Unveiling the Heart of Borneo: A Comprehensive Guide to the Map of Kalimantan
Related Articles: Unveiling the Heart of Borneo: A Comprehensive Guide to the Map of Kalimantan
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Heart of Borneo: A Comprehensive Guide to the Map of Kalimantan. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Heart of Borneo: A Comprehensive Guide to the Map of Kalimantan

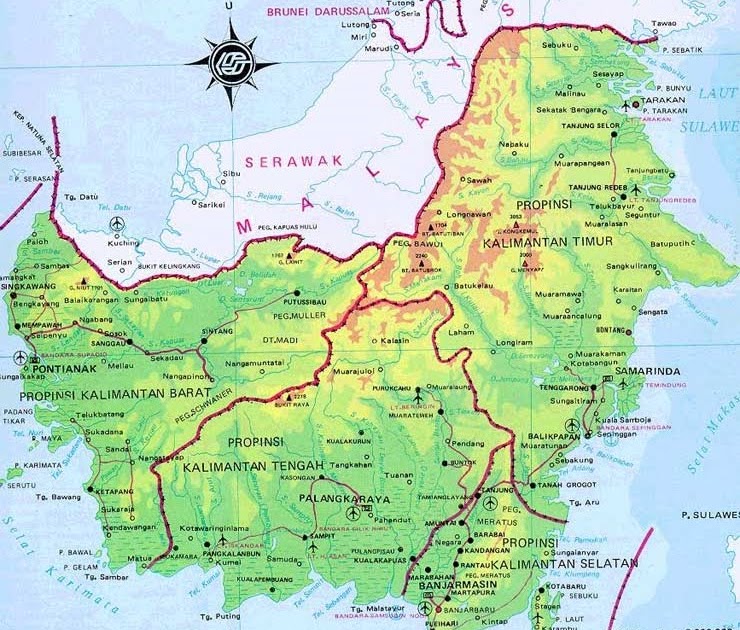
Kalimantan, the third largest island in the world, is a land of breathtaking beauty, rich biodiversity, and profound cultural heritage. It is an integral part of Southeast Asia, encompassing territory belonging to three nations: Indonesia, Malaysia, and Brunei Darussalam. Understanding the map of Kalimantan is crucial for comprehending the island’s complex geography, its diverse ecosystems, and the cultural tapestry woven across its vast expanse.
Delving into the Geography of Kalimantan
The map of Kalimantan reveals a land shaped by the forces of nature. The island is dominated by a central mountain range, the Schwaner Mountains, which stretches from north to south, dividing the island into distinct regions. To the west lies the vast Kapuas River basin, the longest river in Indonesia, while the east is characterized by a series of smaller rivers and coastal plains.
A Mosaic of Ecosystems: The Diverse Landscapes of Kalimantan
Kalimantan’s map is a testament to its ecological richness. It boasts a remarkable array of ecosystems, each with its unique flora and fauna:
- Rainforests: Dominating the island’s interior, these rainforests are renowned for their biodiversity, housing an estimated 10% of the world’s plant species and countless animal species, including endangered orangutans, clouded leopards, and Sumatran rhinos.
- Mangrove Forests: Thriving along the coastlines, these unique ecosystems provide critical habitats for marine life, protect shorelines from erosion, and act as vital carbon sinks.
- Peat Swamps: Characterized by acidic water and dense vegetation, these swamps are home to a diverse array of endemic species and play a crucial role in regulating water flow and carbon storage.
- Coastal Areas: Stretching along the edges of the island, these areas are marked by sandy beaches, coral reefs, and mangrove forests, supporting a thriving marine ecosystem and providing livelihoods for coastal communities.
A Cultural Tapestry: The People of Kalimantan
The map of Kalimantan also reflects the rich cultural diversity of the island. It is home to numerous indigenous groups, each with their own distinct languages, traditions, and ways of life. Some of the major ethnic groups include:
- Dayak: This diverse group comprises numerous sub-tribes, known for their intricate traditional arts, animistic beliefs, and unique customs.
- Banjar: Primarily residing in South Kalimantan, the Banjar people are known for their maritime heritage, their intricate weaving techniques, and their strong Islamic faith.
- Malay: Found in coastal areas and riverine settlements, the Malay people are known for their rich maritime traditions and their role in trade and cultural exchange.
The Importance of the Map of Kalimantan
Understanding the map of Kalimantan is essential for several reasons:
- Conservation and Environmental Management: The map provides a crucial framework for understanding the island’s diverse ecosystems, allowing for targeted conservation efforts and sustainable management of natural resources.
- Economic Development: The map aids in planning infrastructure development, facilitating access to remote areas, and supporting economic growth in a way that minimizes environmental impact.
- Cultural Preservation: The map helps to understand the distribution of indigenous groups, fostering cultural exchange and promoting the preservation of their unique traditions.
- Disaster Risk Management: The map enables accurate assessment of natural hazards such as floods, landslides, and earthquakes, enabling effective disaster preparedness and response.
Frequently Asked Questions about the Map of Kalimantan
Q: What is the political division of Kalimantan?
A: Kalimantan is divided into three parts:
- Indonesian Kalimantan: Comprises the majority of the island, divided into four provinces: Central Kalimantan, East Kalimantan, North Kalimantan, and South Kalimantan.
- Malaysian Kalimantan: Comprises the states of Sarawak and Sabah.
- Brunei: A small sultanate located on the northwestern coast.
Q: What are the major cities in Kalimantan?
A: Some of the major cities in Kalimantan include:
- Banjarmasin (Indonesia): The capital of South Kalimantan, known for its traditional markets and its role as a regional trade center.
- Pontianak (Indonesia): The capital of West Kalimantan, located on the Kapuas River and known for its historical landmarks.
- Samarinda (Indonesia): The capital of East Kalimantan, a major center for the oil and gas industry.
- Kuching (Malaysia): The capital of Sarawak, known for its colonial architecture and its vibrant cultural scene.
- Kota Kinabalu (Malaysia): The capital of Sabah, a gateway to Mount Kinabalu, the highest peak in Southeast Asia.
Q: What are the major rivers in Kalimantan?
A: The major rivers in Kalimantan include:
- Kapuas River: The longest river in Indonesia, flowing through West Kalimantan and providing vital transportation routes.
- Barito River: The second longest river in Indonesia, flowing through Central Kalimantan and supporting a rich biodiversity.
- Mahakam River: A major river in East Kalimantan, known for its oil and gas deposits and its scenic beauty.
Q: What are the major natural resources found in Kalimantan?
A: Kalimantan is rich in natural resources, including:
- Oil and Gas: Large deposits of oil and gas are found in East Kalimantan, making it a major energy producing region.
- Timber: Vast forests provide a valuable source of timber, but unsustainable logging practices pose a threat to the environment.
- Coal: Significant coal deposits are found in East Kalimantan, contributing to the region’s industrial development.
- Palm Oil: Large-scale palm oil plantations have been established in Kalimantan, but their expansion has raised concerns about deforestation and biodiversity loss.
Tips for Exploring the Map of Kalimantan
- Start with a general overview map: Familiarize yourself with the island’s major features, including its political divisions, major cities, and prominent rivers.
- Focus on specific regions: Choose a region of interest and explore its unique features in detail, such as its cultural heritage, natural attractions, or economic activities.
- Use online mapping tools: Websites like Google Maps and OpenStreetMap offer detailed maps of Kalimantan, allowing you to zoom in and explore specific areas.
- Combine maps with other resources: Use maps in conjunction with travel guides, documentaries, and online articles to gain a deeper understanding of the island’s geography, culture, and history.
Conclusion
The map of Kalimantan is more than just a geographical representation; it is a window into a world of breathtaking beauty, rich biodiversity, and profound cultural heritage. Understanding the island’s geography, ecosystems, and diverse populations is crucial for conservation, sustainable development, and cultural preservation. By using maps as a tool for exploration and learning, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complex and fascinating world of Kalimantan.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Heart of Borneo: A Comprehensive Guide to the Map of Kalimantan. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
