Unraveling the Secrets of the Earth: Understanding Liquefaction Maps
Related Articles: Unraveling the Secrets of the Earth: Understanding Liquefaction Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Secrets of the Earth: Understanding Liquefaction Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Secrets of the Earth: Understanding Liquefaction Maps
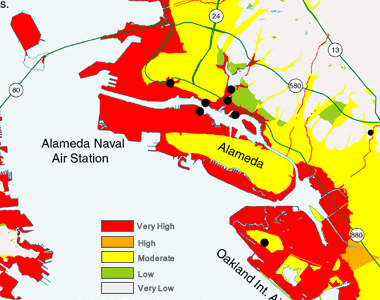
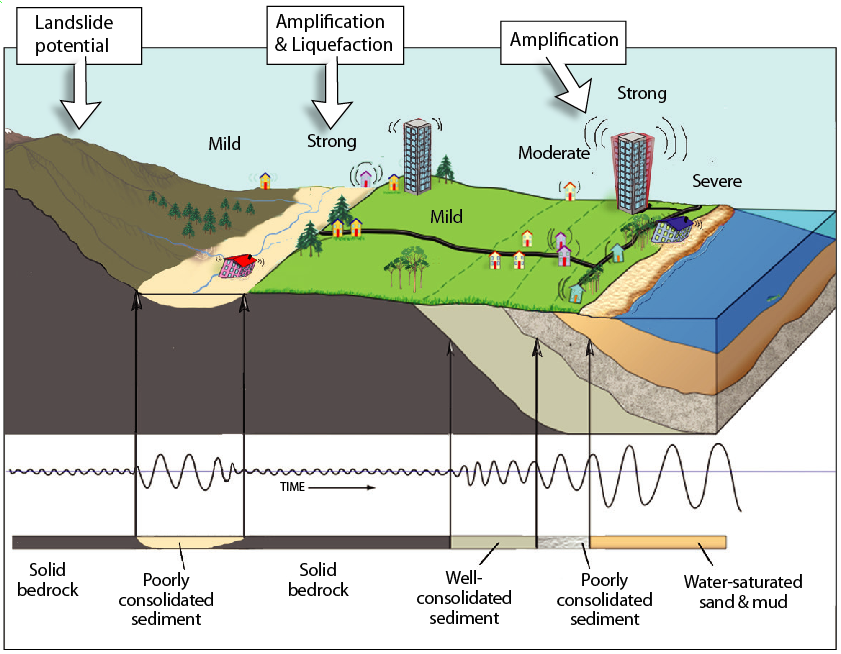
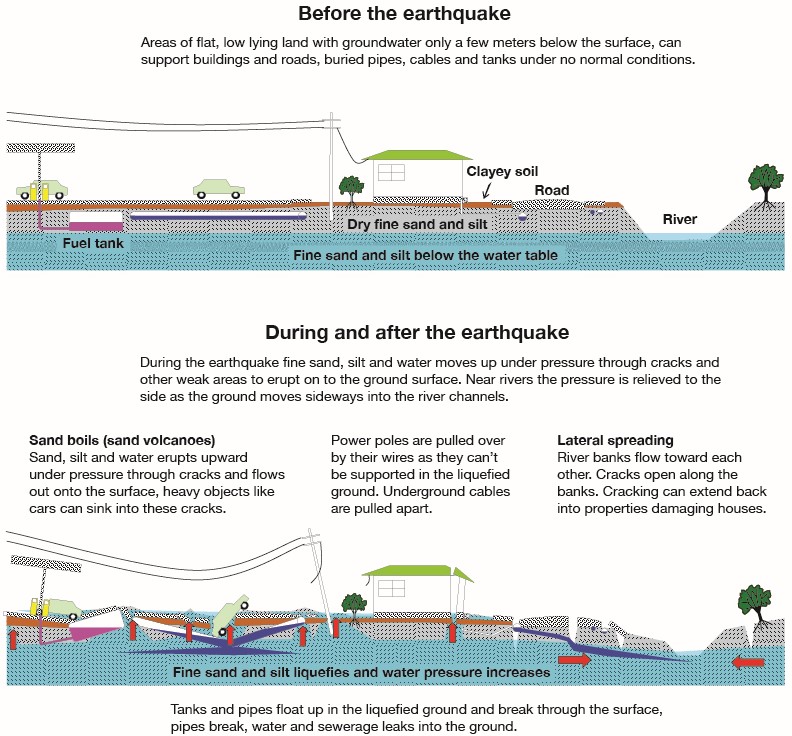
The ground beneath our feet, seemingly solid and stable, can sometimes behave in unexpected and dangerous ways. One such phenomenon, known as soil liquefaction, occurs when saturated, loose soil loses its strength and behaves like a liquid during an earthquake. Understanding the potential for liquefaction is crucial for mitigating its devastating effects, and this is where liquefaction maps come into play.
Delving into the Dynamics of Liquefaction
Liquefaction is a complex process that involves the interplay of several factors:
- Seismic Activity: Earthquakes provide the trigger for liquefaction. The ground shaking disrupts the structure of loose, saturated soil, causing the water within the soil to increase its pressure and effectively "float" the soil particles.
- Soil Characteristics: The susceptibility of soil to liquefaction depends on its composition, grain size, and density. Fine-grained soils with high water content are particularly vulnerable.
- Groundwater Table: The depth of the groundwater table plays a significant role. Soils with a high groundwater table are more prone to liquefaction as the water is readily available to contribute to the pore pressure build-up.
The Crucial Role of Liquefaction Maps
Liquefaction maps are visual representations of the potential for liquefaction in a given area. They are essential tools for:
- Urban Planning and Development: By identifying areas susceptible to liquefaction, planners can make informed decisions regarding land use, building codes, and infrastructure design. This helps minimize the risk of damage and protect lives.
- Disaster Preparedness: Liquefaction maps enable emergency responders to anticipate the potential impacts of an earthquake and plan effective rescue and relief operations. They also help communities prepare for potential evacuations and develop robust disaster preparedness plans.
- Insurance and Risk Assessment: Insurance companies rely on liquefaction maps to assess risk and determine premiums for property insurance. This helps ensure fair pricing and coverage for homeowners in areas with a high risk of liquefaction.
- Infrastructure Design: Liquefaction maps guide engineers in designing bridges, roads, and other infrastructure projects to withstand the forces of liquefaction. This ensures the resilience and safety of these critical assets.
Understanding the Components of a Liquefaction Map
A typical liquefaction map encompasses several key elements:
- Geographic Basemap: A basemap provides the geographical context, often incorporating features like roads, rivers, and buildings.
- Liquefaction Susceptibility Zones: These zones are typically color-coded to indicate the relative likelihood of liquefaction. Areas marked with higher susceptibility require greater attention and mitigation measures.
- Soil Characteristics: The map may incorporate information about soil type, depth to groundwater, and other relevant geological factors.
- Historical Data: Data from past earthquakes and liquefaction events can be incorporated to refine the map and provide a more accurate assessment of risk.
Creating and Updating Liquefaction Maps
The process of creating a liquefaction map involves:
- Geotechnical Investigations: Soil samples are collected and analyzed to determine their properties and susceptibility to liquefaction.
- Seismic Hazard Assessment: The potential for earthquakes in the area is evaluated, considering factors like fault lines and historical seismic activity.
- Modeling and Analysis: Computer models are used to simulate the effects of earthquakes on the soil and predict the likelihood of liquefaction.
- Map Development: The results of the investigations and modeling are compiled to create the liquefaction map, incorporating different levels of susceptibility and risk.
- Regular Updates: Liquefaction maps are dynamic tools that require regular updates as new data becomes available and our understanding of the phenomenon evolves.
Benefits and Importance of Liquefaction Maps
The benefits of using liquefaction maps are multifaceted:
- Reduced Risk of Damage: By identifying areas prone to liquefaction, mitigation measures can be implemented to reduce the risk of damage to buildings, infrastructure, and property.
- Improved Disaster Preparedness: Liquefaction maps enable communities to prepare for earthquakes and other seismic events by developing evacuation plans, identifying safe zones, and stockpiling emergency supplies.
- Enhanced Safety and Resilience: Liquefaction maps contribute to the safety and resilience of communities by informing the design of buildings and infrastructure to withstand the effects of liquefaction.
- Informed Decision-Making: Liquefaction maps provide valuable information for planners, engineers, and policymakers, enabling them to make informed decisions about land use, infrastructure development, and disaster preparedness.
FAQs about Liquefaction Maps
Q: What is the purpose of a liquefaction map?
A: Liquefaction maps identify areas prone to soil liquefaction during earthquakes, providing crucial information for urban planning, disaster preparedness, and infrastructure design.
Q: How are liquefaction maps created?
A: They are created through a combination of geotechnical investigations, seismic hazard assessment, modeling, and analysis, incorporating data on soil properties, earthquake potential, and historical events.
Q: Who uses liquefaction maps?
A: Liquefaction maps are used by a wide range of stakeholders, including urban planners, engineers, emergency responders, insurance companies, and policymakers.
Q: Are liquefaction maps accurate?
A: Liquefaction maps are based on the best available data and scientific understanding, but they are not perfect predictions. The accuracy of a map depends on the quality of the data used and the complexity of the geological conditions in the area.
Q: How often are liquefaction maps updated?
A: The frequency of updates depends on the rate of new data acquisition, changes in understanding of liquefaction, and the level of risk in the area. Maps are generally updated periodically, often in conjunction with new seismic hazard assessments or geotechnical investigations.
Q: What are some examples of mitigation measures for liquefaction?
A: Mitigation measures can include ground improvement techniques like soil compaction, drainage, and ground reinforcement, as well as building design strategies to withstand the effects of liquefaction.
Tips for Utilizing Liquefaction Maps
- Consult with Experts: Always consult with qualified geotechnical engineers and seismologists to interpret liquefaction maps and understand their implications for your specific location.
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of updates to liquefaction maps and new research on liquefaction to ensure you have the most current information.
- Plan for Mitigation: If your property is located in a high-liquefaction risk zone, develop a plan for mitigation measures to protect your buildings and infrastructure.
- Prepare for Emergencies: Develop a family emergency plan that includes evacuation routes, communication procedures, and a safe meeting place in case of an earthquake.
Conclusion
Liquefaction maps are indispensable tools for understanding and mitigating the risks associated with soil liquefaction. By providing visual representations of potential liquefaction zones, they empower communities to plan for earthquakes, protect lives, and ensure the resilience of their infrastructure. As our knowledge of liquefaction evolves and new data becomes available, these maps will continue to play a vital role in shaping our approach to seismic hazard mitigation and ensuring the safety of our built environment.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Secrets of the Earth: Understanding Liquefaction Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
