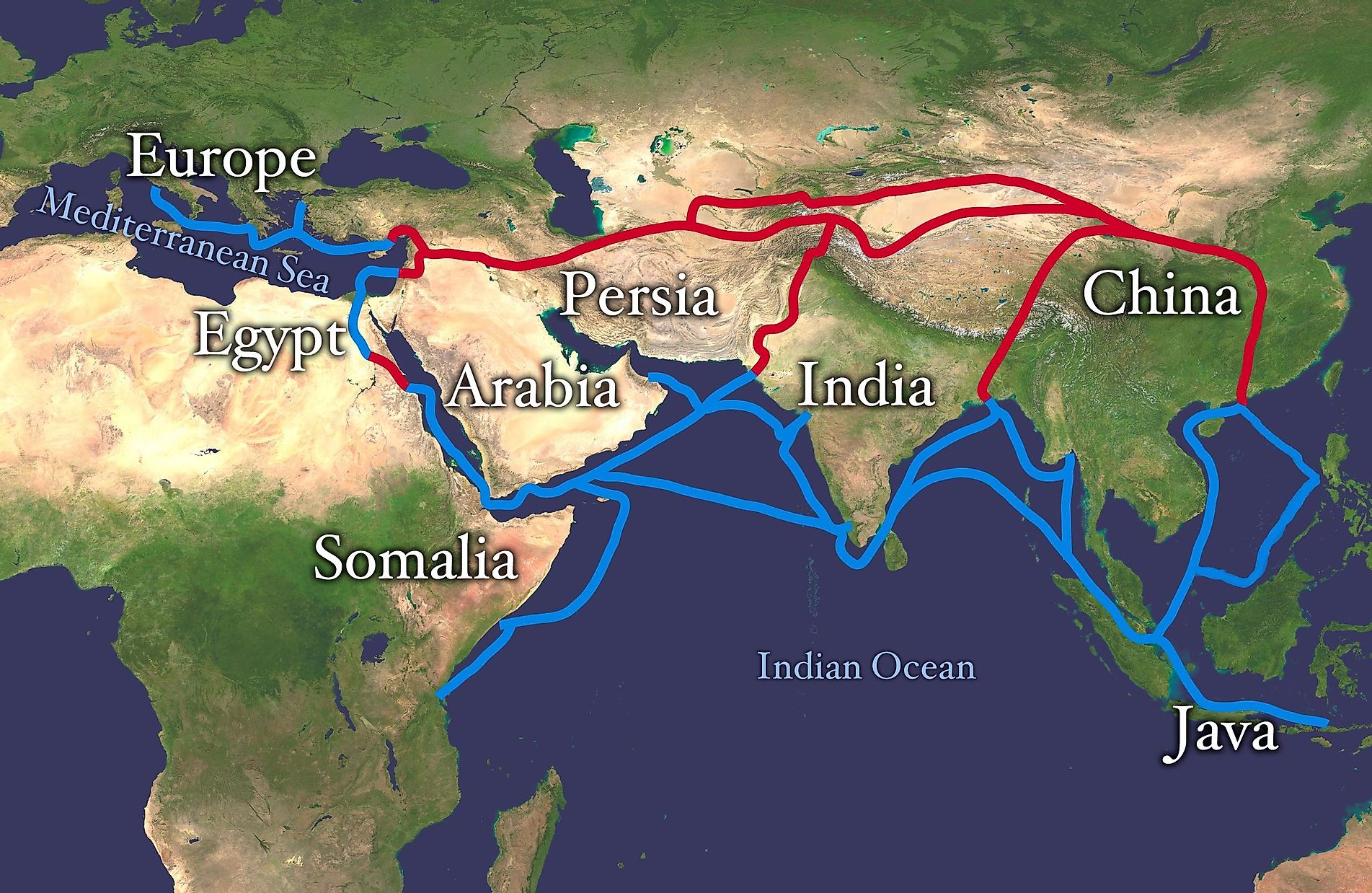
A Network of Routes, Not a Single Path
Contrary to popular perception, the Silk Road was not a singular, well-defined path. Instead, it comprised a complex network of routes, adapting to changing political landscapes and geographical constraints. These routes, primarily land-based, spanned over 4,000 miles, connecting the bustling cities of ancient China in the east to the vibrant metropolises of the Roman Empire in the west.
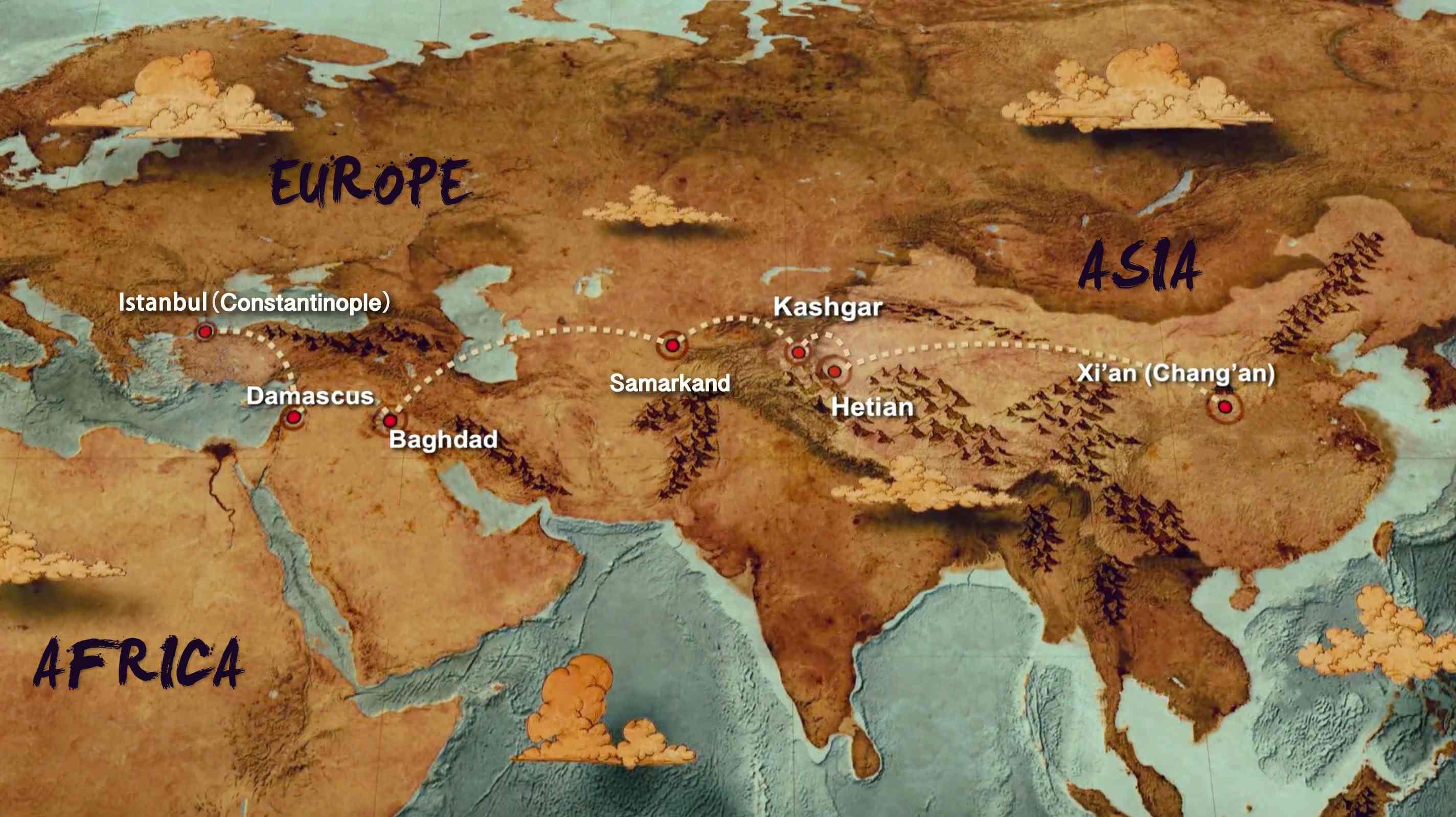
The Eastern Hub: The Starting Point of the Silk Road
The Silk Road originated in the heart of China, with the city of Xi’an (formerly Chang’an) serving as its eastern terminus. This ancient capital, renowned for its grand palaces and bustling markets, was a key hub for trade, with silk, porcelain, and tea being among the coveted goods exported from China.
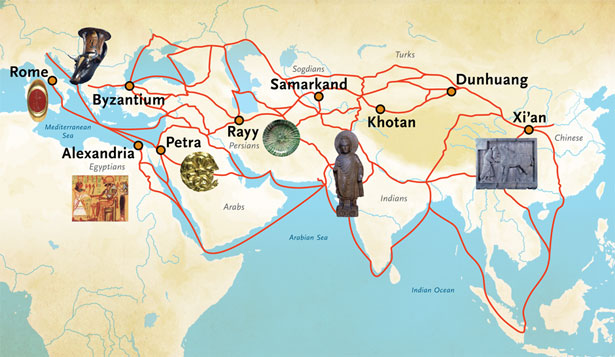
Key Cities Along the Silk Road
The Silk Road was not merely a path; it was a tapestry woven together by a multitude of cities, each playing a distinct role in the exchange of goods and ideas. Here are some of the most prominent cities along the route:
-
Samarkand (Uzbekistan): This city, strategically situated at the crossroads of trade routes, flourished as a center for cultural exchange and artistic expression. It was renowned for its exquisite architecture, including the iconic Registan complex.
-
Bukhara (Uzbekistan): Another major trading hub, Bukhara was a center for Islamic scholarship and learning. Its grand mosques and madrasas attracted scholars from across the Islamic world, contributing to the city’s reputation as a center of knowledge.
-
Kashgar (China): Located in the westernmost part of China, Kashgar served as a critical link between the Silk Road and Central Asia. Its vibrant bazaars offered a diverse array of goods, reflecting the city’s role as a melting pot of cultures.
-
Bactra (Afghanistan): This ancient city, once a flourishing center of Hellenistic culture, became a vital stop on the Silk Road, facilitating trade between Central Asia and the west.
-
Antioch (Turkey): A prominent city in the Roman Empire, Antioch was a major port of entry for goods arriving from the east. Its strategic location and bustling markets made it a key player in the Silk Road trade.
Beyond Trade: The Cultural Impact of the Silk Road
The Silk Road’s impact extended far beyond the exchange of goods. It facilitated the transmission of ideas, knowledge, and cultural practices across vast distances, leading to a remarkable fusion of cultures.
-
Religious Exchange: Buddhism, originating in India, spread eastward along the Silk Road, finding fertile ground in China and other parts of East Asia. Similarly, Christianity and Islam also traveled westward, leaving an indelible mark on the cultures of the regions they traversed.
-
Technological Innovation: The Silk Road served as a conduit for the transmission of technological advancements. Innovations like papermaking, gunpowder, and the compass traveled from China to the west, while the printing press and the astrolabe made their way eastward.
-
Artistic Influence: The Silk Road fostered the exchange of artistic styles and motifs. From the exquisite silk tapestries of China to the intricate mosaics of the Roman Empire, the influence of the Silk Road can be seen in the artistic creations of the time.
The Decline and Legacy of the Silk Road
The Silk Road’s golden age came to an end in the late Middle Ages, primarily due to political instability, the rise of maritime trade, and the Mongol conquests. However, its legacy continues to resonate in the modern world.
-
Cultural Heritage: The Silk Road’s influence can be seen in the architectural marvels, artistic expressions, and cultural traditions of the regions it once connected.
-
Global Trade: The Silk Road’s spirit of international exchange continues to inspire modern trade and economic cooperation.
-
Tourism and Development: The Silk Road has become a popular tourist destination, offering a glimpse into the past and promoting economic development in the regions it traversed.
FAQs About the Silk Road
1. What was the primary purpose of the Silk Road?
The Silk Road was primarily a network of trade routes facilitating the exchange of goods between the east and west. It served as a conduit for the movement of silk, spices, porcelain, precious metals, and other valuable commodities.
2. What were some of the key goods traded along the Silk Road?
Besides silk, other key goods traded along the Silk Road included spices (like pepper, cinnamon, and cloves), porcelain, jade, tea, textiles, glassware, precious metals, and even slaves.
3. How did the Silk Road impact cultural exchange?
The Silk Road facilitated the transmission of ideas, knowledge, and religious beliefs across vast distances, leading to a remarkable fusion of cultures. Buddhism, Christianity, and Islam all spread along the route, influencing the cultural landscape of the regions they traversed.
4. What factors led to the decline of the Silk Road?
The decline of the Silk Road was attributed to a combination of factors, including political instability, the rise of maritime trade, and the Mongol conquests, which disrupted trade routes and led to economic decline.
5. What is the significance of the Silk Road in the modern world?
The Silk Road’s legacy continues to influence the modern world through its cultural heritage, its role in promoting global trade, and its potential for tourism and economic development.
Tips for Exploring the Silk Road Today
- Plan your itinerary carefully: The Silk Road is vast and diverse. Consider your interests and time constraints when planning your trip.
- Research local customs and traditions: Respecting local customs is essential for a positive travel experience.
- Learn a few basic phrases in the local language: Even a few basic phrases can go a long way in enhancing your interactions with locals.
- Be prepared for cultural differences: The Silk Road traversed a diverse range of cultures, and you should be prepared for differences in customs, traditions, and ways of life.
- Take time to explore the local markets: The markets along the Silk Road offer a glimpse into the vibrant cultural tapestry of the region.
Conclusion
The Silk Road stands as a testament to the enduring power of trade and cultural exchange. Its intricate network of routes, bustling cities, and vibrant cultural tapestry left an indelible mark on the world, influencing the flow of goods, ideas, and people for over 1,500 years. Its legacy continues to resonate in the modern world, reminding us of the interconnectedness of civilizations and the transformative power of human interaction. By understanding the map of the ancient Silk Road, we gain a deeper appreciation for the rich history and cultural heritage that shaped our world today.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Tapestry of Trade: A Journey Through the Ancient Silk Road. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
