Unveiling the Student Journey: A Comprehensive Guide to Mapping the Educational Experience
Related Articles: Unveiling the Student Journey: A Comprehensive Guide to Mapping the Educational Experience
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Student Journey: A Comprehensive Guide to Mapping the Educational Experience. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Student Journey: A Comprehensive Guide to Mapping the Educational Experience

In the ever-evolving landscape of education, understanding the student experience is paramount. From initial interest to graduation, students traverse a complex journey shaped by numerous touchpoints, interactions, and emotions. A potent tool for illuminating this journey is the student journey map, a visual representation that charts the student’s experiences, motivations, and pain points across various stages of their educational engagement.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of student journey maps, exploring their construction, applications, and the invaluable insights they provide.
Understanding the Foundation: What is a Student Journey Map?
A student journey map is a visual representation of the student’s experience with an educational institution or program. It is a dynamic, interactive tool that captures the student’s perspective at each stage of their journey, from initial awareness to post-graduation. The map goes beyond simply outlining the steps involved; it delves into the student’s thoughts, feelings, and actions at every touchpoint.
Constructing a Meaningful Map: Key Elements and Stages
Creating a comprehensive student journey map requires a structured approach that incorporates essential elements:
-
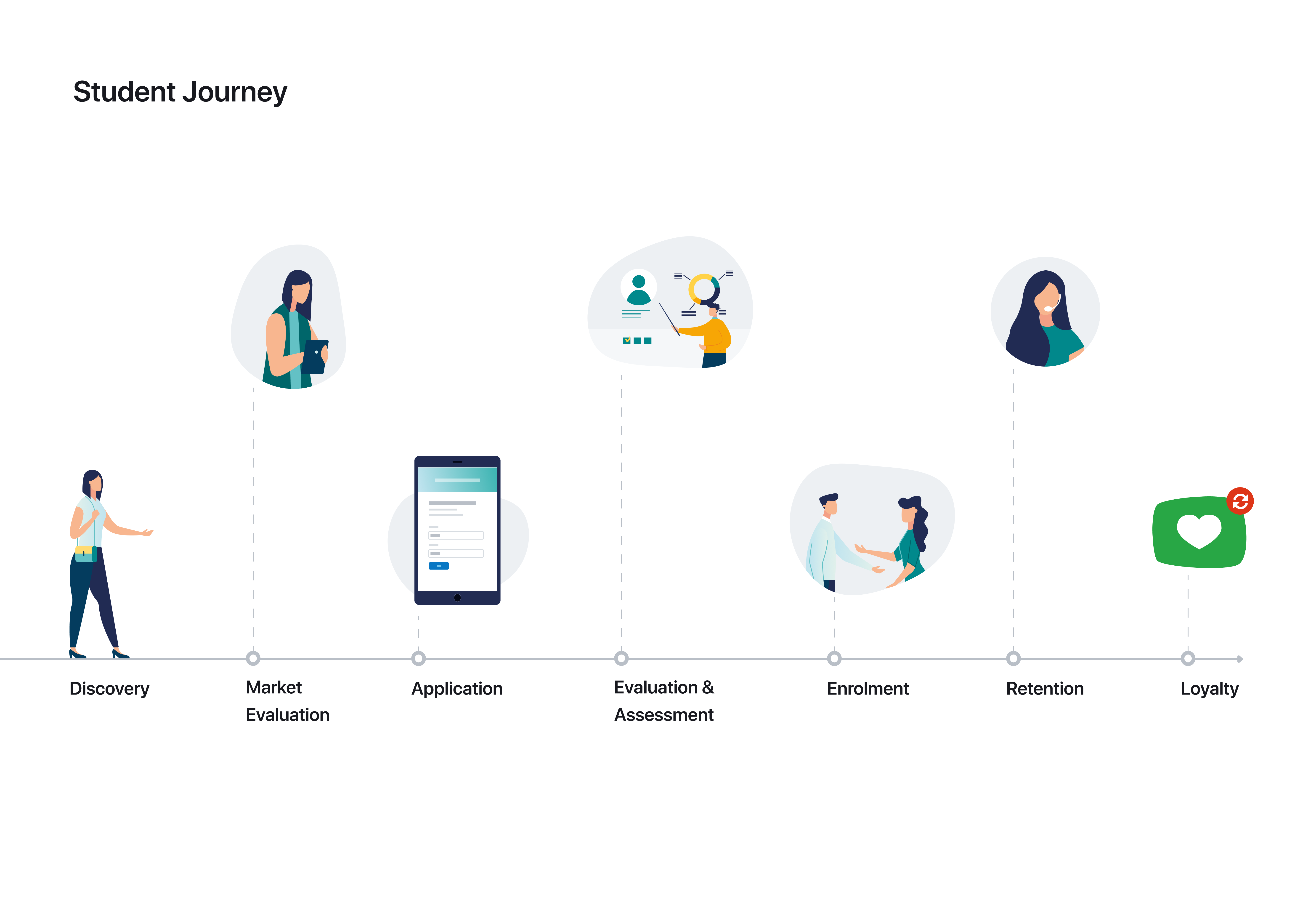
Identify the Stages: The journey is divided into distinct stages, each representing a significant phase in the student’s experience. These stages can vary depending on the context, but common examples include:
- Awareness: The initial stage where the student becomes aware of the educational institution or program.
- Consideration: The stage where the student explores options, gathers information, and weighs different choices.
- Decision: The stage where the student makes a definitive decision to enroll.
- Enrollment: The stage where the student completes the enrollment process and becomes an official student.
- Onboarding: The stage where the student acclimates to the new environment and begins their studies.
- Engagement: The stage where the student actively participates in their studies and interacts with the institution.
- Graduation: The stage where the student successfully completes their program and receives their degree or certification.
- Alumni: The stage where the student becomes an alumnus of the institution, maintaining a connection and potentially contributing to the institution’s community.
-
Define Touchpoints: Each stage consists of specific touchpoints, representing interactions between the student and the institution or program. These touchpoints can be online or offline, and they encompass:
- Website: The institution’s website, including its content, design, and functionality.
- Social Media: The institution’s presence on social media platforms, including their content, engagement, and responsiveness.
- Marketing Materials: Brochures, flyers, advertisements, and other promotional materials.
- Admissions Process: The process of applying, interviewing, and receiving acceptance.
- Orientation: Welcome events, workshops, and introductory programs for new students.
- Academic Advising: Interactions with academic advisors regarding course selection, program planning, and academic progress.
- Faculty and Staff: Interactions with professors, instructors, and other staff members.
- Peer Interactions: Interactions with fellow students, both in and out of the classroom.
- Campus Events: Social events, extracurricular activities, and other campus-wide activities.
- Career Services: Support and guidance regarding career exploration, job searching, and professional development.
- Alumni Network: Opportunities to connect with alumni, network, and seek mentorship.
-
Capture the Student Perspective: For each touchpoint, the map should capture the student’s:
- Thoughts: What the student thinks about the touchpoint, including their perceptions, expectations, and opinions.
- Feelings: How the student feels about the touchpoint, including their emotions, motivations, and frustrations.
- Actions: What the student does in response to the touchpoint, including their behaviors, decisions, and interactions.
- Pain Points: Any challenges, difficulties, or frustrations the student encounters at the touchpoint.
- Opportunities: Any potential areas for improvement, enhancement, or innovation.
Benefits of Student Journey Mapping: Unveiling Insights for Educational Success
The construction of a student journey map is not merely an academic exercise; it serves as a vital tool for improving the educational experience and achieving strategic objectives. The benefits of this approach are manifold:
-
Deepened Understanding of Student Needs: By capturing the student’s perspective at each stage, the map provides a nuanced understanding of their needs, motivations, and challenges. This knowledge empowers institutions to tailor their offerings and services to better meet student expectations.
-
Enhanced Student Engagement and Retention: By identifying pain points and opportunities for improvement, the map enables institutions to address student concerns and enhance their overall experience. This, in turn, fosters student engagement, satisfaction, and retention.
-
Improved Marketing and Recruitment Strategies: The map reveals the student’s journey from initial awareness to enrollment, highlighting the touchpoints that influence their decision-making. This enables institutions to optimize their marketing and recruitment strategies, attracting a wider pool of qualified candidates.
-
Streamlined Operations and Processes: By identifying inefficiencies and bottlenecks in the student journey, the map facilitates process optimization and resource allocation. This can lead to smoother operations, reduced administrative burden, and improved student satisfaction.
-
Data-Driven Decision-Making: The map provides a robust framework for collecting and analyzing data related to the student experience. This data can be used to inform decision-making, prioritize initiatives, and measure the impact of interventions.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Student Journey Maps
1. How is a student journey map different from a user journey map?
While both user journey maps and student journey maps aim to map the experience of individuals, they differ in their focus. User journey maps typically focus on the interactions of a customer with a product or service, while student journey maps center on the interactions of a student with an educational institution or program.
2. What are some common tools for creating student journey maps?
Various tools can be used to create student journey maps, depending on the desired level of detail and interactivity. Some popular options include:
- Spreadsheets: Simple, readily available tools for basic mapping.
- Mind Mapping Software: Tools like MindManager and XMind allow for visually representing relationships and connections.
- Diagramming Software: Tools like Lucidchart and Visio offer more advanced features for creating detailed, interactive maps.
- Collaborative Platforms: Tools like Miro and Mural enable collaborative mapping and real-time feedback.
3. How can we gather data for a student journey map?
Data collection methods for student journey maps can be qualitative or quantitative:
- Surveys: Questionnaires can be used to gather student feedback on their experiences, perceptions, and expectations.
- Interviews: One-on-one interviews provide in-depth insights into student perspectives and challenges.
- Focus Groups: Group discussions can uncover shared experiences, perceptions, and pain points.
- Observations: Observing student behavior and interactions can provide valuable insights into their real-time experiences.
- Data Analytics: Analyzing student data, such as enrollment records, academic performance, and course evaluations, can reveal patterns and trends.
4. How often should a student journey map be updated?
The frequency of updates depends on the institution’s context and the pace of change within the educational landscape. Regular updates are essential to ensure the map remains relevant and reflects the evolving student experience. Ideally, updates should occur at least annually, or more frequently if significant changes occur in the institution’s offerings, processes, or technology.
Tips for Effective Student Journey Mapping
-
Focus on the Student: The map should be centered around the student’s perspective, capturing their thoughts, feelings, and actions. Avoid focusing solely on institutional processes or objectives.
-
Incorporate Visuals: Visual elements, such as icons, diagrams, and timelines, enhance the map’s clarity, engagement, and memorability.
-
Emphasize Key Touchpoints: Highlight the touchpoints that have the most significant impact on the student’s experience, either positive or negative.
-
Use Data to Validate Insights: Back up qualitative insights with quantitative data, such as enrollment statistics, retention rates, and student feedback surveys.
-
Engage Stakeholders: Involve relevant stakeholders, such as faculty, staff, administrators, and students, in the mapping process. This ensures a shared understanding of the student journey and fosters collaboration for improvement.
-
Continuously Iterate and Improve: The student journey map is a living document that should be continuously updated and improved based on feedback, data analysis, and new insights.
Conclusion: Embracing the Student Journey for Educational Excellence
The student journey map is a powerful tool for understanding the student experience, identifying areas for improvement, and fostering a more engaged and successful educational environment. By embracing a student-centric approach and leveraging the insights gleaned from the map, institutions can create a more personalized, supportive, and rewarding experience for their students, ultimately contributing to their academic success and personal growth.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Student Journey: A Comprehensive Guide to Mapping the Educational Experience. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
