Unveiling the Depths: A Comprehensive Guide to Bathymetric Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Depths: A Comprehensive Guide to Bathymetric Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Depths: A Comprehensive Guide to Bathymetric Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Depths: A Comprehensive Guide to Bathymetric Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Depths: A Comprehensive Guide to Bathymetric Maps
- 3.1 What is a Bathymetric Map?
- 3.2 The Importance of Bathymetric Maps: Unveiling the Ocean’s Mysteries
- 3.3 Methods of Creating Bathymetric Maps: From Traditional to Modern
- 3.4 FAQs about Bathymetric Maps: Addressing Common Questions
- 3.5 Tips for Understanding Bathymetric Maps: Decoding the Depths
- 3.6 Conclusion: The Importance of Bathymetric Maps in a Changing World
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Depths: A Comprehensive Guide to Bathymetric Maps

The Earth’s surface is a tapestry of diverse landscapes, but beneath the waves lies a hidden world teeming with life and geological wonders. Understanding this submerged realm is crucial for various fields, from navigation and resource exploration to environmental management and scientific research. Enter the bathymetric map, a powerful tool that provides a detailed representation of the ocean floor’s topography, revealing its depths, features, and secrets.
What is a Bathymetric Map?
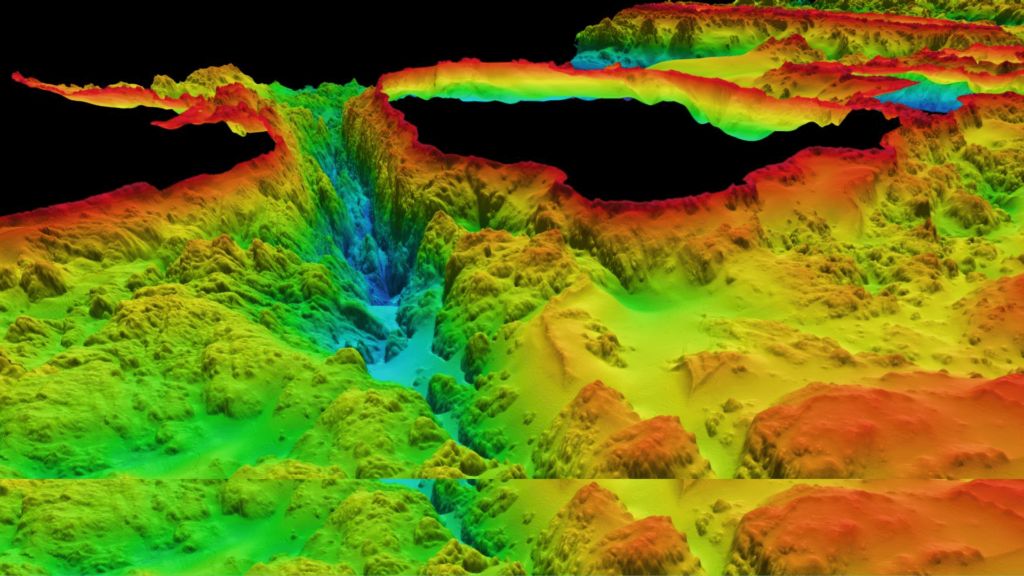
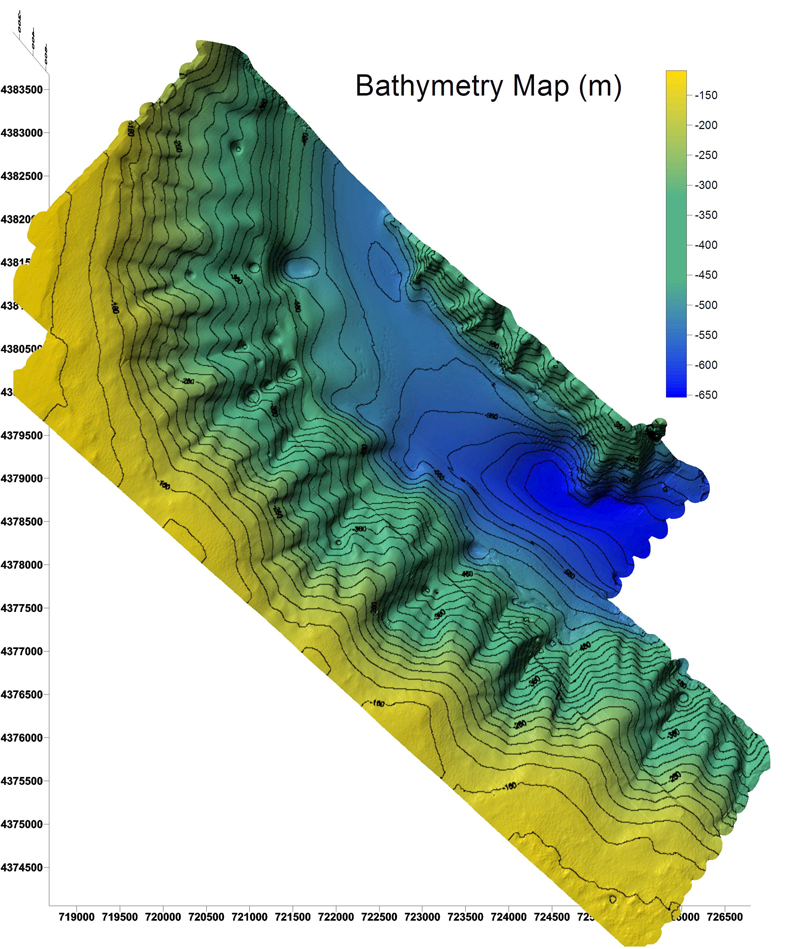
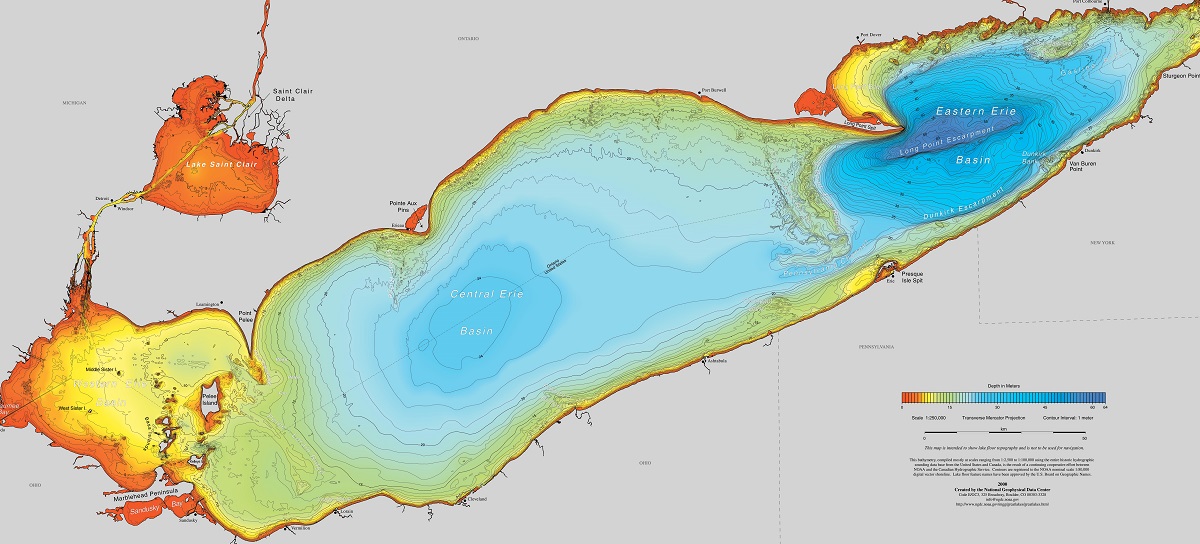
A bathymetric map, essentially a topographical map of the ocean floor, illustrates the underwater terrain’s contours and elevations. It uses lines of equal depth, known as isobaths, to depict the seabed’s shape, much like contour lines on a land map represent changes in elevation. These maps are invaluable for visualizing the underwater landscape, providing insights into the ocean’s geological formations, marine ecosystems, and potential hazards.
The Importance of Bathymetric Maps: Unveiling the Ocean’s Mysteries
Bathymetric maps are not merely static representations of the ocean floor; they are dynamic tools with far-reaching implications. Their significance extends across various disciplines, playing a vital role in:
1. Navigation and Safety:
- Seabed Mapping for Safe Navigation: Bathymetric data is crucial for mariners, enabling them to navigate safely through treacherous waters, identify potential hazards like shallow reefs and shipwrecks, and optimize shipping routes.
- Underwater Navigation and Exploration: Submersibles and underwater robots rely on detailed bathymetric maps to navigate complex underwater environments, facilitating exploration and research.
- Coastal Management and Safety: Accurate bathymetric data is essential for coastal management, informing decisions about shoreline protection, harbor construction, and the placement of offshore structures.
2. Resource Exploration and Management:
- Exploration of Marine Resources: Bathymetric maps guide the search for valuable marine resources like oil and gas deposits, minerals, and potential fishing grounds.
- Sustainable Fisheries Management: Understanding the ocean floor’s topography allows for the identification of essential fish habitats and the implementation of sustainable fishing practices.
- Marine Energy Exploration: Bathymetric data is vital for assessing the feasibility of harnessing marine energy resources, such as tidal power and wave energy.
3. Environmental Monitoring and Conservation:
- Understanding Marine Ecosystems: Bathymetric maps provide crucial insights into the distribution of marine species, their habitats, and the impact of environmental changes.
- Monitoring Coastal Erosion and Sea Level Rise: Bathymetric data plays a crucial role in tracking changes in coastal environments, informing strategies to combat erosion and mitigate the effects of sea level rise.
- Marine Conservation and Protected Areas: Bathymetric maps assist in identifying and protecting vulnerable marine ecosystems, contributing to the conservation of biodiversity.
4. Scientific Research and Understanding:
- Understanding Plate Tectonics and Geological Processes: Bathymetric data provides valuable insights into the Earth’s geological processes, including plate tectonics, volcanic activity, and the formation of submarine canyons.
- Climate Change Research: Bathymetric maps contribute to understanding the impact of climate change on ocean currents, sea level rise, and the distribution of marine life.
- Oceanographic Research: Bathymetric data is essential for studying ocean currents, wave patterns, and the movement of sediments.
Methods of Creating Bathymetric Maps: From Traditional to Modern
The creation of bathymetric maps has evolved significantly over time, transitioning from traditional methods to advanced technologies:
1. Traditional Methods:
- Soundings: This traditional method involved dropping a weighted line with a marked rope into the water to measure depth. While simple, it was time-consuming and limited in scope.
- Echo Sounding: This technique utilizes sound waves to measure the time it takes for a signal to travel from the vessel to the seabed and back. This method provided a more efficient way to map the ocean floor but still had limitations in resolution.
2. Modern Technologies:
- Multibeam Sonar: This sophisticated technology emits a fan of sound waves, capturing a wider swath of the seabed at once. It provides high-resolution bathymetric data, enabling detailed mapping of the ocean floor.
- Side-Scan Sonar: This technology uses sound waves to create images of the ocean floor, revealing features like shipwrecks, underwater structures, and geological formations.
- Remote Sensing: Satellite altimetry uses radar signals to measure the height of the ocean surface, which can be used to infer the underlying bathymetry.
- LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): This technology uses laser pulses to measure distances to the ocean floor, providing highly accurate bathymetric data for shallow water areas.
3. Data Integration and Analysis:
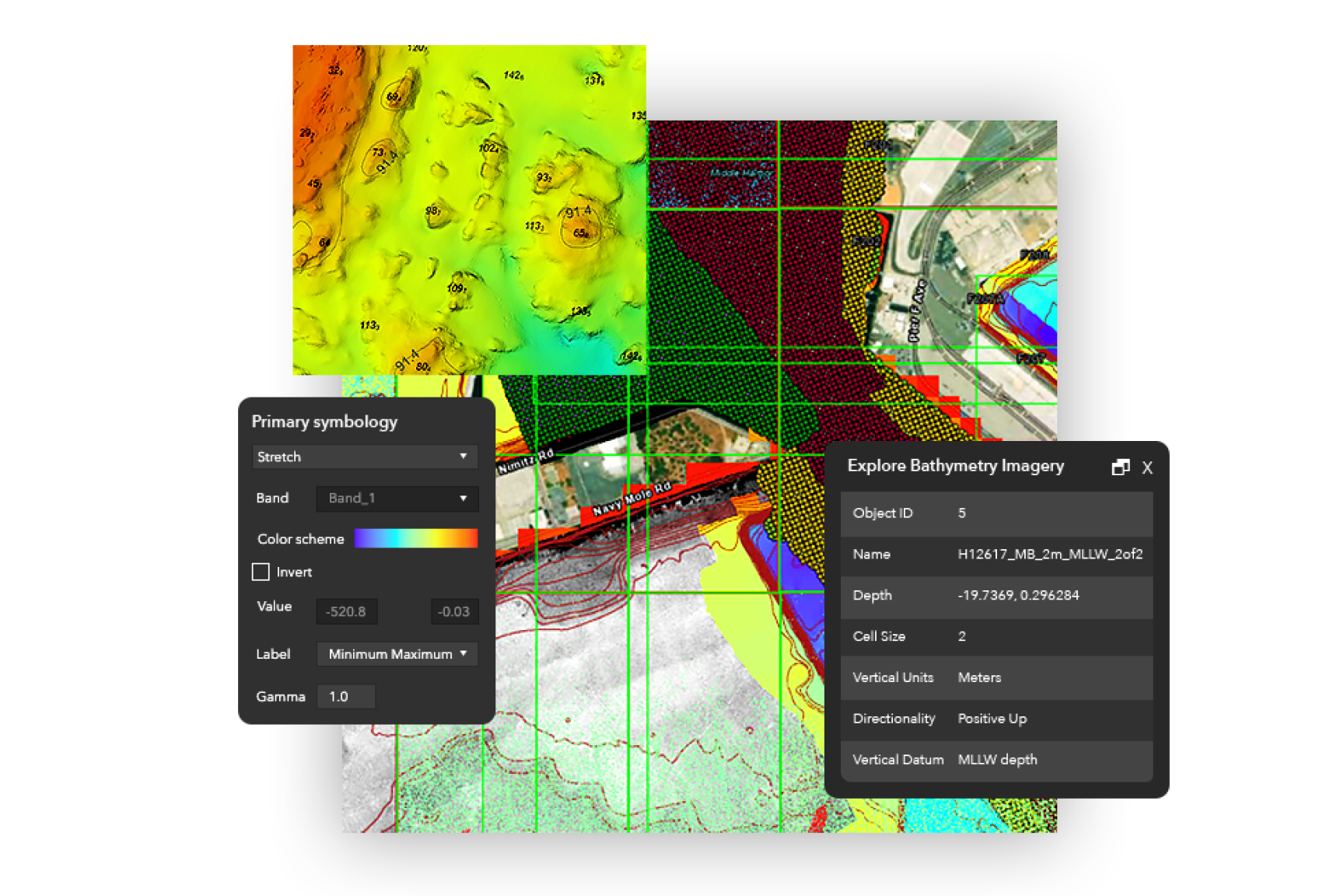
- GIS (Geographic Information System): This software allows for the integration of bathymetric data with other geographic information, enabling comprehensive analysis and visualization of the ocean floor.
- Computer Modeling and Simulation: Sophisticated computer models utilize bathymetric data to simulate ocean currents, wave propagation, and other oceanographic phenomena.
FAQs about Bathymetric Maps: Addressing Common Questions
1. What is the difference between a bathymetric map and a nautical chart?
A bathymetric map primarily focuses on the ocean floor’s topography, depicting depths and contours. In contrast, a nautical chart is designed for navigation, incorporating bathymetric information alongside additional details like coastlines, navigational aids, and hazards.
2. Are bathymetric maps available for all parts of the ocean?
While significant progress has been made in mapping the ocean floor, large portions remain uncharted. The availability of bathymetric maps varies depending on the location, accessibility, and the intensity of mapping efforts.
3. How accurate are bathymetric maps?
The accuracy of bathymetric maps depends on the methods used for data collection and the resolution of the data. Modern technologies like multibeam sonar provide highly accurate data, while traditional methods may have lower accuracy.
4. What are the applications of bathymetric maps in marine research?
Bathymetric maps play a crucial role in various marine research areas, including:
- Understanding ocean currents and circulation patterns.
- Studying the distribution and behavior of marine life.
- Investigating the impact of climate change on the ocean floor.
- Exploring the geological history of the ocean basins.
5. How can I access bathymetric data?
Various organizations and government agencies make bathymetric data publicly available. These include:
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA): Provides bathymetric data for the United States.
- International Hydrographic Organization (IHO): Coordinates international efforts in hydrographic surveying and charting.
- European Marine Observation and Data Network (EMODNET): Provides bathymetric data for European waters.
6. What are the future trends in bathymetric mapping?
Future developments in bathymetric mapping are expected to focus on:
- Improving the resolution and accuracy of data acquisition.
- Expanding the coverage of bathymetric maps to previously uncharted areas.
- Developing new technologies for mapping complex underwater environments.
- Integrating bathymetric data with other oceanographic data for comprehensive analysis.
Tips for Understanding Bathymetric Maps: Decoding the Depths
1. Familiarize yourself with the map’s legend: Understand the symbols and colors used to represent depth, contours, and other features.
2. Identify the scale of the map: Determine the relationship between the map’s distance and the actual distance on the ocean floor.
3. Analyze the contours: Pay attention to the spacing and shape of the isobaths to understand the shape and steepness of the underwater terrain.
4. Consider the context: Look for nearby features, such as coastlines, islands, and geological formations, to understand the context of the bathymetric data.
5. Use online resources: Explore interactive bathymetric maps and online tools for visualizing and analyzing bathymetric data.
Conclusion: The Importance of Bathymetric Maps in a Changing World
Bathymetric maps are essential tools for understanding and navigating the Earth’s submerged realm. They provide vital information for navigation, resource exploration, environmental management, and scientific research. As our understanding of the ocean deepens, the importance of bathymetric data continues to grow, informing decisions about our interactions with this vital resource. By embracing the power of bathymetric maps, we unlock a deeper understanding of the ocean’s secrets, paving the way for responsible exploration, sustainable management, and the conservation of this precious ecosystem.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Depths: A Comprehensive Guide to Bathymetric Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
