Unveiling the Frozen Frontier: A Comprehensive Look at the Tundra’s Global Distribution
Related Articles: Unveiling the Frozen Frontier: A Comprehensive Look at the Tundra’s Global Distribution
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Frozen Frontier: A Comprehensive Look at the Tundra’s Global Distribution. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Frozen Frontier: A Comprehensive Look at the Tundra’s Global Distribution

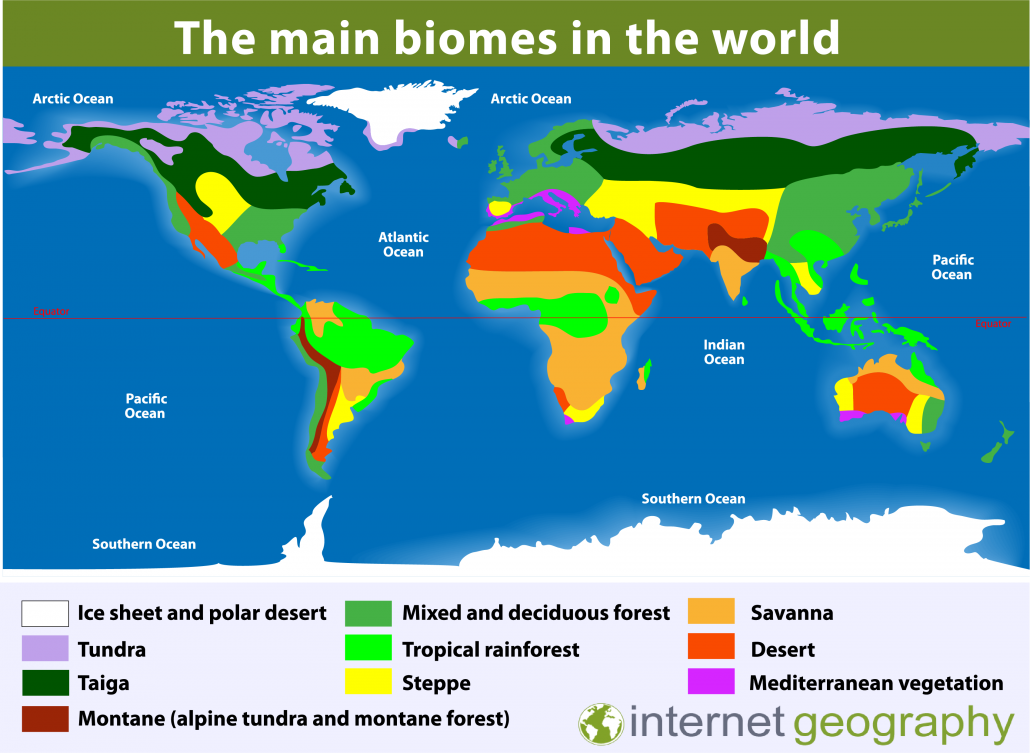
The tundra, a biome characterized by its frigid temperatures, permafrost, and limited plant life, occupies a significant portion of the Earth’s surface. Understanding its geographical distribution is crucial for comprehending the delicate balance of ecosystems and the impact of climate change. This article delves into the global distribution of the tundra, exploring its distinct characteristics, ecological significance, and the challenges it faces.
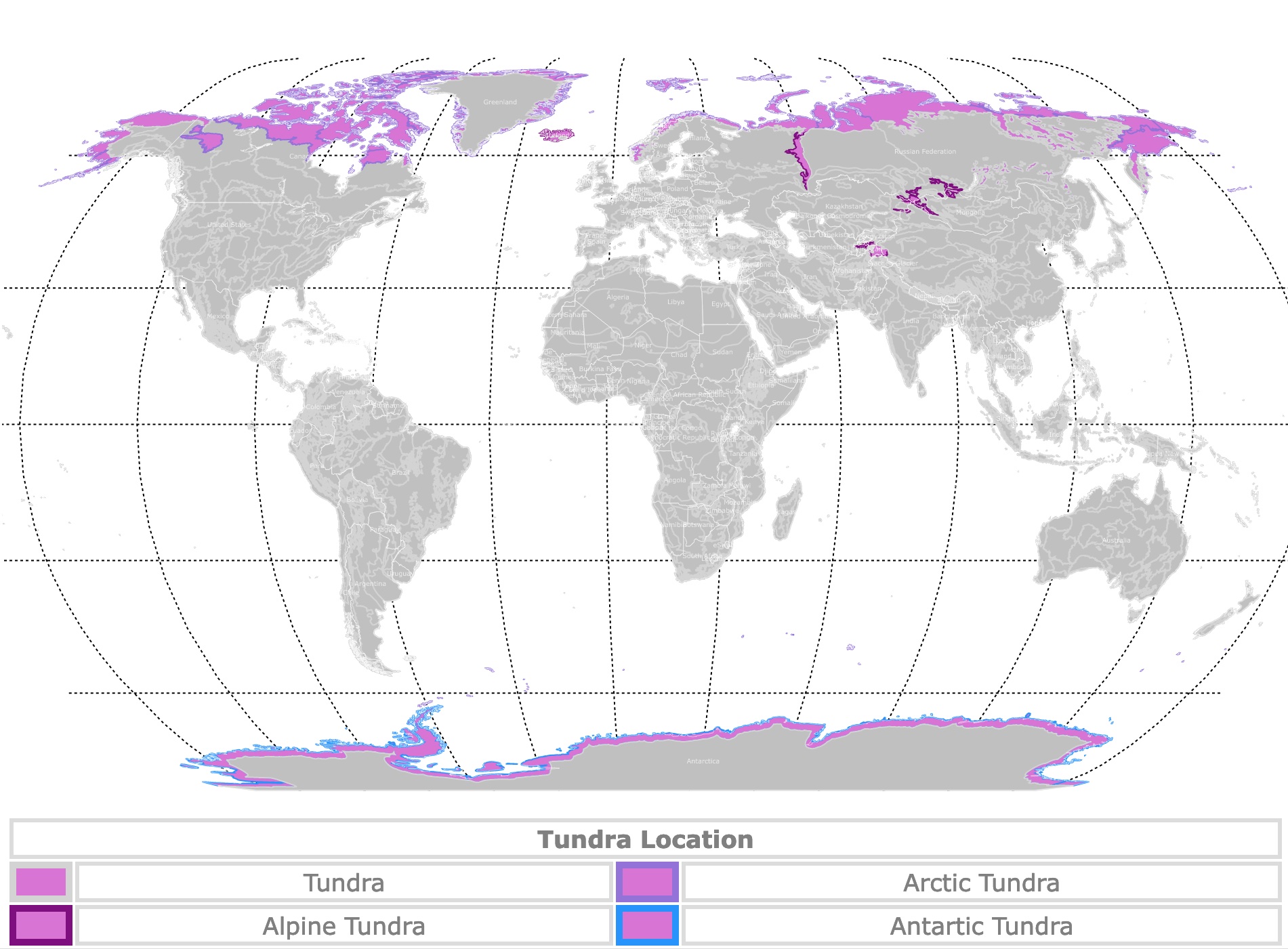
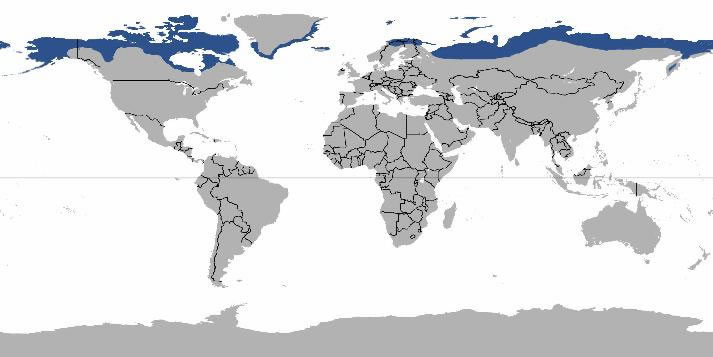
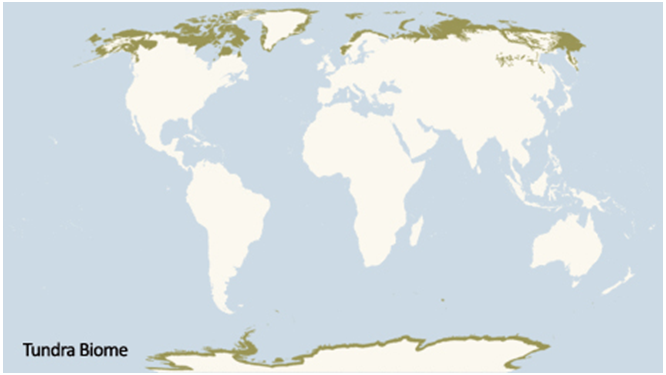
A Global Map of the Tundra:
The tundra biome encompasses a vast, circumpolar region surrounding the Arctic and extending southward across the high-altitude mountains of the world.
- Arctic Tundra: This region encircles the Arctic Ocean, stretching across northern portions of North America, Europe, and Asia. Countries like Canada, Russia, Greenland, Norway, Finland, Sweden, and Iceland house significant portions of the Arctic tundra.
- Alpine Tundra: Found at high elevations above the treeline, alpine tundra occurs in mountainous regions across the globe. The Himalayas, Andes, Alps, and Rocky Mountains are notable examples of locations hosting alpine tundra ecosystems.
Distinctive Features of the Tundra:
The tundra’s harsh conditions create a unique and resilient ecosystem:
- Permafrost: The defining characteristic of the tundra is permafrost, a layer of permanently frozen ground that lies beneath the surface. Permafrost plays a critical role in shaping the landscape, influencing water drainage, and impacting plant growth.
- Low Temperatures: The tundra experiences extremely cold temperatures for extended periods, with average annual temperatures ranging from -15°C to 5°C. During the short summer months, temperatures rise above freezing, allowing for a brief period of plant growth.
- Limited Precipitation: The tundra receives relatively low precipitation, primarily in the form of snow. This limited rainfall contributes to the dry conditions and further restricts plant growth.
- Short Growing Season: The tundra’s short growing season, typically lasting only a few months, limits the types of plants that can thrive in this environment.
- Unique Flora and Fauna: Despite the harsh conditions, the tundra supports a diverse array of life, including specialized plants adapted to survive the cold and limited growing season. Notable examples include lichens, mosses, dwarf shrubs, and grasses. The fauna includes Arctic foxes, caribou, musk oxen, and various migratory bird species.
Ecological Importance of the Tundra:
The tundra plays a vital role in the global ecosystem:
- Carbon Sink: The permafrost acts as a massive carbon sink, storing vast amounts of organic matter. As temperatures rise, permafrost thaws, releasing methane and carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, contributing to climate change.
- Habitat for Diverse Species: The tundra provides essential habitat for numerous species of plants and animals, many of which are adapted to the unique conditions.
- Water Regulation: The tundra’s frozen ground influences water flow and drainage, impacting water availability in downstream regions.
- Climate Regulation: The tundra’s albedo, or reflectivity, plays a crucial role in regulating the Earth’s energy balance. Snow and ice reflect sunlight, helping to cool the planet.
Challenges Facing the Tundra:
The tundra faces numerous challenges, particularly due to climate change:
- Permafrost Thaw: As global temperatures rise, permafrost thaws at an accelerating rate, leading to soil erosion, changes in vegetation, and the release of greenhouse gases.
- Habitat Loss and Fragmentation: Human activities, such as oil and gas exploration, mining, and infrastructure development, are fragmenting tundra habitats and impacting wildlife populations.
- Pollution: Industrial activities and transportation contribute to air and water pollution, further stressing the fragile tundra ecosystem.
- Climate Change Impacts: The tundra is particularly vulnerable to climate change, with rising temperatures leading to changes in vegetation, permafrost thaw, and disruptions to the delicate balance of the ecosystem.
FAQs about the Tundra’s Location:
-
Q: What is the difference between the Arctic tundra and the alpine tundra?
- A: The Arctic tundra is found at high latitudes surrounding the Arctic Ocean, while the alpine tundra occurs at high elevations above the treeline in mountainous regions. Both share similar characteristics, such as cold temperatures, permafrost, and limited plant life.
-
Q: Where is the largest expanse of tundra located?
- A: The largest expanse of tundra is found in Russia, covering vast areas of Siberia.
-
Q: Are there any countries that don’t have tundra?
- A: While the tundra is primarily found in the northern hemisphere, some high-altitude mountain ranges in the southern hemisphere, such as the Andes, also contain alpine tundra ecosystems. However, countries located in the tropics and near the equator generally lack tundra.
Tips for Understanding the Tundra’s Location:
- Utilize Online Maps: Interactive maps, such as Google Maps and ArcGIS, provide detailed information on the global distribution of the tundra.
- Explore Educational Websites: Websites dedicated to geography, ecology, and climate change offer comprehensive information on the tundra and its location.
- Consult Geographic Atlases: Traditional atlases often include maps depicting major biomes, including the tundra.
Conclusion:
The tundra, a vast and unique biome, plays a vital role in the global ecosystem. Its location in the frigid Arctic and high-altitude mountains highlights its resilience and adaptability to harsh conditions. Understanding the tundra’s distribution and the challenges it faces is essential for informing conservation efforts and mitigating the impacts of climate change on this fragile and important ecosystem. By recognizing its ecological importance and the threats it faces, we can work towards protecting this frozen frontier for future generations.



![[Frozen Frontier] A map for the Frozen Frontier campaign : r/Koibu](https://i.redd.it/60q98l8d7f2z.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Frozen Frontier: A Comprehensive Look at the Tundra’s Global Distribution. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
