Unveiling the Landscape of Drought: A Comprehensive Look at Drought Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape of Drought: A Comprehensive Look at Drought Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Landscape of Drought: A Comprehensive Look at Drought Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape of Drought: A Comprehensive Look at Drought Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Landscape of Drought: A Comprehensive Look at Drought Maps
- 3.1 The Essence of Drought Maps: A Visual Representation of Water Scarcity
- 3.2 Understanding the Data Behind Drought Maps: A Multifaceted Approach
- 3.3 Types of Drought Maps: Tailoring Insights to Specific Needs
- 3.4 The Significance of Drought Maps: Unlocking Critical Insights
- 3.5 FAQs About Drought Maps: Addressing Common Questions
- 3.6 Tips for Utilizing Drought Maps Effectively: Maximizing their Potential
- 3.7 Conclusion: Drought Maps as a Tool for Resilience and Adaptation
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Landscape of Drought: A Comprehensive Look at Drought Maps

Drought, a silent and insidious threat, can have devastating consequences for ecosystems, economies, and human well-being. Understanding its patterns and predicting its potential impact are crucial for mitigating its effects and building resilience. Drought maps, powerful tools for visualizing and analyzing drought conditions, provide invaluable insights into this complex phenomenon.
The Essence of Drought Maps: A Visual Representation of Water Scarcity
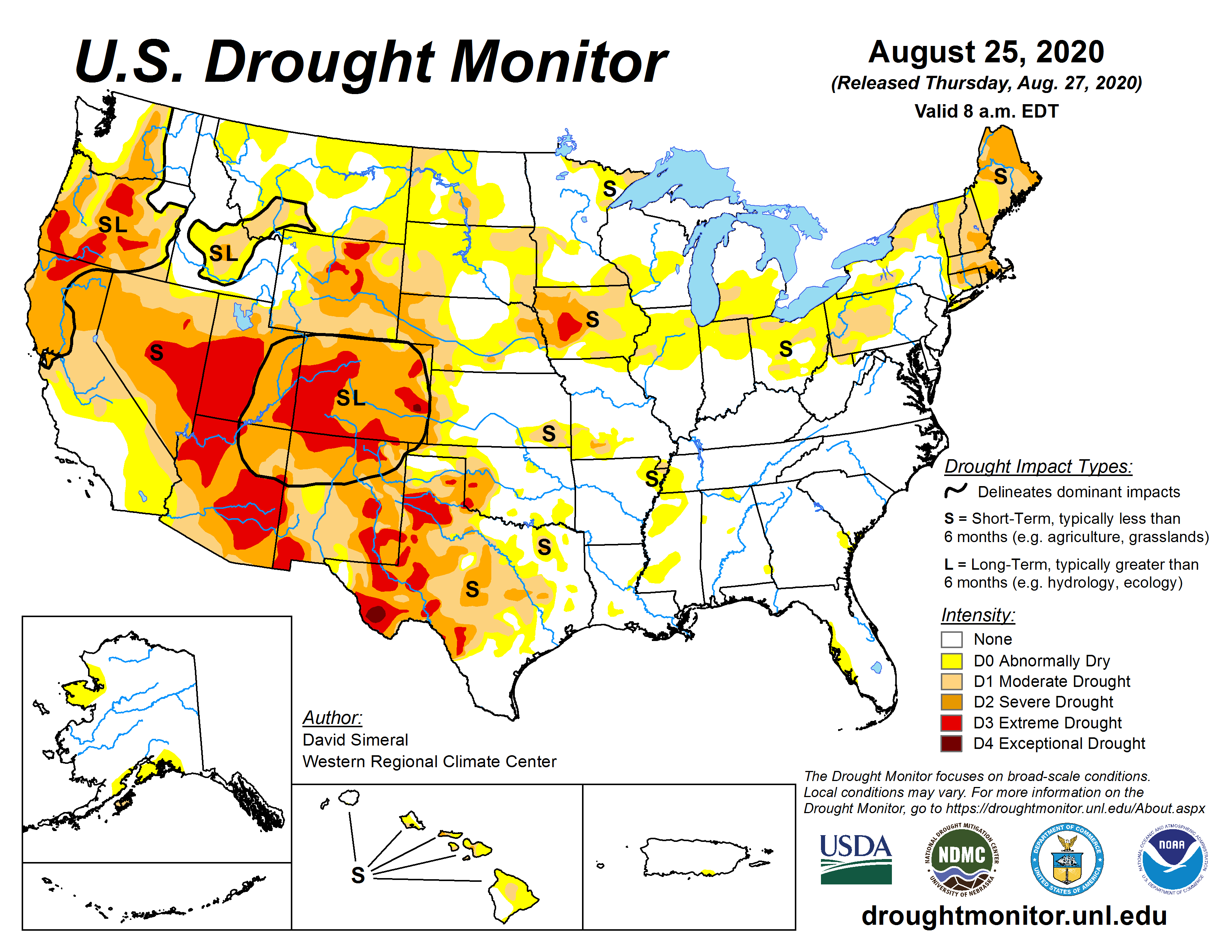
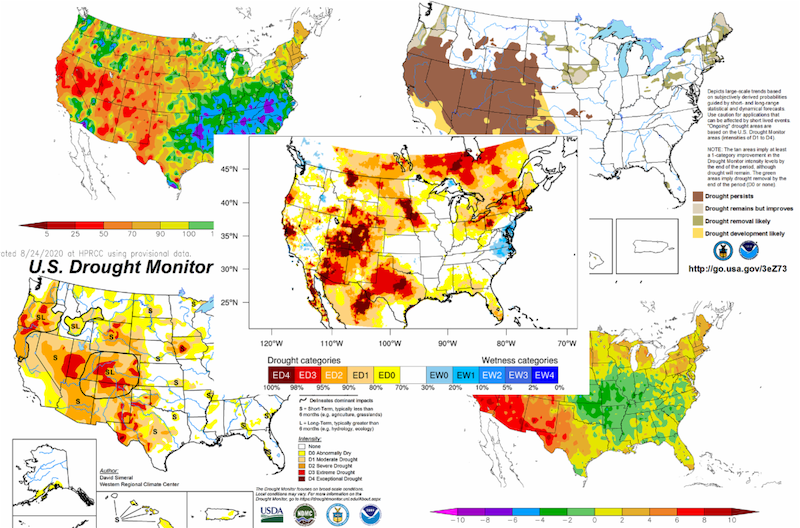
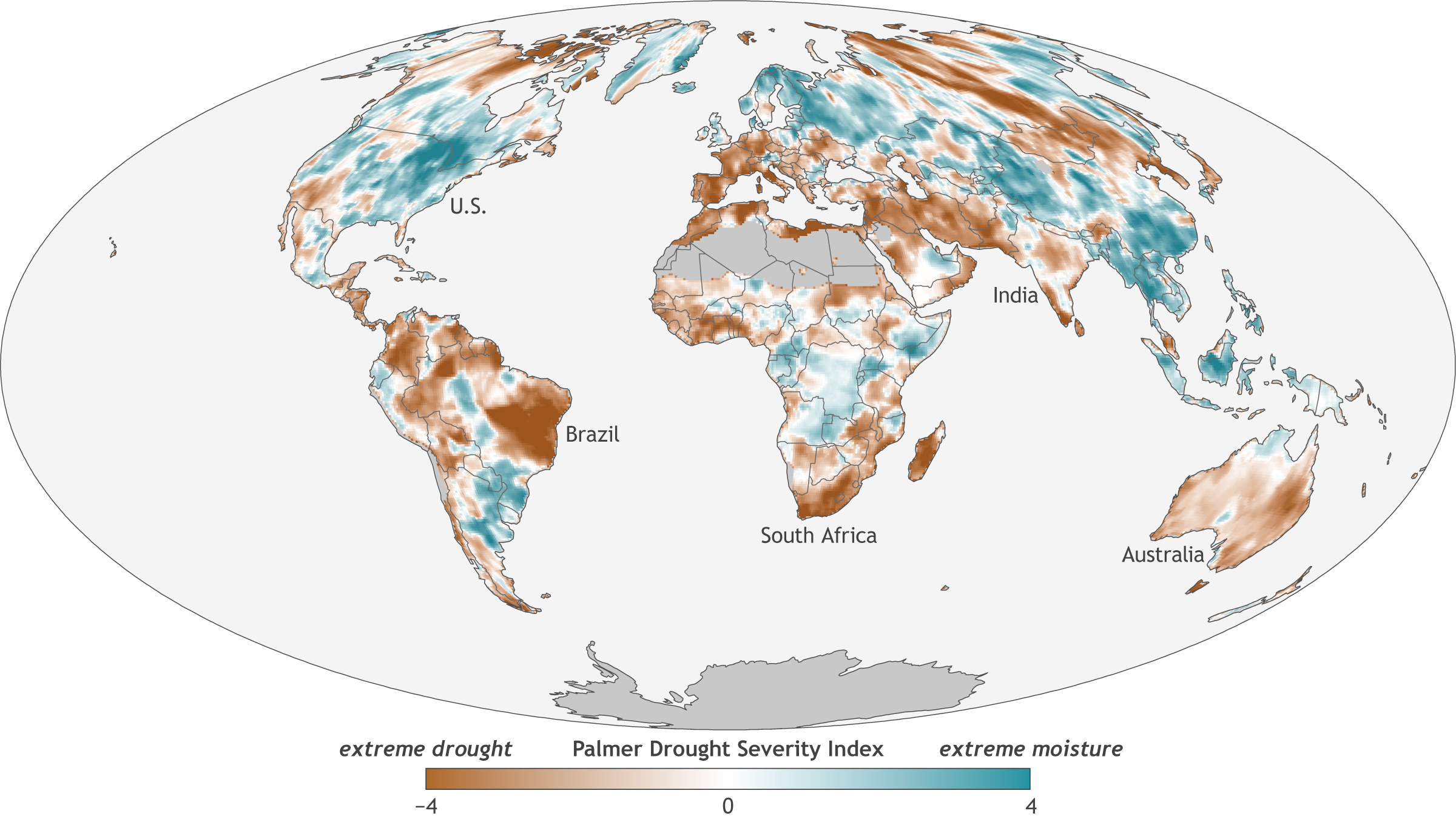
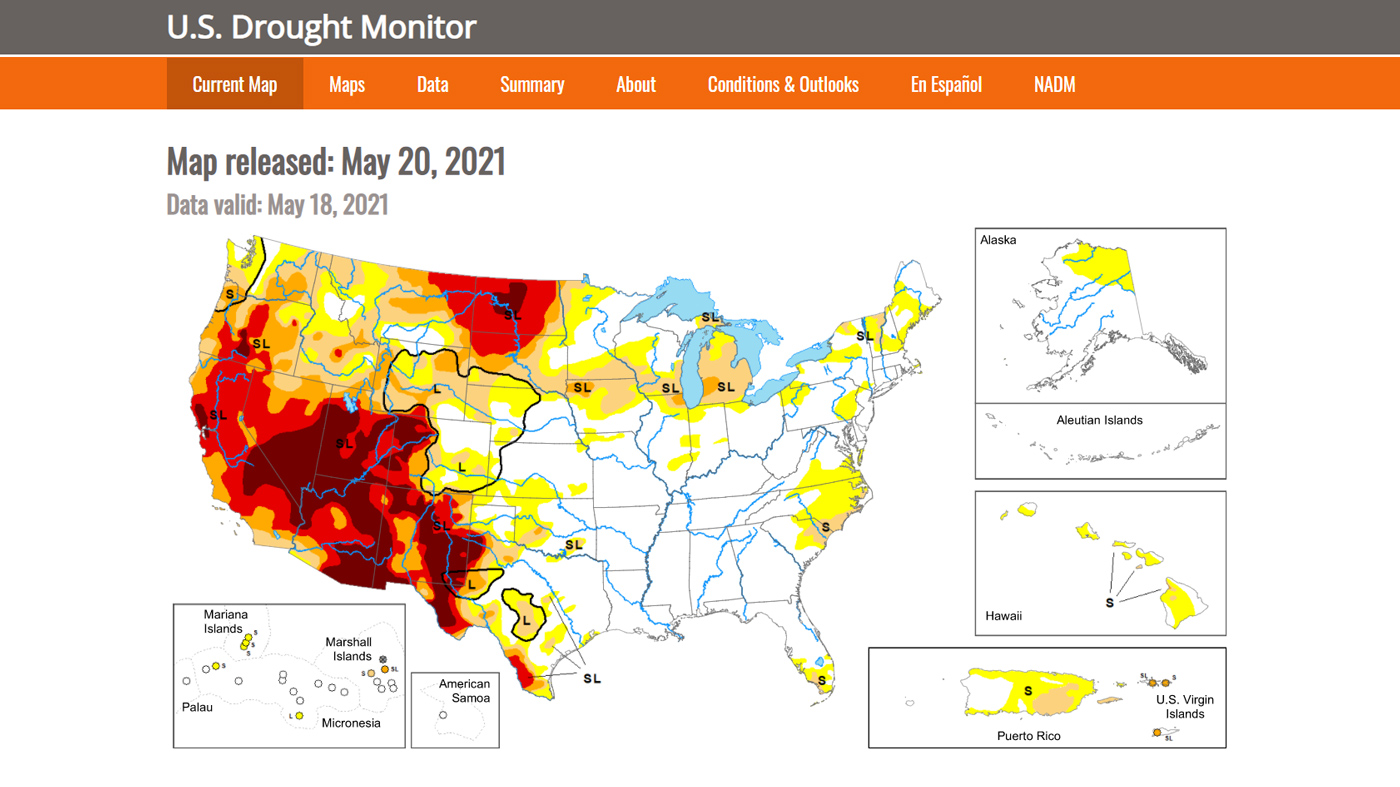
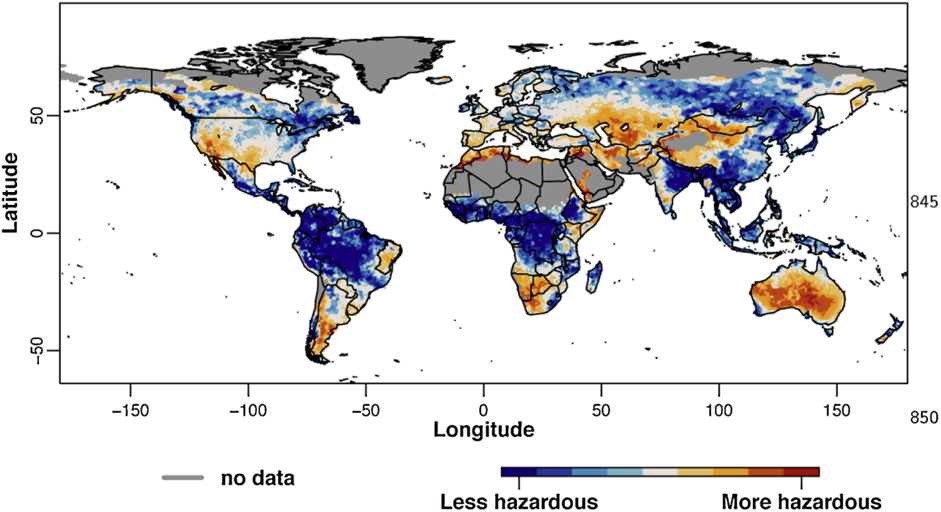
Drought maps are visual representations of drought severity across geographic regions. They utilize data collected from various sources, including satellite imagery, weather stations, and hydrological models, to depict the spatial distribution and intensity of drought conditions. These maps typically employ color-coded scales, where different shades represent varying levels of drought severity, ranging from mild to extreme.
Understanding the Data Behind Drought Maps: A Multifaceted Approach
The creation of drought maps relies on a diverse range of data sources, each offering unique perspectives on drought conditions. Key data sources include:
- Satellite Imagery: Satellites equipped with sensors capture images of the Earth’s surface, providing insights into vegetation health, soil moisture, and water bodies. These data are crucial for assessing the impact of drought on vegetation and water resources.
- Weather Station Data: Ground-based weather stations record crucial meteorological variables such as rainfall, temperature, and humidity. These data are used to assess the temporal and spatial distribution of precipitation deficits, a key indicator of drought.
- Hydrological Models: These models simulate the movement and storage of water in various hydrological systems, including rivers, lakes, and groundwater. They provide insights into water availability and the potential impacts of drought on water resources.
Types of Drought Maps: Tailoring Insights to Specific Needs
Drought maps can be categorized based on the type of data they utilize and the specific aspects of drought they highlight. Some common types include:
- Palmer Drought Severity Index (PDSI) Maps: These maps use a standardized index based on precipitation and temperature data to assess drought severity over long periods. They are particularly useful for understanding long-term drought trends and their historical context.
- Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) Maps: These maps focus on precipitation deficits, using a standardized index to compare current rainfall to historical averages. They are valuable for assessing short-term drought conditions and identifying areas experiencing rainfall anomalies.
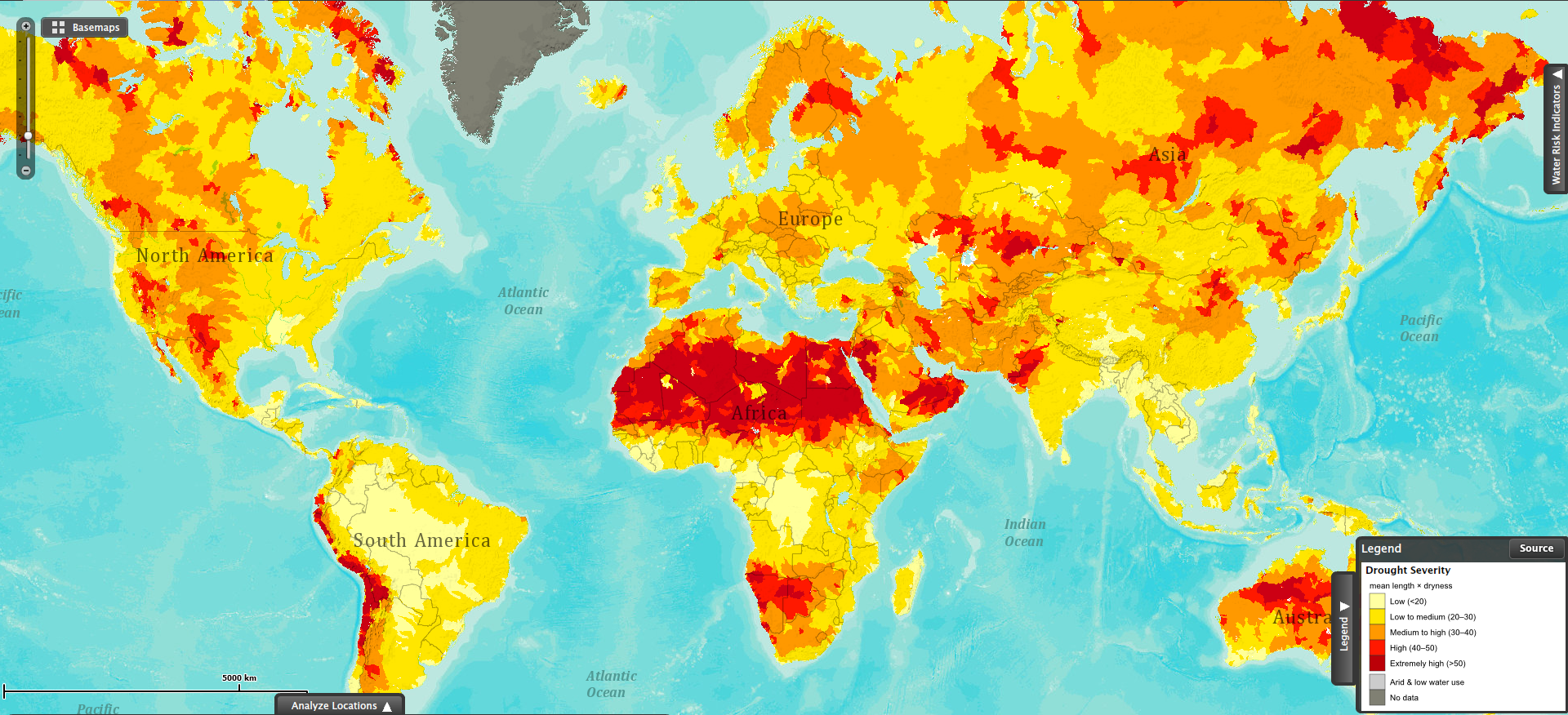
- Vegetation Health Maps: These maps utilize satellite imagery to assess the health of vegetation, providing insights into the impact of drought on plant growth and productivity. They are particularly useful for monitoring agricultural areas and assessing potential impacts on food security.
- Soil Moisture Maps: These maps utilize satellite data and models to estimate soil moisture levels, providing insights into the availability of water for plants and the potential for drought-induced crop failures.
The Significance of Drought Maps: Unlocking Critical Insights
Drought maps serve as vital tools for various stakeholders, providing crucial insights for informed decision-making and effective drought management:
- Water Resource Managers: Drought maps enable water resource managers to monitor drought conditions, anticipate water shortages, and implement appropriate water conservation measures.
- Agricultural Sector: Farmers and agricultural agencies can utilize drought maps to assess the impact of drought on crop yields, identify vulnerable areas, and develop strategies to mitigate losses.
- Emergency Response Agencies: Drought maps help emergency response agencies identify drought-affected regions, anticipate potential humanitarian crises, and plan for effective disaster relief efforts.
- Researchers and Scientists: Drought maps provide valuable data for researchers studying drought dynamics, climate change impacts, and the development of drought prediction models.
FAQs About Drought Maps: Addressing Common Questions
1. How often are drought maps updated?
The frequency of drought map updates varies depending on the data source and the specific application. Some maps are updated daily, while others are updated weekly, monthly, or even annually.
2. What are the limitations of drought maps?
Drought maps, while powerful tools, have limitations. They rely on data that may be incomplete, inaccurate, or have spatial and temporal biases. Additionally, they may not capture all aspects of drought, such as the social and economic impacts.
3. How can drought maps be used to predict future drought conditions?
Drought maps, in conjunction with climate models and historical data, can be used to develop drought prediction models. These models can provide insights into the likelihood of future droughts and their potential severity.
4. What are some examples of drought maps and where can I access them?
Numerous organizations and agencies provide access to drought maps, including:
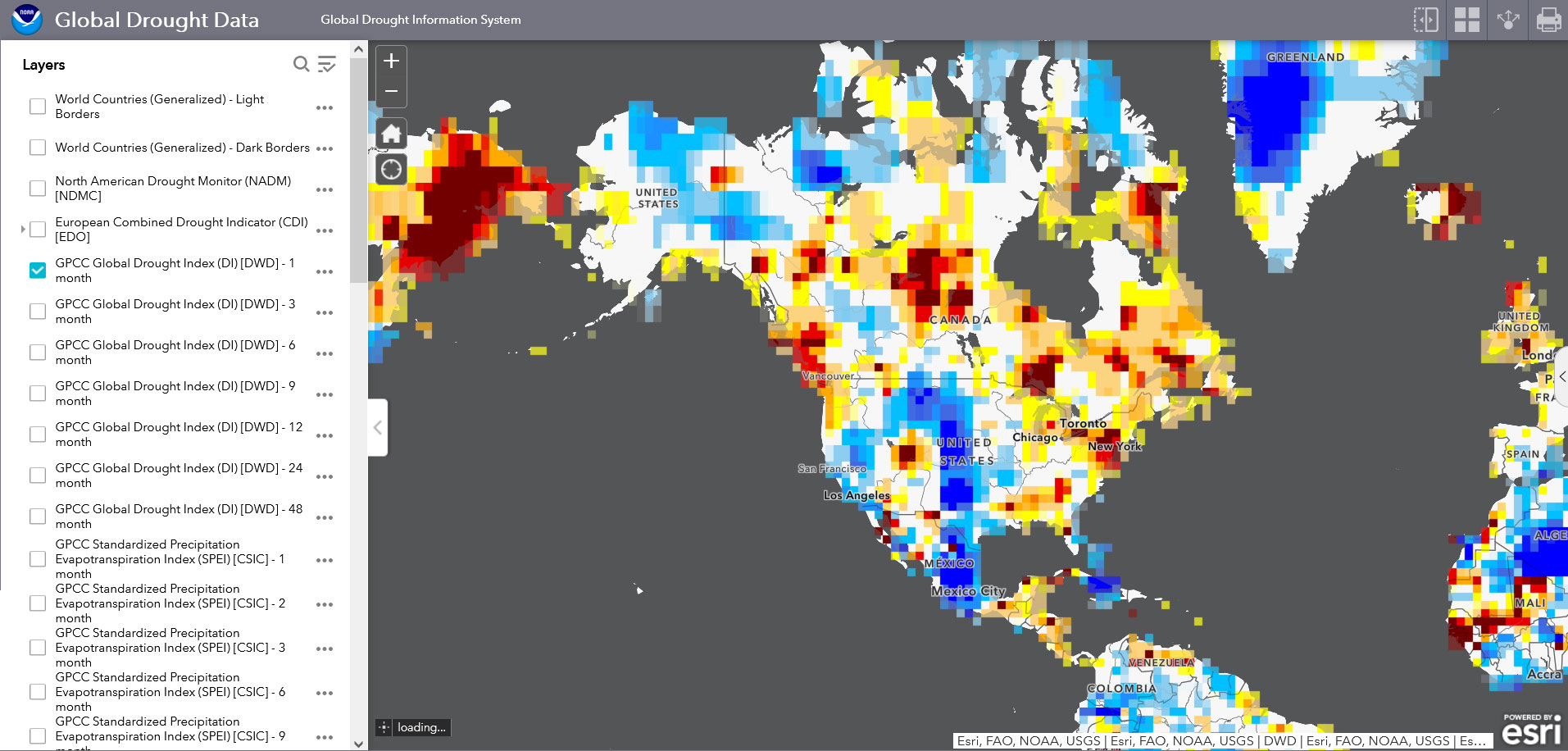
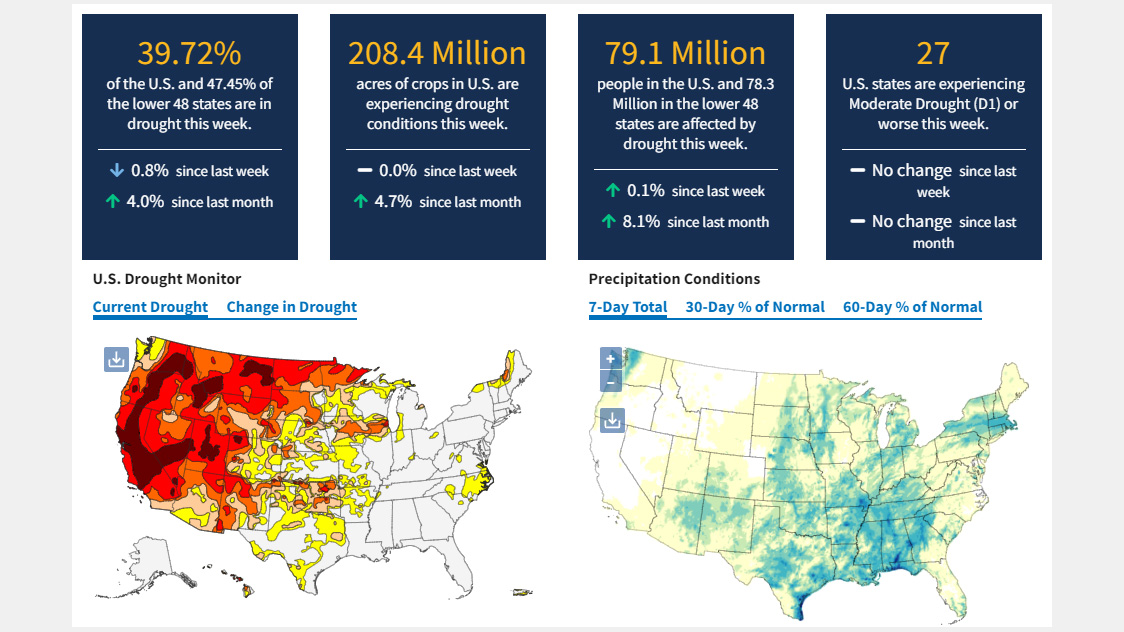
- United States Drought Monitor (USDM): https://droughtmonitor.unl.edu/
- European Drought Observatory (EDO): https://edo.jrc.ec.europa.eu/
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA): https://www.noaa.gov/
- National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA): https://www.nasa.gov/
5. How can I contribute to drought monitoring and mapping?
Citizen science initiatives, such as the Community Collaborative Rain, Hail & Snow Network (CoCoRaHS), enable individuals to contribute to drought monitoring by reporting rainfall data.
Tips for Utilizing Drought Maps Effectively: Maximizing their Potential
- Understand the data sources and limitations of the map.
- Consider the scale and resolution of the map.
- Compare different drought maps to gain a comprehensive understanding.
- Integrate drought maps with other data sources.
- Use drought maps to inform decision-making and planning.
Conclusion: Drought Maps as a Tool for Resilience and Adaptation
Drought maps are indispensable tools for understanding and managing drought, a growing challenge in a changing climate. By providing a visual representation of drought conditions, they empower stakeholders to make informed decisions, mitigate the impacts of drought, and build resilience to this complex and persistent threat. As technology advances and data availability increases, drought maps will continue to evolve, providing increasingly sophisticated insights into the dynamics of drought and its implications for human society and the natural world.
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Landscape of Drought: A Comprehensive Look at Drought Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
