Unveiling the Power of USCA Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing This Essential Tool
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of USCA Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing This Essential Tool
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of USCA Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing This Essential Tool. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of USCA Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing This Essential Tool
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Power of USCA Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing This Essential Tool
- 3.1 Defining the USCA Map: A Framework for Environmental Stewardship
- 3.2 Applications of USCA Maps: A Multifaceted Tool for Environmental Management
- 3.3 Benefits of Utilizing USCA Maps: A Powerful Tool for Sustainable Development
- 3.4 FAQs Regarding USCA Maps: Addressing Common Questions and Concerns
- 3.5 Tips for Effective Utilization of USCA Maps: Maximizing Their Impact
- 3.6 Conclusion: Empowering Environmental Management Through Visualization and Understanding
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Power of USCA Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing This Essential Tool

In the realm of environmental management and resource conservation, the ability to effectively visualize and understand complex spatial data is paramount. Enter the USCA map, a powerful tool that empowers decision-makers and stakeholders with a comprehensive and insightful view of critical environmental information. This article delves into the intricacies of USCA maps, exploring their purpose, components, applications, and benefits, providing a comprehensive understanding of this essential resource.
Defining the USCA Map: A Framework for Environmental Stewardship
The acronym USCA stands for "Upstream, Source, Contribution, and Area." A USCA map, therefore, is a visual representation of the spatial relationships between various environmental components, primarily focusing on water resources. It serves as a framework for analyzing and managing the sources, pathways, and impacts of pollutants and other environmental stressors within a defined watershed or geographic region.
Key Components of a USCA Map:
- Upstream: This element identifies the origins of pollutants and other environmental factors. It encompasses upstream sources like industrial facilities, agricultural operations, or urban areas that discharge pollutants into the water system.
- Source: This component details the specific point or area where pollutants are released into the environment. It can include industrial discharge points, agricultural runoff areas, or stormwater outfalls.
- Contribution: This element quantifies the amount of pollutants or other environmental stressors originating from each source. It involves assessing the volume, concentration, and type of pollutants released from each source.
- Area: This component defines the geographical extent of the impacted area, encompassing the water bodies, land areas, and ecosystems affected by the pollutants or stressors originating from upstream sources.
Applications of USCA Maps: A Multifaceted Tool for Environmental Management
USCA maps find widespread applications in various environmental management contexts, proving invaluable for:
1. Water Quality Management:
- Identifying Pollution Sources: USCA maps facilitate the identification of key pollution sources within a watershed, allowing for targeted interventions to mitigate their impact.
- Prioritizing Remediation Efforts: By visualizing the contributions of different sources, USCA maps help prioritize remediation efforts, ensuring resources are allocated efficiently to address the most significant sources of pollution.
- Developing Watershed Management Plans: USCA maps provide a comprehensive understanding of the watershed’s dynamics, enabling the development of effective management plans to protect and restore water quality.
2. Habitat Conservation and Restoration:
- Assessing Habitat Degradation: USCA maps can help identify sources of habitat degradation, such as agricultural runoff, industrial discharges, or urban sprawl, facilitating targeted conservation efforts.
- Prioritizing Restoration Projects: By visualizing the spatial relationships between habitat degradation sources and affected areas, USCA maps assist in prioritizing restoration projects to maximize their impact.
- Monitoring Habitat Recovery: USCA maps can be used to monitor the effectiveness of habitat restoration projects by tracking changes in pollution levels and habitat conditions over time.
3. Climate Change Adaptation:
- Assessing Climate Change Impacts: USCA maps can be used to assess the potential impacts of climate change on water resources, such as increased drought frequency or altered precipitation patterns.
- Developing Adaptation Strategies: By understanding the spatial distribution of climate change impacts, USCA maps can support the development of tailored adaptation strategies for water management and resource conservation.
- Evaluating Adaptation Measures: USCA maps can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of adaptation measures, such as water conservation strategies or infrastructure improvements, by monitoring changes in water quality and resource availability.
4. Public Participation and Education:
- Engaging Stakeholders: USCA maps provide a clear and accessible visual representation of environmental issues, facilitating stakeholder engagement in decision-making processes.
- Raising Awareness: USCA maps can be used to educate the public about environmental challenges and the importance of responsible resource management.
- Promoting Collaborative Solutions: By visualizing the interconnectedness of environmental issues, USCA maps foster collaboration among stakeholders to develop sustainable solutions.
Benefits of Utilizing USCA Maps: A Powerful Tool for Sustainable Development
The adoption of USCA maps offers numerous benefits for environmental management and sustainable development:
1. Improved Decision-Making: USCA maps provide a comprehensive understanding of the spatial relationships between environmental factors, enabling informed decision-making based on data-driven insights.
2. Enhanced Efficiency: By prioritizing interventions and allocating resources effectively, USCA maps optimize environmental management efforts, maximizing impact and minimizing costs.
3. Increased Transparency and Accountability: The visual representation of environmental data fosters transparency and accountability in decision-making processes, promoting public trust and engagement.
4. Facilitated Collaboration: USCA maps serve as a common platform for stakeholders to share information, collaborate on solutions, and coordinate efforts towards achieving shared environmental goals.
5. Improved Public Understanding: The accessibility and clarity of USCA maps enhance public understanding of environmental issues, fostering environmental stewardship and promoting responsible resource use.
FAQs Regarding USCA Maps: Addressing Common Questions and Concerns
1. What data is used to create USCA maps?
USCA maps rely on a wide range of data sources, including:
- Water Quality Monitoring Data: Data on pollutant levels, water flow rates, and other water quality parameters.
- Land Use and Land Cover Data: Information on the types of land uses within a watershed, such as agricultural areas, urban areas, and forests.
- Hydrological Data: Data on water flow patterns, stream networks, and watershed boundaries.
- Environmental Stressors Data: Information on sources of pollution, such as industrial facilities, agricultural operations, and urban runoff.
2. How are USCA maps created?
USCA maps are typically created using Geographic Information System (GIS) software. This software allows for the integration and analysis of various spatial data layers, enabling the visualization of the spatial relationships between different environmental components.
3. What are the limitations of USCA maps?
While powerful, USCA maps do have some limitations:
- Data Availability: The accuracy and completeness of USCA maps depend on the availability of reliable data sources.
- Data Uncertainty: Environmental data can be subject to uncertainties, which can impact the accuracy of USCA maps.
- Complexity of Environmental Systems: Environmental systems are complex and dynamic, and USCA maps may not capture all the intricacies of these systems.
4. How can USCA maps be used to improve environmental management?
USCA maps can be used to:
- Identify and prioritize pollution sources.
- Develop targeted remediation strategies.
- Monitor the effectiveness of environmental management interventions.
- Engage stakeholders and promote public understanding of environmental issues.
5. What are the future directions for USCA map development?
Future developments in USCA map technology are likely to focus on:
- Integration of new data sources: Incorporating data from remote sensing, citizen science, and other emerging sources to enhance the accuracy and comprehensiveness of USCA maps.
- Development of advanced analytical techniques: Utilizing artificial intelligence and machine learning to improve the analysis and interpretation of environmental data.
- Increased accessibility and user-friendliness: Making USCA maps more accessible and user-friendly for a wider range of stakeholders.
Tips for Effective Utilization of USCA Maps: Maximizing Their Impact
1. Engage Stakeholders: Involve relevant stakeholders in the development and use of USCA maps to ensure their relevance and promote buy-in.
2. Use Clear and Concise Communication: Present USCA maps in a clear and concise manner, using visuals and infographics to enhance understanding.
3. Foster Collaboration: Encourage collaboration among stakeholders to leverage the insights derived from USCA maps and develop effective solutions.
4. Regularly Update and Reassess: Periodically update and reassess USCA maps based on new data and changing environmental conditions.
5. Promote Continuous Learning: Use USCA maps as a platform for ongoing learning and knowledge sharing, fostering a culture of environmental stewardship.
Conclusion: Empowering Environmental Management Through Visualization and Understanding
USCA maps represent a powerful tool for visualizing and understanding complex environmental data. By providing a comprehensive overview of the spatial relationships between environmental components, they empower decision-makers and stakeholders to make informed decisions, prioritize interventions, and promote sustainable resource management. Their ability to identify pollution sources, assess habitat degradation, and support climate change adaptation strategies makes them invaluable for protecting and restoring our environment. As data availability and analytical capabilities continue to evolve, USCA maps are poised to play an even more significant role in shaping a more sustainable future.

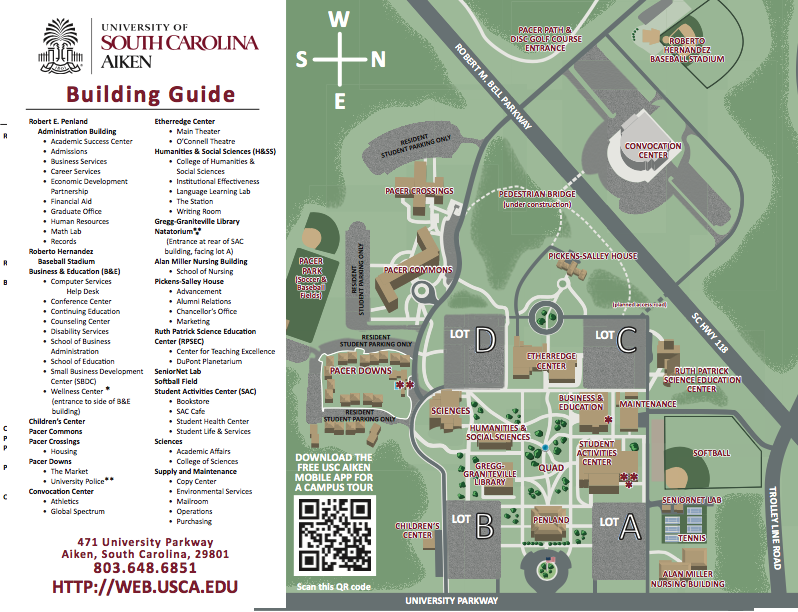

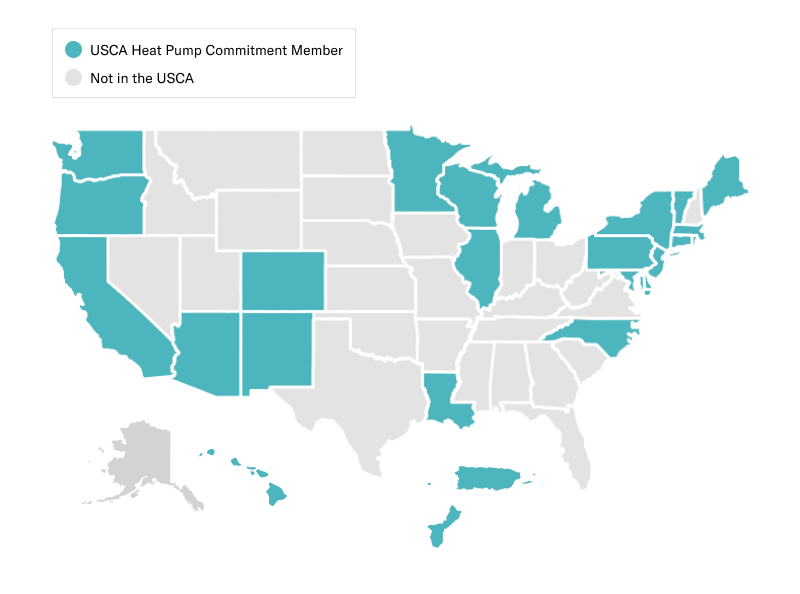
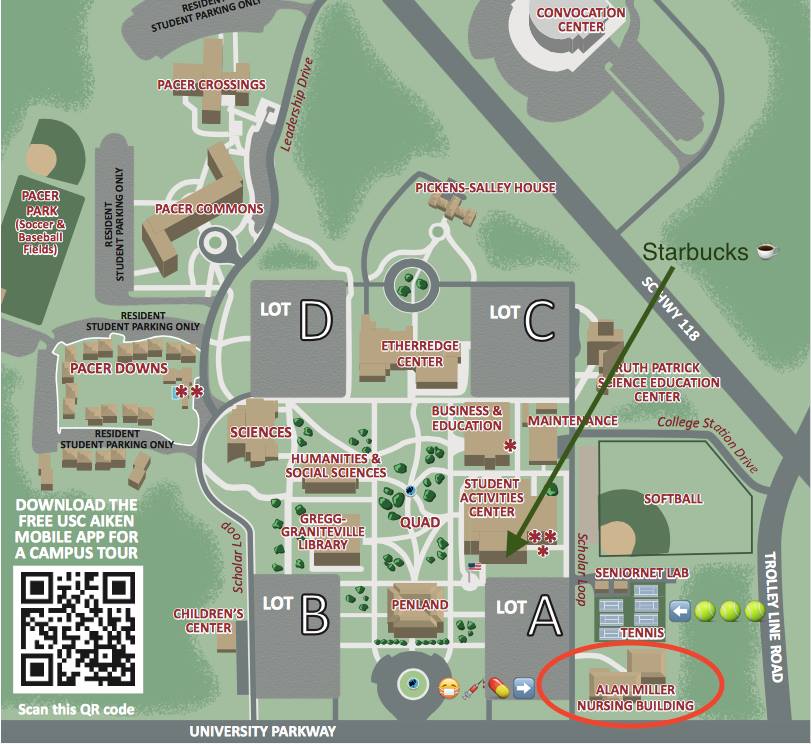
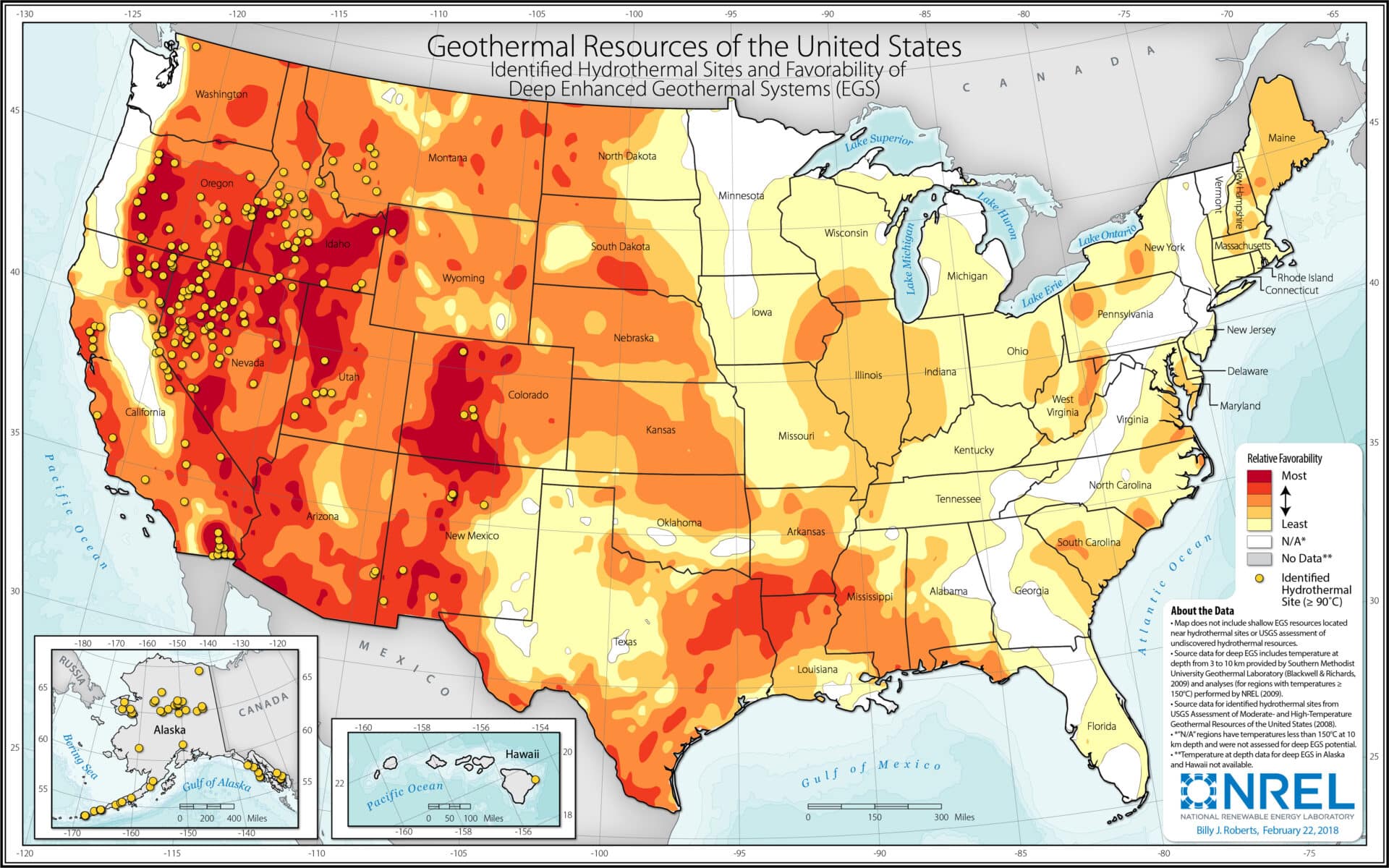


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of USCA Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing This Essential Tool. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
