Navigating Venezuela’s Political Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Country’s Map
Related Articles: Navigating Venezuela’s Political Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Country’s Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating Venezuela’s Political Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Country’s Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating Venezuela’s Political Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Country’s Map
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating Venezuela’s Political Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Country’s Map
- 3.1 Historical Context: From Colonialism to Independence
- 3.2 The 20th Century: Shifting Power Dynamics
- 3.3 The 21st Century: Polarization and Regionalism
- 3.4 Key Features of Venezuela’s Political Map
- 3.5 Importance and Benefits of Understanding Venezuela’s Political Map
- 3.6 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 3.7 Tips for Understanding Venezuela’s Political Map
- 3.8 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Navigating Venezuela’s Political Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Country’s Map
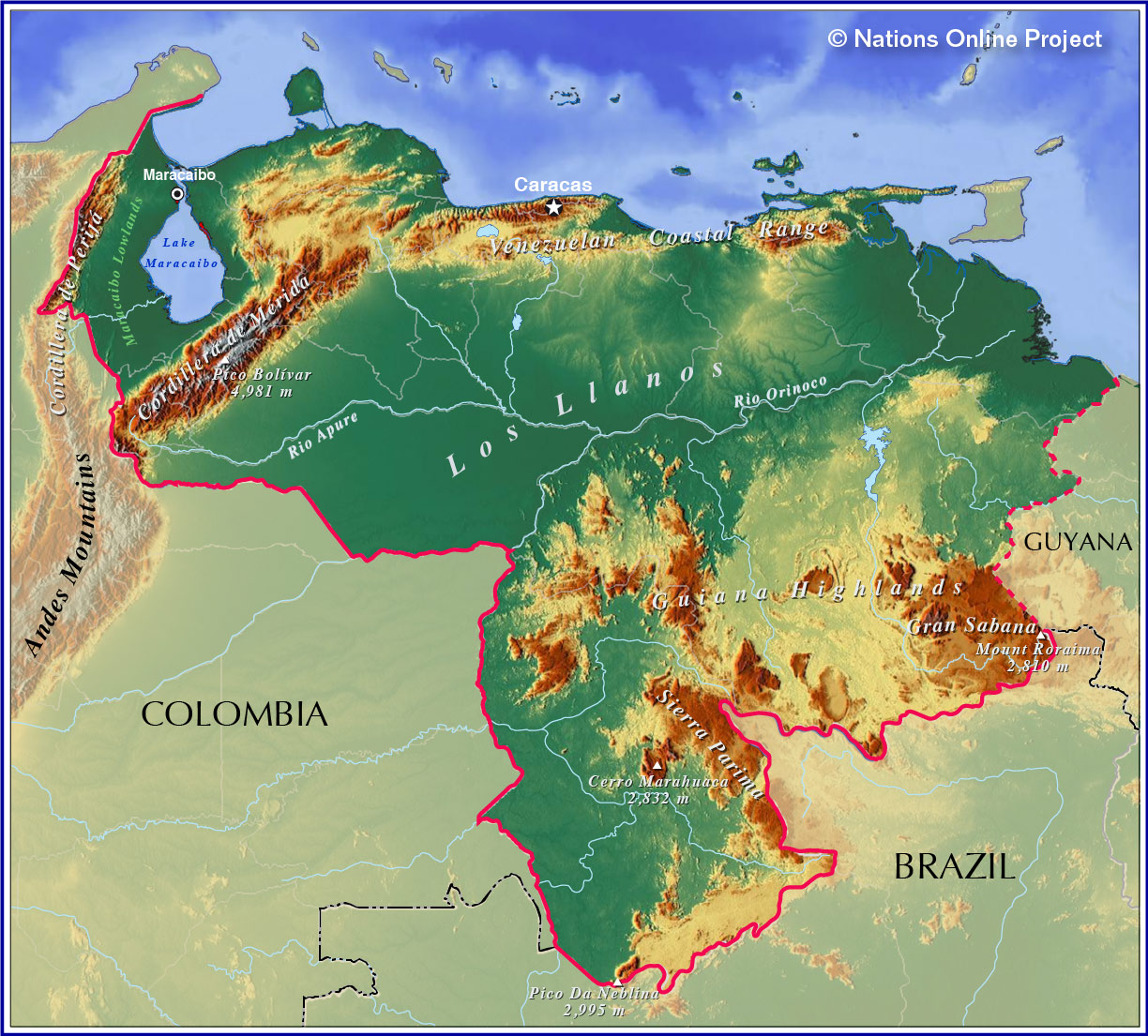
Venezuela, a nation nestled in the northern reaches of South America, boasts a rich history and a complex political landscape. Understanding the country’s political map is crucial for comprehending its current state and the intricate forces that shape its future. This comprehensive guide provides a detailed analysis of Venezuela’s political map, delving into its historical evolution, key features, and the significance of its regional divisions.
Historical Context: From Colonialism to Independence
Venezuela’s political map has been shaped by a confluence of historical factors, starting with its colonial past. Under Spanish rule, the country was divided into provinces, with each province possessing its own administrative structure. This early division laid the foundation for the regional identities that persist today.
The struggle for independence from Spain in the early 19th century saw the emergence of powerful regional leaders who played pivotal roles in the fight against colonial rule. These figures, like Simón Bolívar, contributed to the formation of a nascent Venezuelan identity, but also sowed the seeds of regionalism and political fragmentation.
Following independence, Venezuela’s political map underwent several transformations. The country experimented with different forms of government, including federalism and centralism, leading to periods of political instability and territorial disputes. The 19th century witnessed the rise and fall of numerous political factions, each vying for control of the country’s resources and power.
The 20th Century: Shifting Power Dynamics
The 20th century brought about significant changes to Venezuela’s political map. The discovery of vast oil reserves in the early 20th century transformed the country’s economy and led to a period of unprecedented prosperity. However, this newfound wealth also fueled political corruption and exacerbated existing regional inequalities.
The rise of the socialist movement in the mid-20th century, led by figures like Rómulo Betancourt, introduced a new dimension to Venezuelan politics. The adoption of a multi-party system, with the formation of the Democratic Action (AD) and the Social Christian COPEI, marked a departure from the traditional two-party system dominated by the Conservatives and Liberals.
The oil boom also fueled the rise of the Venezuelan state, which increasingly centralized power and resources. This trend continued into the late 20th century, leading to the concentration of political and economic power in the hands of the central government.
The 21st Century: Polarization and Regionalism
The turn of the 21st century witnessed a dramatic shift in Venezuela’s political landscape. The election of Hugo Chávez in 1998 marked the beginning of a new era of socialist-inspired governance. Chávez’s policies, aimed at empowering the poor and marginalized, sparked a wave of social and political change.
Chávez’s socialist revolution, however, also led to a deepening of political polarization. The country became divided between those who supported his policies and those who opposed them. This division was reflected in the political map, with certain regions becoming strongholds of Chavismo, while others remained centers of opposition.
The death of Chávez in 2013 and the subsequent rise of Nicolás Maduro further deepened the political crisis. The country has been plagued by economic hardship, political instability, and human rights abuses. The political map has become increasingly fractured, with opposition groups challenging Maduro’s authority and calling for democratic reforms.
Key Features of Venezuela’s Political Map
Venezuela’s political map is characterized by several key features:
-
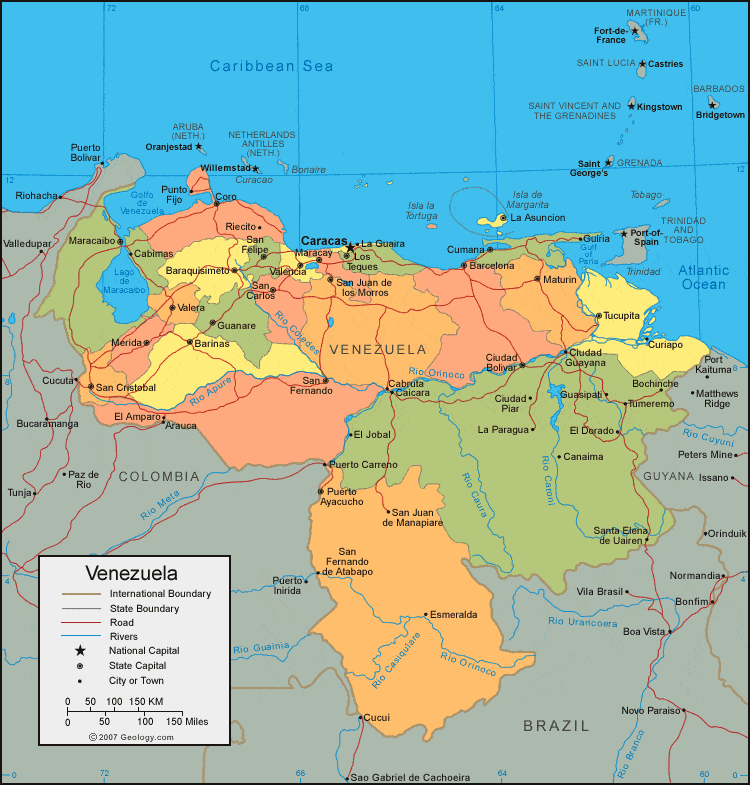
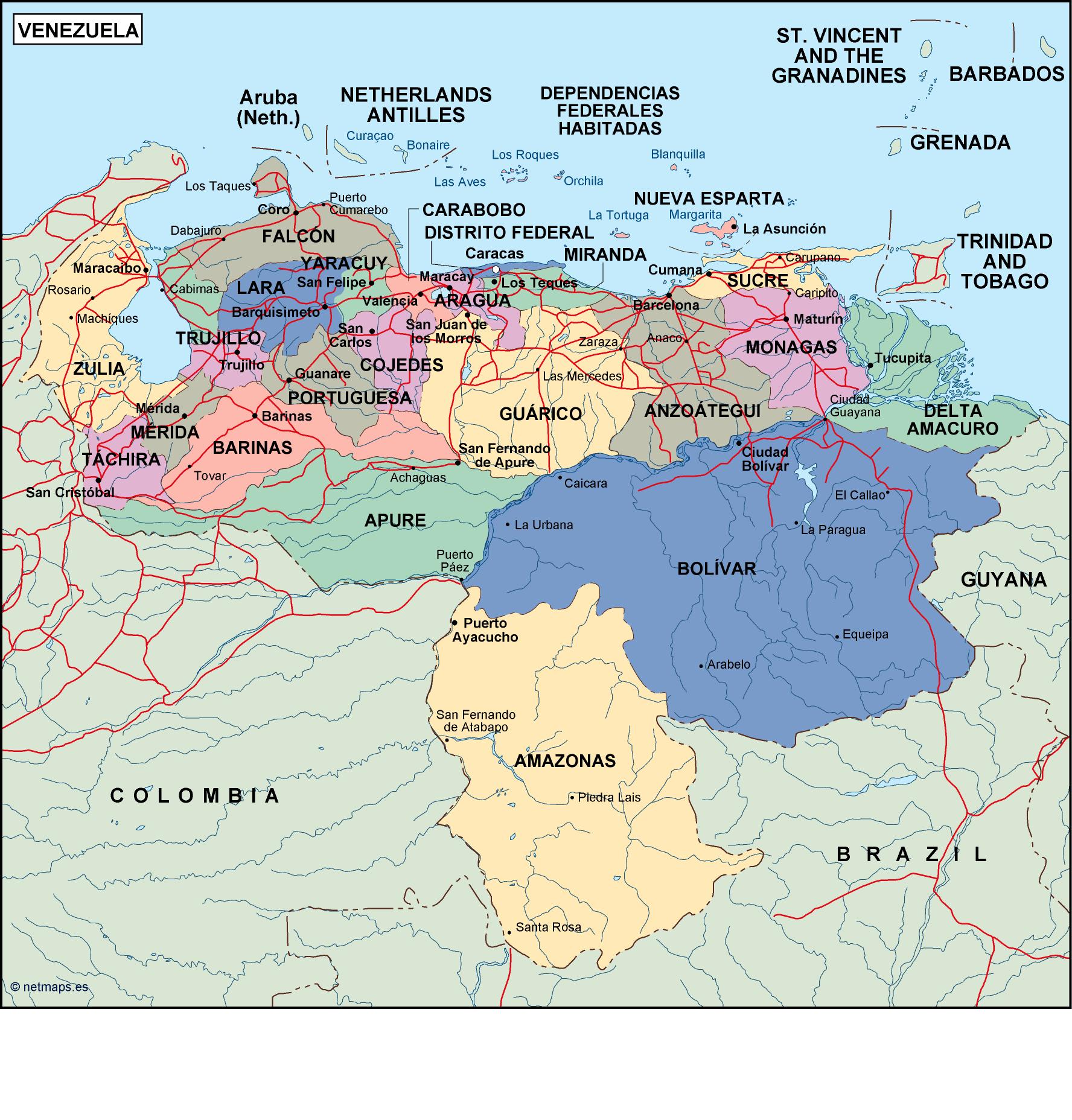
Regionalism: The country is divided into 23 states, each with its own governor and legislature. This decentralized structure reflects the historical importance of regional identities and the ongoing struggle for power between the central government and regional authorities.
-
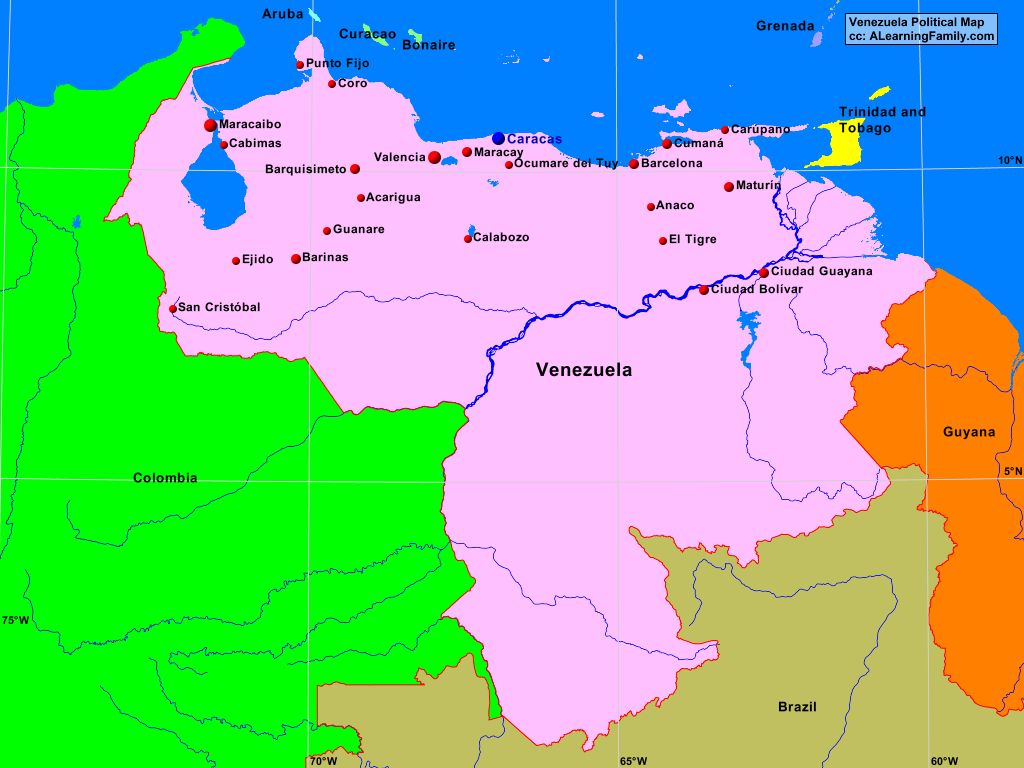
Urban-Rural Divide: Venezuela exhibits a stark urban-rural divide, with the majority of the population concentrated in major cities like Caracas, Valencia, and Maracaibo. This divide is reflected in the political map, with urban areas generally supporting more progressive policies and rural areas often leaning towards more traditional values.
-
Oil Dependency: Venezuela’s economy is heavily reliant on oil exports, which has created a concentration of wealth and political power in the oil-producing regions of the country. This dependence has also contributed to regional disparities and fueled political conflict.
-
Political Polarization: The political map of Venezuela is characterized by a deep divide between supporters of the current government and opposition groups. This polarization has created a climate of distrust and instability, making it difficult to find common ground and move forward with political reforms.
Importance and Benefits of Understanding Venezuela’s Political Map
Understanding Venezuela’s political map is crucial for several reasons:
-
Informed Decision-Making: By analyzing the regional dynamics and political trends, policymakers, investors, and international organizations can make more informed decisions about their engagement with Venezuela.
-
Conflict Resolution: Recognizing the underlying causes of regional tensions and political divisions can help facilitate dialogue and promote conflict resolution.
-
Economic Development: Understanding the geographic distribution of resources and the challenges faced by different regions can inform strategies for sustainable economic development.
-
Humanitarian Aid: By mapping the areas most affected by poverty, food insecurity, and other social problems, humanitarian organizations can better target their assistance efforts.
-
International Relations: Understanding the political landscape of Venezuela is essential for fostering diplomatic relations and promoting regional stability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are the main political parties in Venezuela?
Venezuela has a multi-party system, with several major parties competing for power. The most prominent parties include:
- United Socialist Party of Venezuela (PSUV): The ruling party, led by Nicolás Maduro.
- Democratic Action (AD): A center-left party with a long history of opposition to the government.
- Social Christian COPEI: A center-right party that has been part of the opposition since the 1990s.
- Popular Will (VP): A center-right party that has been a vocal critic of the government.
- Justice First (PJ): A center-left party that has been in the opposition since the 1990s.
2. What is the role of the states in Venezuela’s political system?
Venezuela is a federal republic, with 23 states and a capital district (Caracas). Each state has its own governor, legislature, and administrative structure. States have a degree of autonomy in areas like education, healthcare, and infrastructure, but the central government retains significant power over key areas such as oil production, foreign policy, and defense.
3. What are the major regional divisions in Venezuela?
Venezuela can be broadly divided into several regions, each with its own distinct characteristics:
- The Andes Region: Located in the west, this region is characterized by its mountainous terrain, rich agricultural land, and indigenous populations.
- The Llanos Region: Situated in the center of the country, this region is known for its vast plains, cattle ranching, and oil production.
- The Delta Amacuro Region: Located in the east, this region is characterized by its dense rainforest, rivers, and indigenous communities.
- The Coastal Region: Situated along the Caribbean coast, this region is known for its beaches, tourism, and fishing industry.
- The Guayana Region: Located in the south, this region is characterized by its vast forests, mineral resources, and indigenous populations.
4. How has Venezuela’s political map changed over time?
Venezuela’s political map has undergone significant changes over the centuries. The country has experienced periods of both centralization and decentralization, reflecting the shifting power dynamics between the central government and regional authorities. The discovery of oil and the rise of the socialist movement have also played a significant role in shaping the country’s political map.
5. What are the challenges facing Venezuela’s political system?
Venezuela’s political system is currently facing numerous challenges, including:
- Political Polarization: The deep divide between the government and the opposition has created a climate of distrust and instability.
- Economic Crisis: The country is experiencing a severe economic crisis, with high inflation, unemployment, and shortages of basic goods.
- Human Rights Abuses: There have been widespread reports of human rights abuses under the current government.
- Corruption: Corruption is a major problem in Venezuela, undermining the rule of law and hindering economic development.
- Lack of Democracy: The government has been accused of suppressing dissent and limiting democratic freedoms.
Tips for Understanding Venezuela’s Political Map
- Study the History: Understanding the historical context of Venezuela’s political map is crucial for comprehending its current state.
- Follow Current Events: Stay informed about the latest political developments in Venezuela by reading news sources and following experts on social media.
- Analyze Regional Data: Pay attention to regional data on economic indicators, social conditions, and political trends.
- Engage in Dialogue: Engage in discussions with people from different regions of Venezuela to gain diverse perspectives on the country’s political landscape.
- Support Democratic Reforms: Advocate for democratic reforms that promote transparency, accountability, and respect for human rights.
Conclusion
Venezuela’s political map is a dynamic and complex entity, shaped by a confluence of historical, social, and economic factors. Understanding the country’s regional divisions, political trends, and historical context is crucial for navigating the challenges and opportunities facing Venezuela. By engaging with the political map, policymakers, investors, and citizens can contribute to a more stable, just, and prosperous future for the nation.
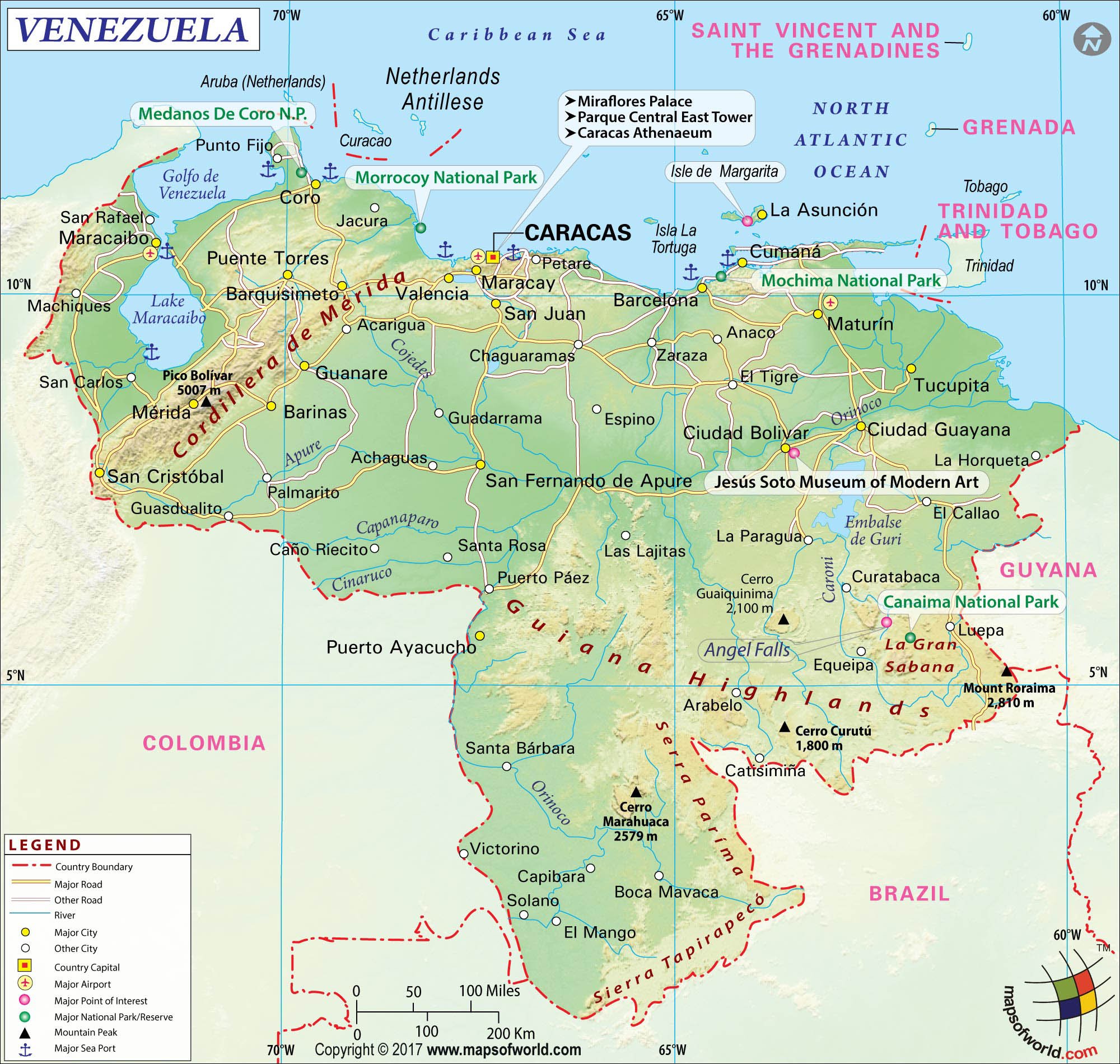
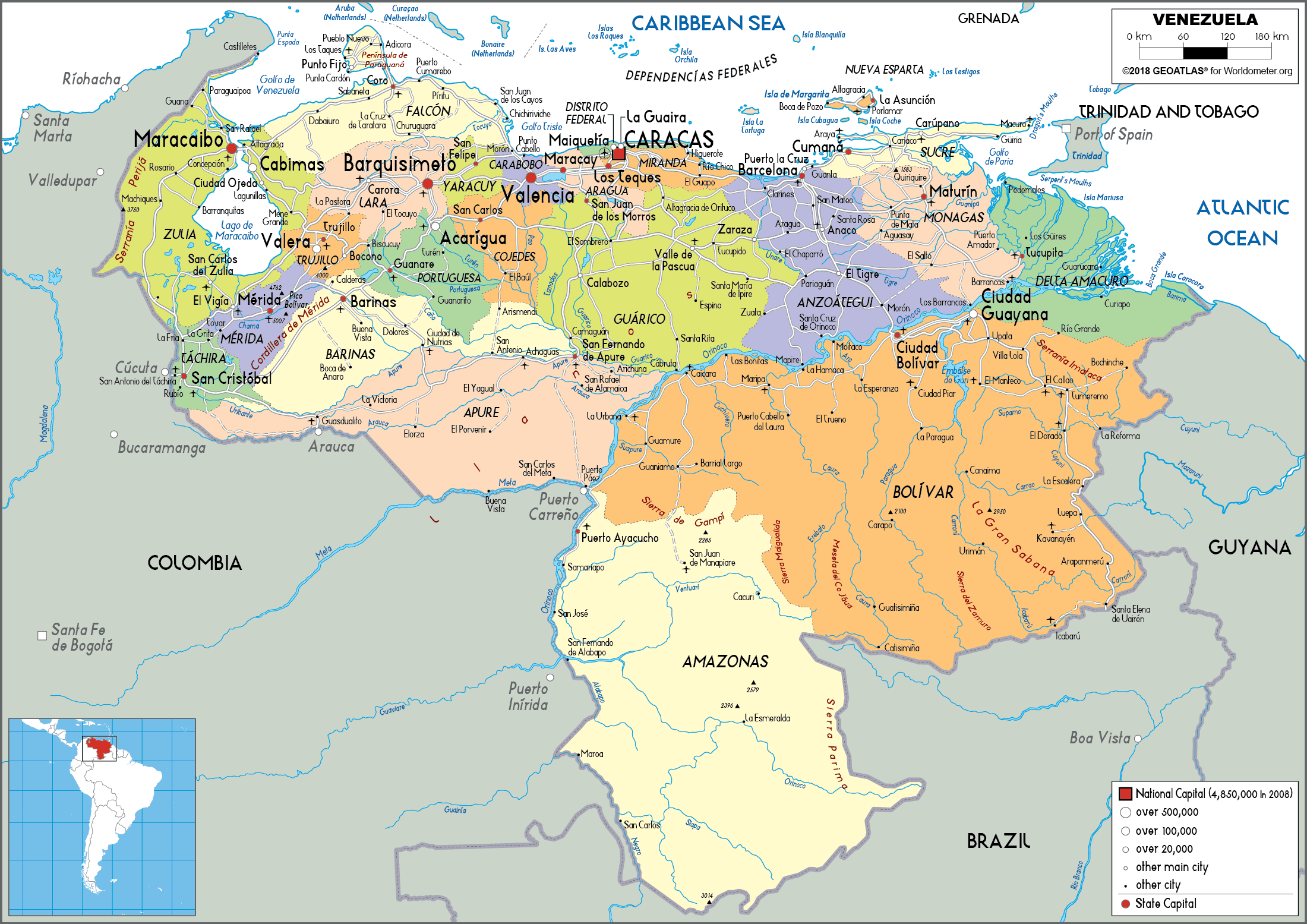

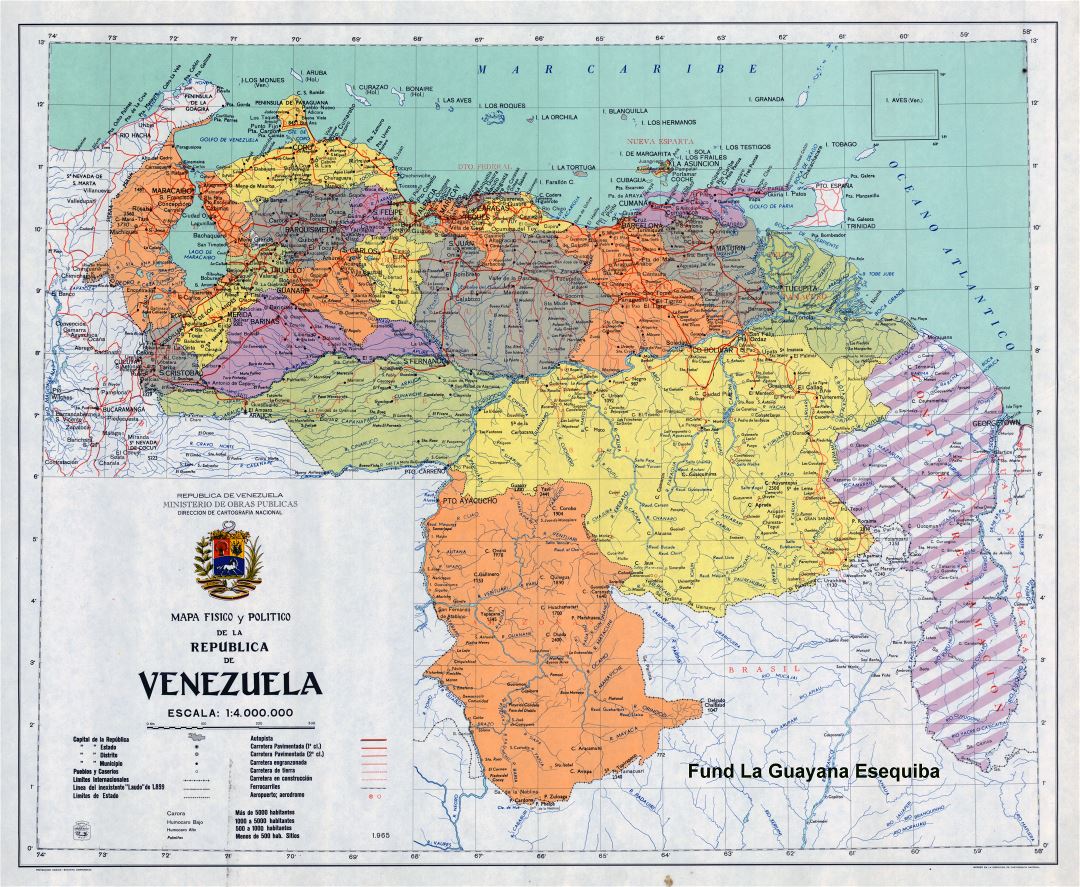

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Venezuela’s Political Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Country’s Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
