Unveiling the Secrets of the Wind: A Comprehensive Guide to Windrose Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Secrets of the Wind: A Comprehensive Guide to Windrose Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Secrets of the Wind: A Comprehensive Guide to Windrose Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Secrets of the Wind: A Comprehensive Guide to Windrose Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Secrets of the Wind: A Comprehensive Guide to Windrose Maps
- 3.1 Understanding the Windrose Map: A Visual Representation of Wind Direction and Frequency
- 3.2 Applications of Windrose Maps: Unveiling the Wind’s Influence
- 3.3 Creating a Windrose Map: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 3.4 Windrose Maps: A Powerful Tool for Understanding and Utilizing the Wind
- 3.5 FAQs: Demystifying the Windrose Map
- 3.6 Tips for Utilizing Windrose Maps: Maximizing Their Potential
- 3.7 Conclusion: Embracing the Power of the Wind
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Secrets of the Wind: A Comprehensive Guide to Windrose Maps

The wind, an invisible force that shapes our landscapes and influences our lives, has long been a subject of fascination and study. Understanding its patterns and direction is crucial in various fields, from meteorology and aviation to architecture and agriculture. To visualize and analyze this intricate dance of air currents, cartographers and scientists have developed a powerful tool: the windrose map.
Understanding the Windrose Map: A Visual Representation of Wind Direction and Frequency
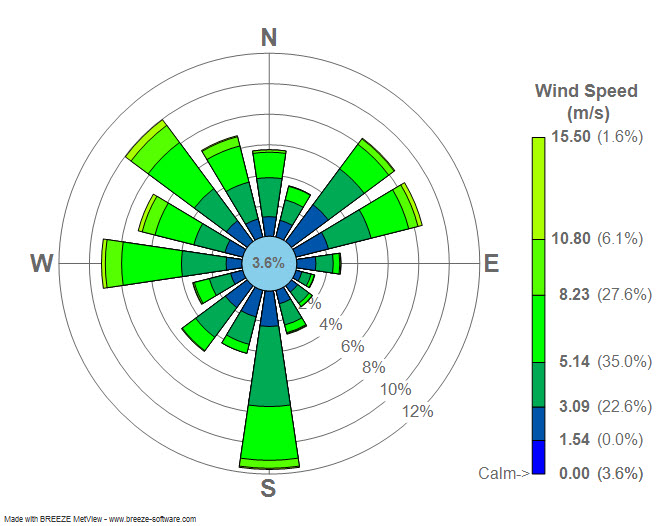
A windrose map, often referred to simply as a "wind rose," is a specialized graphical representation that depicts the prevailing wind directions and their relative frequencies at a specific location. It serves as a visual compass, offering a clear understanding of the wind’s dominant patterns and their impact on the environment.
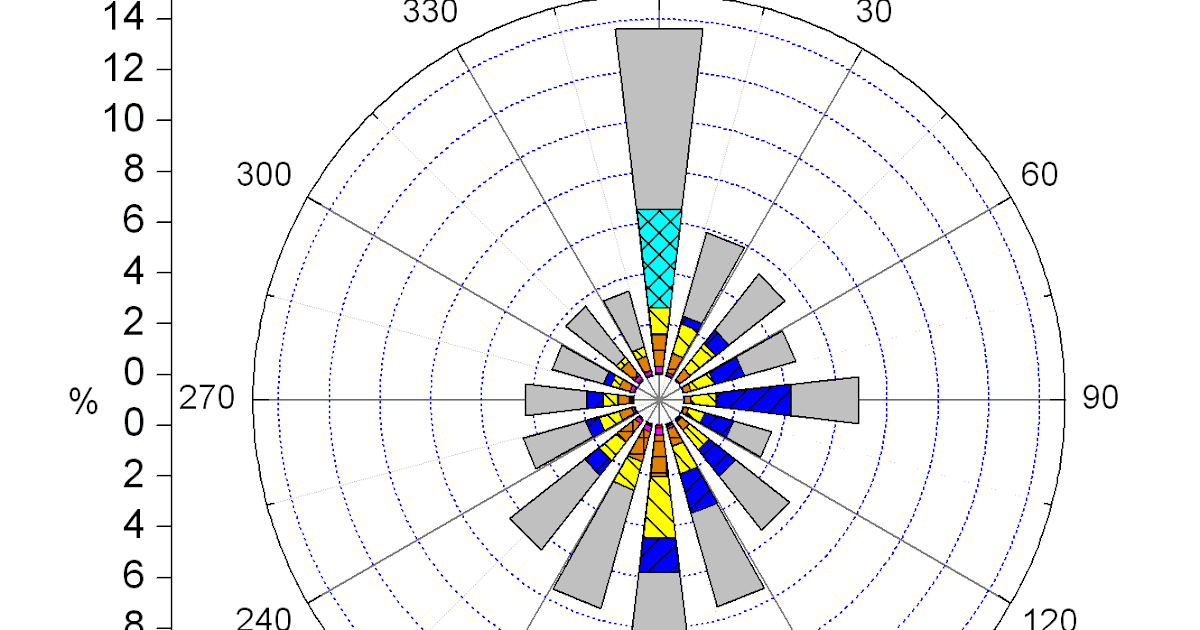
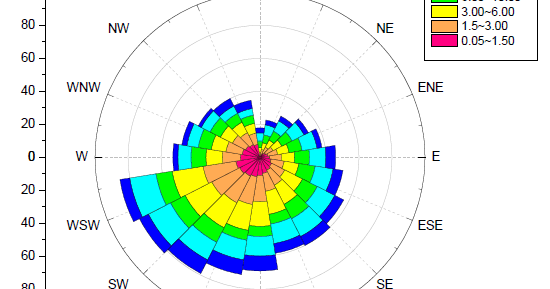
The map typically takes the form of a circular diagram, with its center representing the location of interest. From this center, eight or more lines radiate outward, each representing a specific wind direction. The length of each line corresponds to the frequency or strength of the wind blowing from that direction.
Key Components of a Windrose Map:
- Cardinal Directions: The primary directions of North, South, East, and West are represented by the four cardinal points on the wind rose.
- Intercardinal Directions: The intermediate directions, such as Northeast, Southeast, Northwest, and Southwest, are also depicted, providing a more detailed representation of wind patterns.
- Wind Frequency: The length of each line radiating from the center of the wind rose indicates the frequency of winds blowing from that direction. Longer lines represent more frequent winds, while shorter lines indicate less frequent winds.
- Wind Speed: In some cases, wind speed is also incorporated into the wind rose, often represented by different colors or shades. This provides further insight into the intensity of wind patterns.
Applications of Windrose Maps: Unveiling the Wind’s Influence
Windrose maps find application in a wide range of fields, providing valuable insights into the impact of wind on various aspects of our world:
1. Meteorology and Climatology:
- Weather Forecasting: Windrose maps are essential tools for meteorologists, helping them to understand prevailing wind patterns and predict weather conditions.
- Climate Analysis: By analyzing windrose data over extended periods, climatologists can gain insights into long-term wind trends and their influence on regional climates.
- Air Quality Monitoring: Windrose maps are used to study the dispersion of pollutants and air contaminants, assisting in the development of air quality management strategies.
2. Aviation and Air Transportation:
- Airport Design and Operations: Windrose maps are crucial for airport design and operations, ensuring safe takeoffs and landings by identifying prevailing wind directions and wind shear zones.
- Aircraft Performance: Windrose maps provide pilots with valuable information about wind conditions, impacting flight planning, fuel consumption, and flight duration.
- Air Traffic Control: Windrose data is integrated into air traffic control systems, assisting in managing air traffic flow and ensuring safety in airspace.
3. Architecture and Urban Planning:
- Building Design: Windrose maps help architects design buildings that are optimized for natural ventilation and energy efficiency, minimizing wind loads and maximizing comfort.
- Urban Planning: Understanding prevailing wind patterns allows urban planners to design cities that promote pedestrian comfort and minimize wind-related issues like dust accumulation.
- Sustainable Design: Windrose maps play a crucial role in the development of sustainable urban environments, enabling the integration of renewable energy sources like wind turbines.
4. Agriculture and Forestry:
- Crop Management: Windrose maps help farmers understand wind patterns that can impact crop growth, pollination, and irrigation needs.
- Forestry Management: Understanding wind patterns is essential for managing forest health, preventing wind damage, and ensuring sustainable forestry practices.
- Wind-Resistant Crops: Windrose maps assist in the selection of wind-resistant crops and the development of windbreak systems to protect crops from wind damage.
5. Renewable Energy:
- Wind Farm Development: Windrose maps are indispensable for selecting suitable locations for wind farms, ensuring optimal wind resource utilization and power generation.
- Wind Energy Potential: Windrose data provides valuable information about wind speed and frequency, enabling the assessment of wind energy potential in specific areas.
- Wind Turbine Design: Windrose maps help engineers design wind turbines that are optimized for the prevailing wind conditions, maximizing energy output and minimizing noise pollution.
6. Environmental Studies:
- Dust and Sand Storm Prediction: Windrose maps are used to predict the movement and intensity of dust and sand storms, enabling early warning systems and mitigation strategies.
- Coastal Erosion: Windrose data helps scientists understand the impact of wind on coastal erosion and develop strategies for coastal protection.
- Pollination Studies: Windrose maps are used to study the movement of pollen and its impact on plant reproduction and biodiversity.
Creating a Windrose Map: A Step-by-Step Guide
Creating a windrose map involves a combination of data collection, analysis, and visualization:
1. Data Collection:
- Meteorological Data: The most reliable source of wind data is meteorological stations that record wind speed and direction at regular intervals.
- Historical Data: Historical wind records can be accessed from meteorological archives, providing insights into long-term wind patterns.
- Remote Sensing: Satellites and other remote sensing technologies can be used to collect wind data over large areas.
2. Data Analysis:
- Wind Frequency: The data is analyzed to determine the frequency of winds blowing from different directions.
- Wind Speed: Wind speed data is analyzed to understand the intensity of wind patterns.
- Seasonal Variations: Wind patterns can vary significantly with seasons, so data is often analyzed separately for different seasons.
3. Visualization:
- Software Tools: Specialized software programs like ArcGIS, QGIS, and MATLAB are used to create windrose maps from the analyzed data.
- Graphical Representation: The data is visualized in a circular diagram, with lines radiating from the center representing wind directions.
- Color Coding: Different colors or shades are often used to represent wind speed or other parameters, enhancing the visual clarity of the map.
Windrose Maps: A Powerful Tool for Understanding and Utilizing the Wind
Windrose maps offer a unique and valuable tool for understanding the wind’s influence on our environment and society. By visualizing wind patterns and frequencies, these maps provide valuable insights for various applications, ranging from weather forecasting and airport design to urban planning and renewable energy development.
FAQs: Demystifying the Windrose Map
1. What is the difference between a wind rose and a compass rose?
While both are circular diagrams, a compass rose depicts the cardinal directions (North, South, East, West) and intercardinal directions for navigation purposes. A wind rose, on the other hand, focuses on wind direction and frequency, with the length of each line representing the frequency of winds blowing from that direction.
2. How do I interpret a windrose map?
The length of each line radiating from the center of the wind rose indicates the frequency of winds blowing from that direction. Longer lines represent more frequent winds, while shorter lines indicate less frequent winds.
3. Can windrose maps be used to predict wind speed?
While windrose maps typically represent wind direction and frequency, some windrose maps may incorporate wind speed, often represented by different colors or shades. However, for accurate wind speed prediction, dedicated wind speed data is required.
4. Are windrose maps accurate?
The accuracy of windrose maps depends on the quality and quantity of data used to create them. Wind patterns can vary significantly over time and space, so windrose maps should be interpreted within the context of the data used to create them.
5. What are the limitations of windrose maps?
Windrose maps provide a simplified representation of wind patterns and do not capture all the complexities of wind behavior. They do not account for factors like wind gusts, wind shear, or the influence of terrain on wind patterns.
Tips for Utilizing Windrose Maps: Maximizing Their Potential
1. Understand the Data: Before interpreting a windrose map, it’s crucial to understand the data used to create it, including the time period, location, and data source.
2. Consider Seasonal Variations: Wind patterns can vary significantly with seasons, so it’s important to consider seasonal windrose maps when making decisions.
3. Combine with Other Data: Windrose maps are most effective when combined with other relevant data, such as topography, land use, and meteorological data.
4. Use Appropriate Software: Specialized software programs can enhance the analysis and visualization of windrose data, enabling more accurate interpretations and insights.
5. Seek Expert Advice: For complex applications, it’s advisable to consult with experts in meteorology, wind energy, or other relevant fields to ensure accurate interpretation and utilization of windrose maps.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of the Wind
Windrose maps offer a powerful and versatile tool for understanding and utilizing the wind’s influence on our environment and society. By providing a visual representation of wind direction and frequency, these maps assist in a wide range of applications, from weather forecasting and airport design to urban planning and renewable energy development. As we continue to explore and harness the power of the wind, windrose maps will play an increasingly important role in shaping our future.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Secrets of the Wind: A Comprehensive Guide to Windrose Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
