Unveiling the Significance of Materiality Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Unveiling the Significance of Materiality Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Significance of Materiality Maps: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Significance of Materiality Maps: A Comprehensive Guide

In the dynamic landscape of business operations, navigating the complexities of stakeholder expectations and environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors is paramount. Enter the materiality map, a powerful tool that serves as a compass for organizations seeking to prioritize and address issues most relevant to their success and sustainability.
Understanding the Essence of Materiality Maps
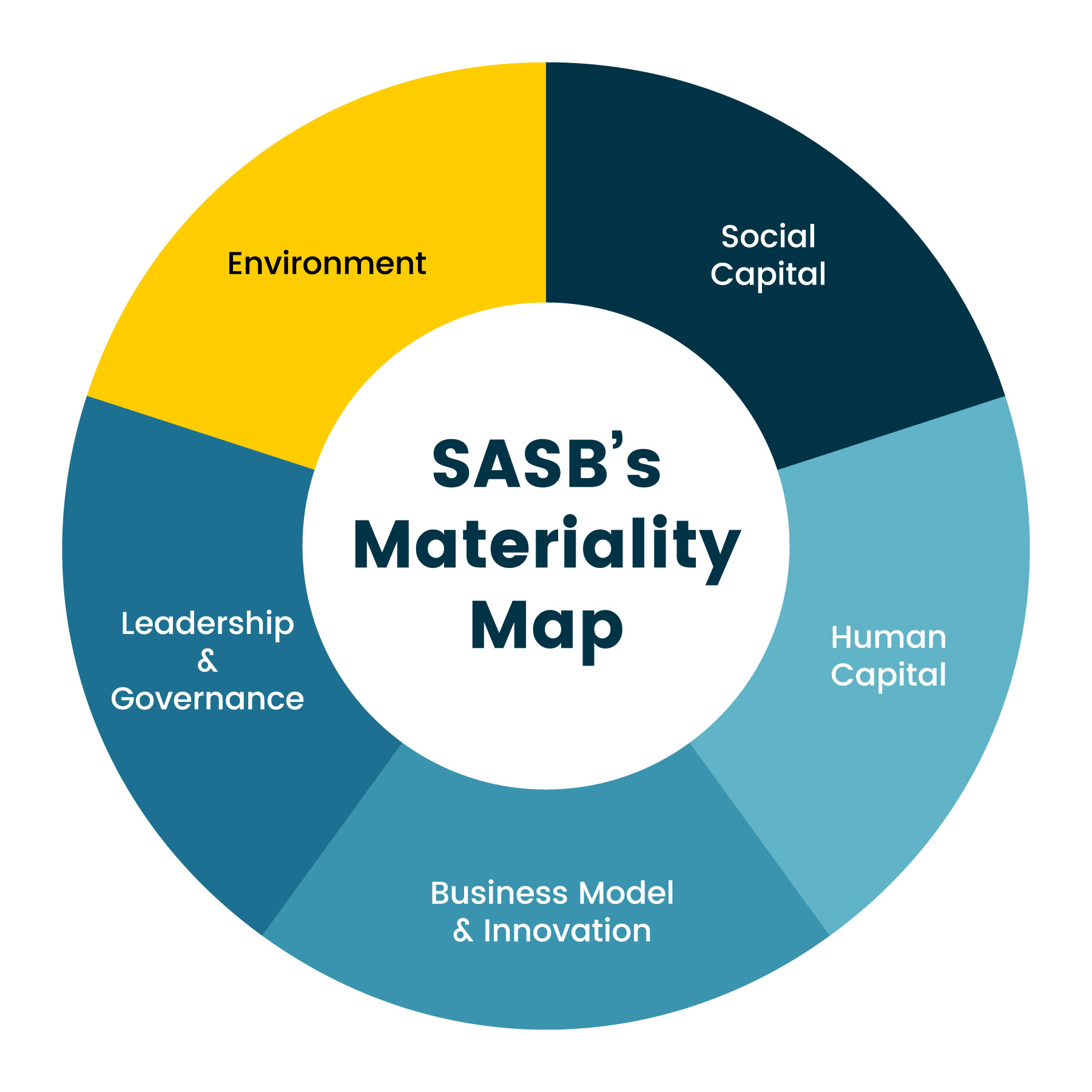
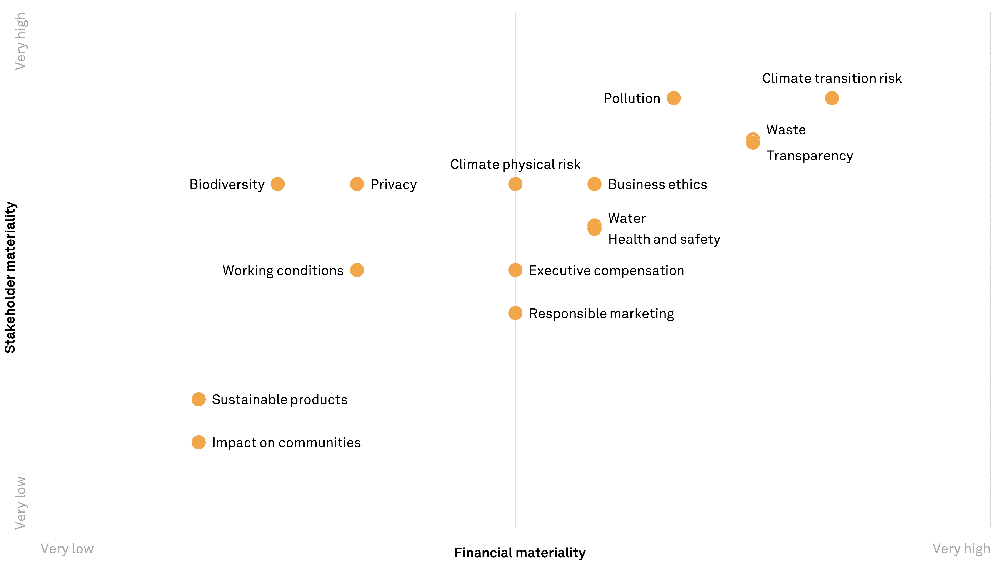
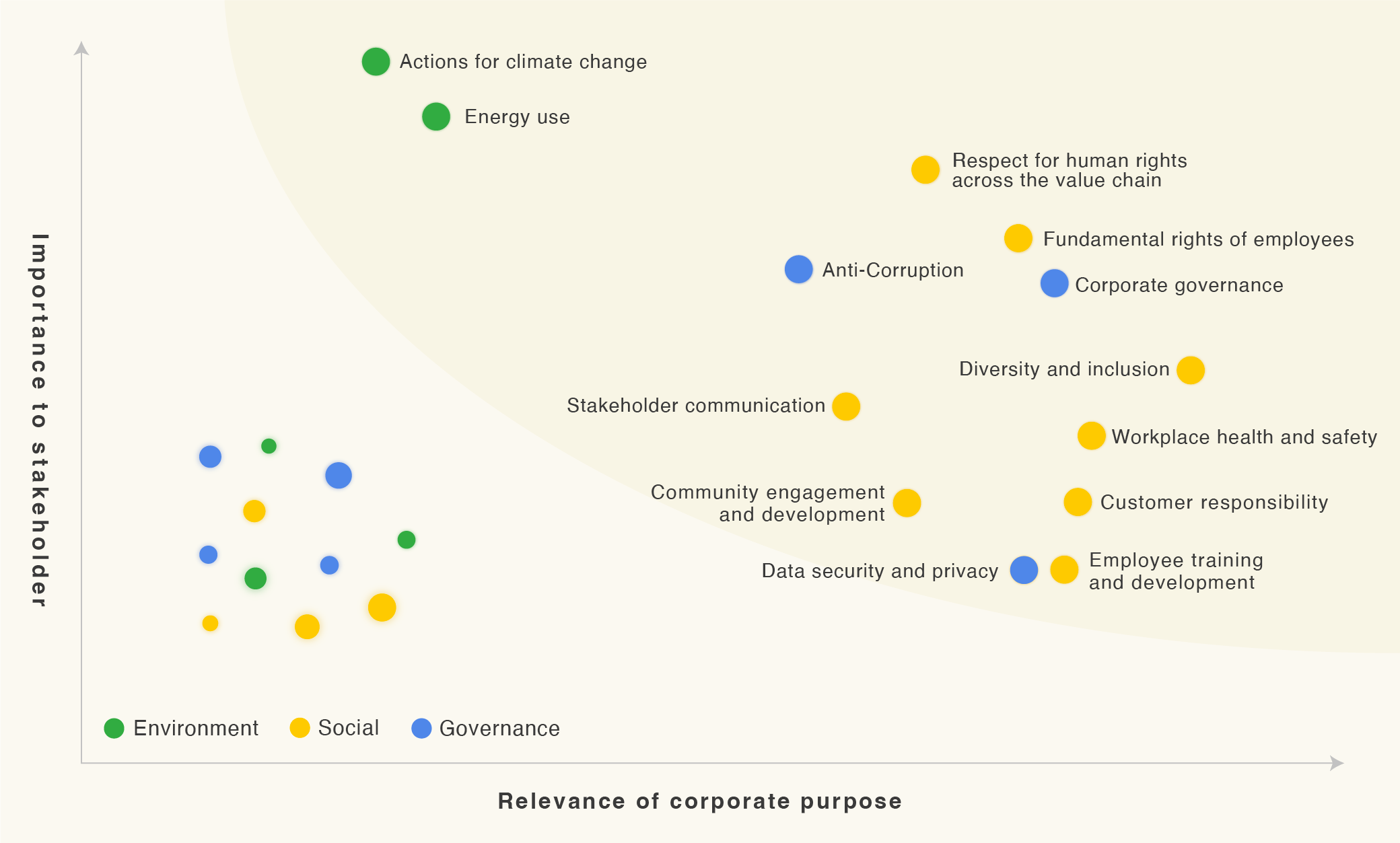
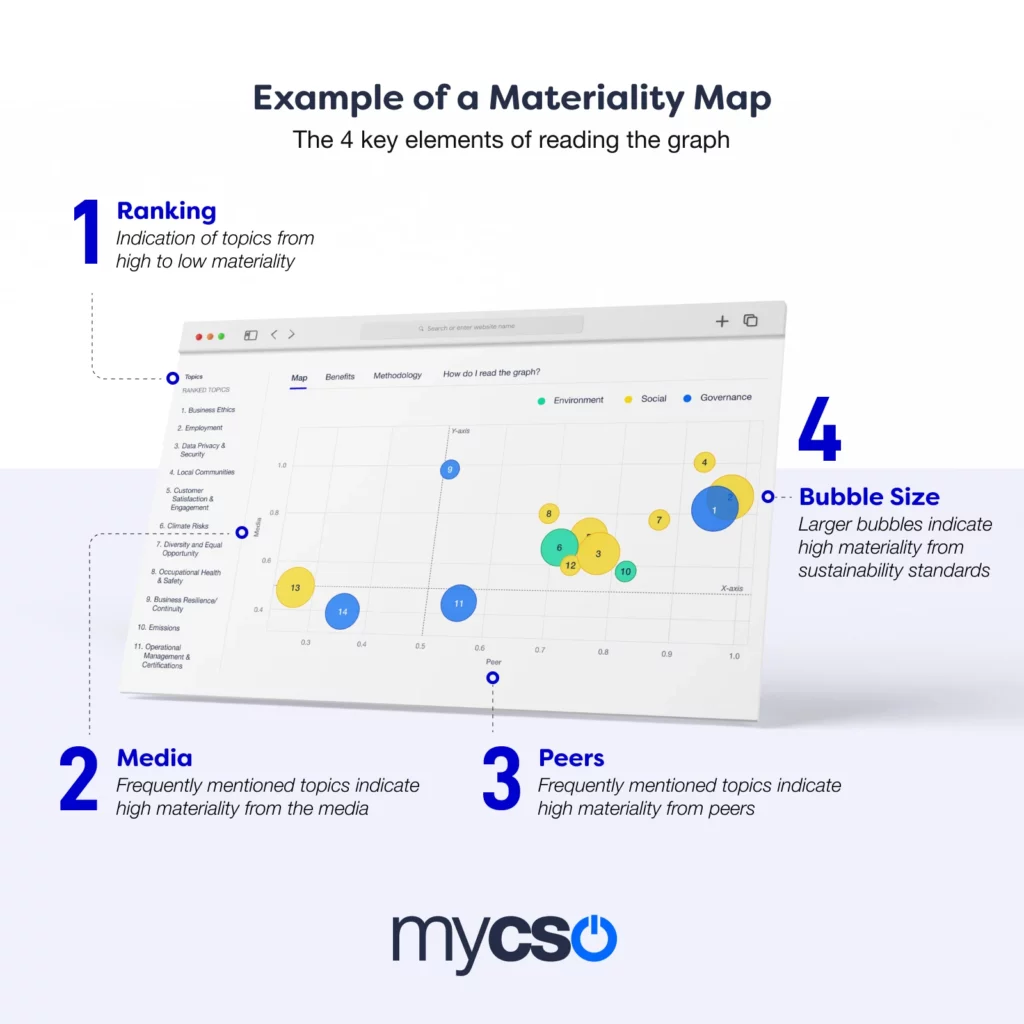
A materiality map is a visual representation that identifies and prioritizes the most important issues for an organization, considering both internal and external perspectives. It serves as a bridge between an organization’s values, strategies, and its stakeholders, providing a clear framework for decision-making and action.
Key Components of a Materiality Map
A comprehensive materiality map typically encompasses the following elements:
- Stakeholder Analysis: Identifying and understanding the key stakeholders, their expectations, and their influence on the organization.
- Issue Identification: A thorough examination of potential risks, opportunities, and impacts across various dimensions, including environmental, social, economic, and governance factors.
- Impact Assessment: Analyzing the potential impact of identified issues on the organization’s financial performance, reputation, and overall sustainability.
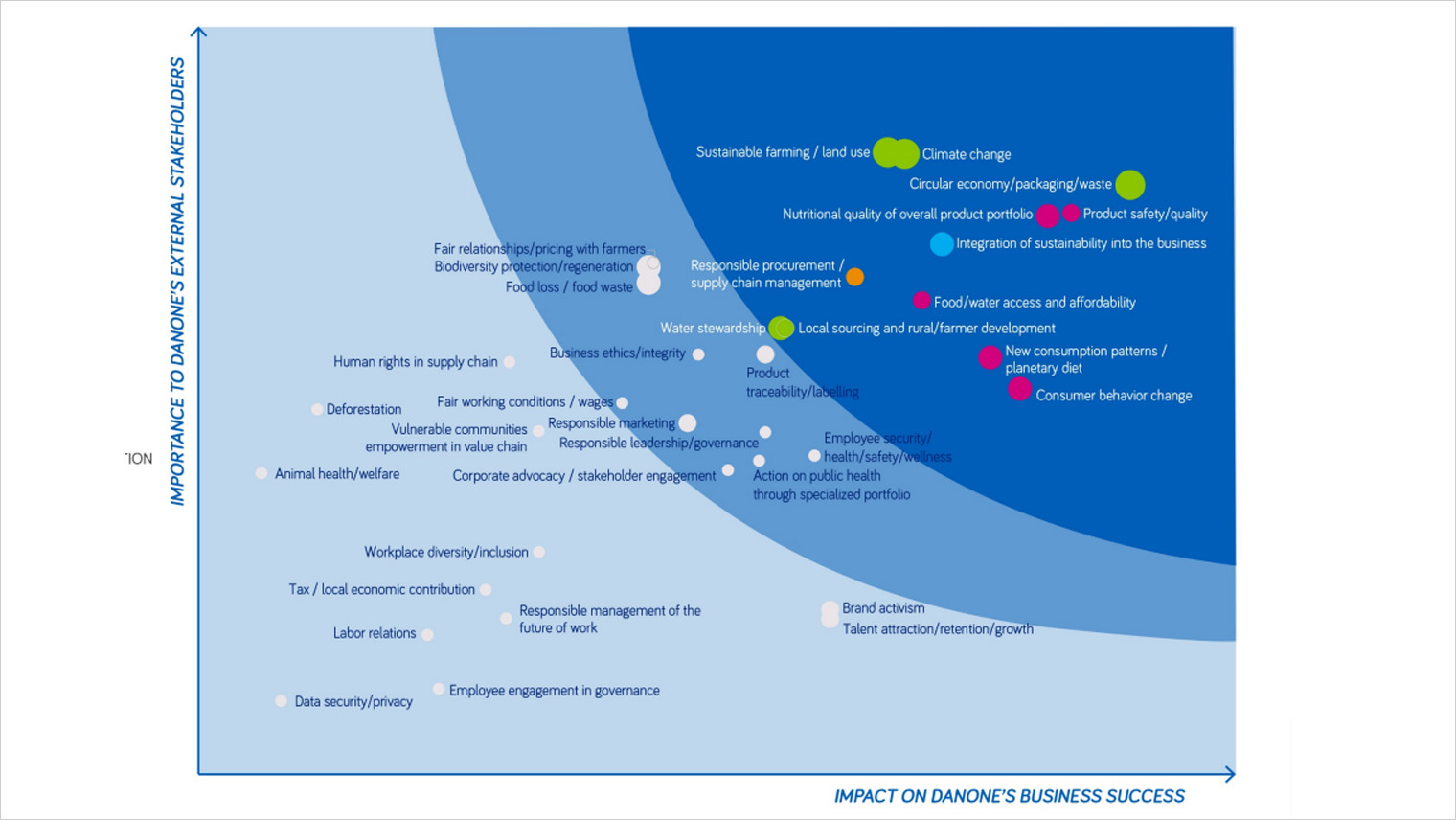
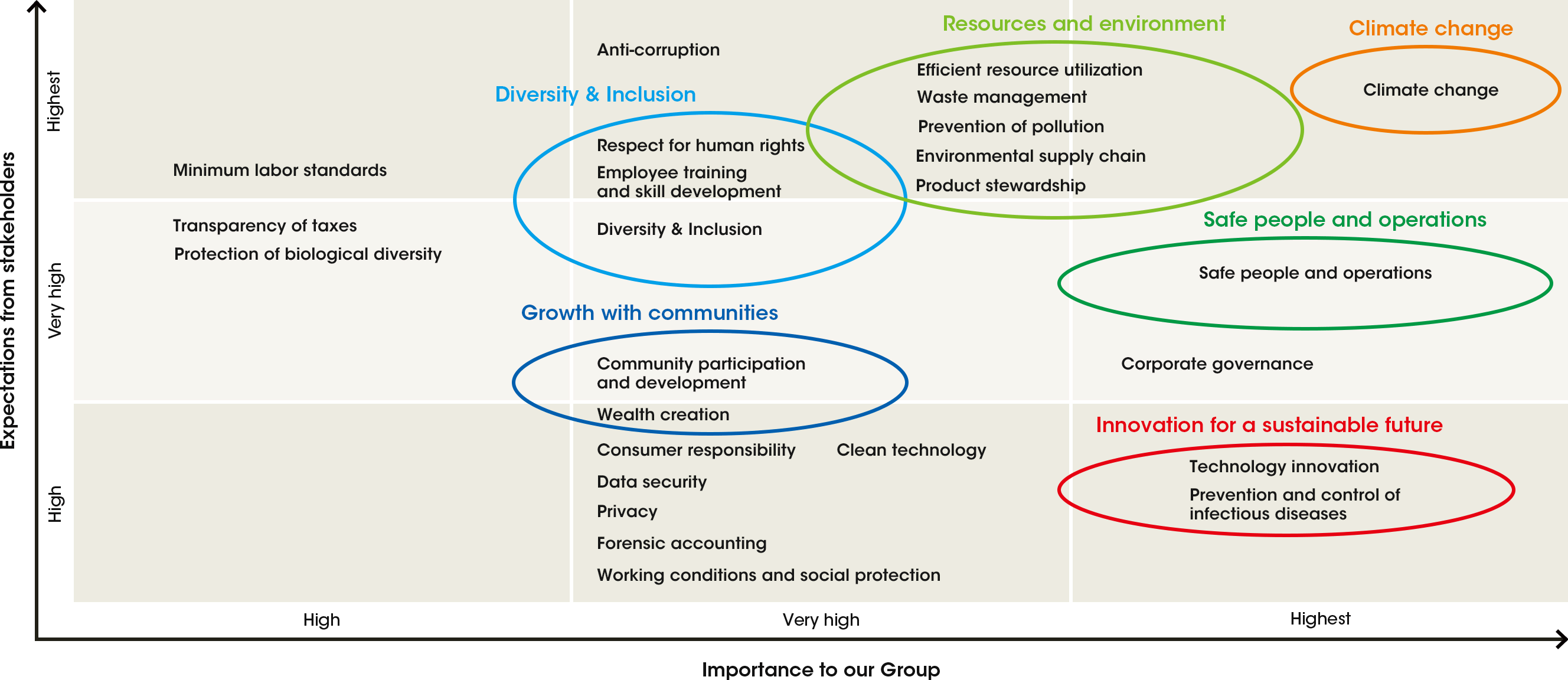
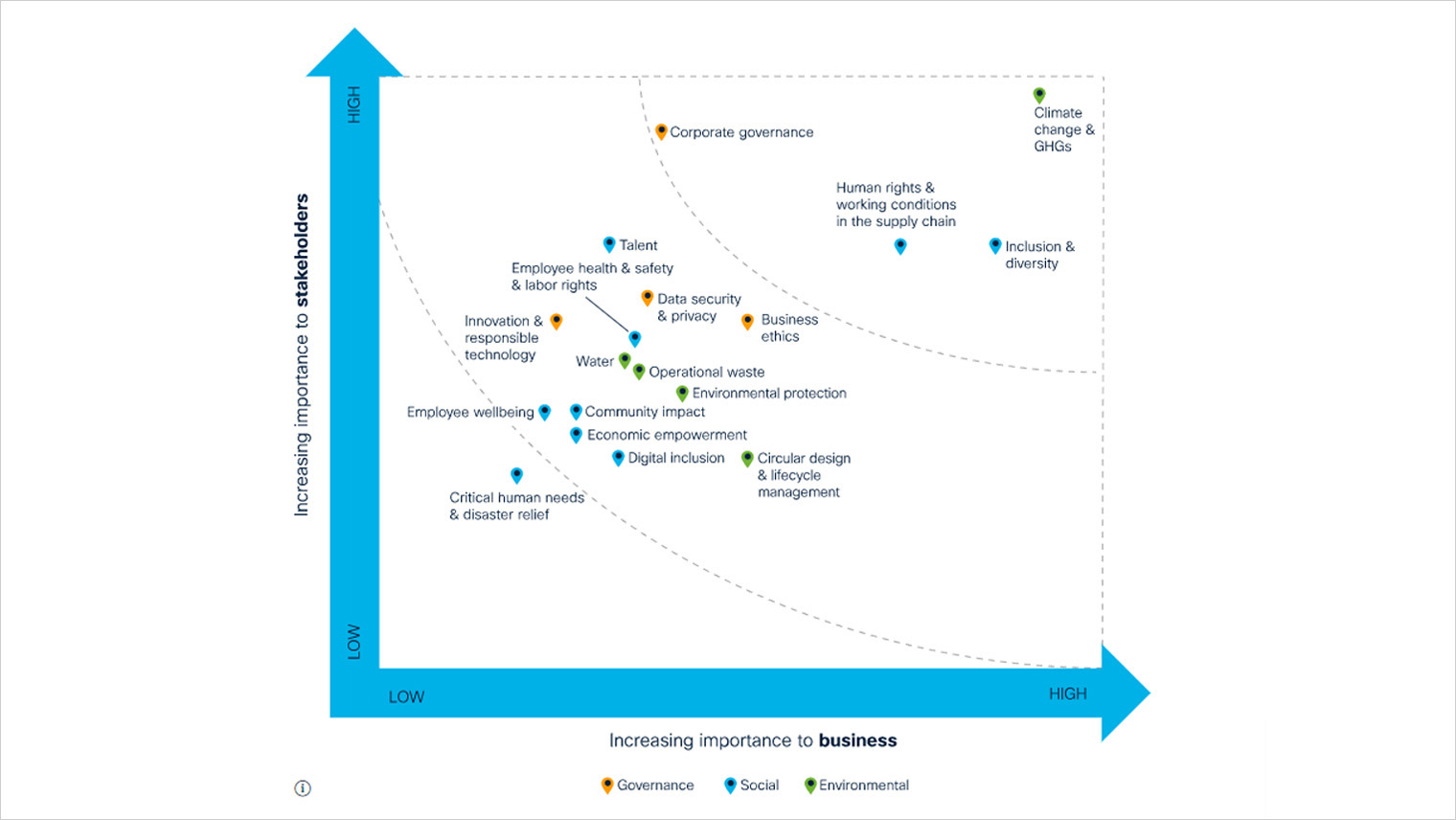
- Prioritization: Ranking issues based on their materiality, considering both their importance to stakeholders and their significance to the organization’s success.
- Strategic Alignment: Connecting prioritized issues to the organization’s strategic goals and objectives, ensuring alignment between sustainability efforts and core business operations.
The Value Proposition of Materiality Maps
Materiality maps offer a multitude of benefits for organizations of all sizes and sectors:
- Enhanced Stakeholder Engagement: By identifying and addressing the most important issues for stakeholders, organizations can foster trust, transparency, and stronger relationships.
- Improved Risk Management: Materiality maps help organizations proactively identify and mitigate potential risks, leading to more informed decision-making and reduced vulnerability.
- Strategic Alignment: By linking material issues to strategic goals, organizations can ensure that sustainability efforts are integrated into core business operations, driving long-term value creation.
- Enhanced Reporting and Communication: Materiality maps provide a clear framework for reporting on sustainability performance, enabling effective communication with stakeholders and demonstrating accountability.
- Competitive Advantage: Organizations that prioritize material issues and demonstrate a commitment to sustainability can gain a competitive edge by attracting investors, customers, and talent.
The Process of Developing a Materiality Map
Creating a robust and effective materiality map involves a structured and collaborative process:
1. Define the Scope: Clearly define the organization’s boundaries, including its operations, supply chain, and key stakeholders.
2. Identify Stakeholders: Conduct a thorough analysis of key stakeholders, considering their influence, expectations, and potential impact on the organization.
3. Identify Issues: Gather information on potential risks, opportunities, and impacts across various dimensions, including environmental, social, economic, and governance factors.
4. Assess Impact: Analyze the potential impact of identified issues on the organization’s financial performance, reputation, and overall sustainability.
5. Prioritize Issues: Rank issues based on their materiality, considering both their importance to stakeholders and their significance to the organization’s success.
6. Develop the Map: Visualize the prioritized issues on a materiality map, typically using a two-axis framework that reflects the importance to stakeholders and the importance to the organization.
7. Communicate and Implement: Share the materiality map with stakeholders, communicate its significance, and develop action plans to address the prioritized issues.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Materiality Maps
1. What is the difference between materiality and sustainability?
Materiality focuses on the issues that are most important to stakeholders and the organization’s success, while sustainability encompasses a broader range of environmental, social, and governance issues. Materiality helps identify the most critical sustainability issues that require attention.
2. How often should a materiality map be updated?
Materiality maps should be reviewed and updated regularly, ideally at least annually or whenever significant changes occur in the organization’s operations, stakeholder landscape, or industry trends.
3. Who should be involved in developing a materiality map?
Developing a materiality map requires a collaborative effort involving representatives from various departments, including sustainability, finance, legal, operations, and communications, as well as external stakeholders.
4. What are the best practices for developing a materiality map?
- Use a structured and transparent process.
- Involve stakeholders in the process.
- Use objective and verifiable data to assess impact.
- Prioritize issues based on their materiality.
- Align the map with strategic goals.
- Regularly review and update the map.
Tips for Effective Materiality Map Development
- Start with a clear definition of the organization’s purpose and values.
- Use a variety of data sources to identify and assess issues.
- Consider both quantitative and qualitative factors.
- Involve external stakeholders in the process.
- Communicate the map clearly and effectively.
- Use the map as a guide for decision-making and action.
Conclusion
Materiality maps are essential tools for organizations seeking to navigate the complex world of stakeholder engagement and ESG issues. By identifying and prioritizing the most important issues, organizations can enhance risk management, improve stakeholder relationships, and drive sustainable value creation. As the business landscape continues to evolve, materiality maps will play an increasingly crucial role in helping organizations achieve long-term success and sustainability.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Significance of Materiality Maps: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
