Navigating the World: Understanding the Power of Latitude and Longitude Grids on Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the World: Understanding the Power of Latitude and Longitude Grids on Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World: Understanding the Power of Latitude and Longitude Grids on Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World: Understanding the Power of Latitude and Longitude Grids on Maps

Maps, those ubiquitous representations of our world, have evolved over centuries, becoming increasingly sophisticated tools for navigation, exploration, and understanding our planet. One of the most fundamental and enduring innovations in cartography is the use of latitude and longitude grids. These invisible lines, crisscrossing the globe, provide a precise and universal system for pinpointing any location on Earth, enabling us to navigate with accuracy and communicate geographical information effectively.
The Foundation of Global Positioning: Latitude and Longitude
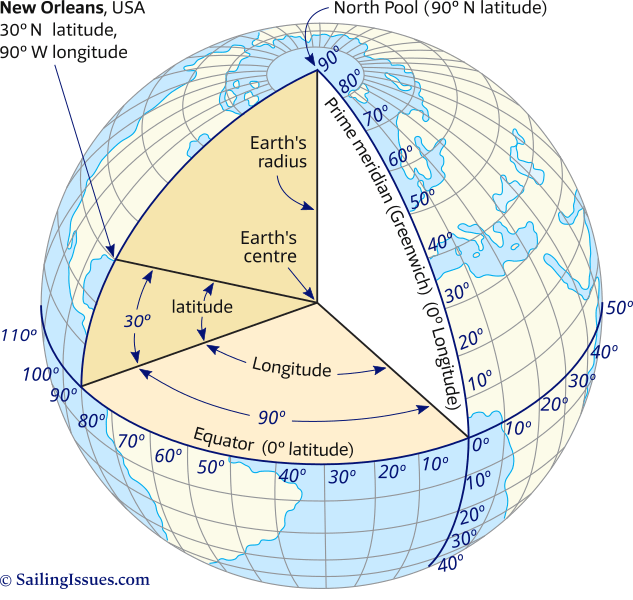
Imagine the Earth as a giant orange, sliced into segments. Latitude lines, running horizontally like the orange’s peel, measure distance north or south of the equator, which is the imaginary line circling the Earth at 0 degrees. Each degree of latitude is approximately 69 miles (111 kilometers) apart, creating a system of parallel lines that divide the globe into zones. The North Pole sits at 90 degrees North, while the South Pole resides at 90 degrees South.
Longitude lines, on the other hand, run vertically, like the orange’s segments. They measure distance east or west of the prime meridian, an imaginary line that passes through Greenwich, England, at 0 degrees. Each degree of longitude, however, varies in distance depending on the latitude, converging at the poles. The International Date Line, roughly 180 degrees from the prime meridian, marks the transition between days.
The Power of Intersection: Finding Your Place
The beauty of the latitude and longitude grid lies in its ability to pinpoint any location on Earth by identifying the intersection of a specific latitude line and a specific longitude line. This intersection forms a unique coordinate, expressed as a pair of numbers, such as 40.7128° N, 74.0060° W, which precisely locates the Empire State Building in New York City.
This system allows for consistent and unambiguous communication of location, regardless of the map’s scale or projection. Whether you’re navigating by land, sea, or air, the latitude and longitude grid provides a universal language for pinpointing your position and guiding your journey.
Applications Beyond Navigation: Unveiling the World’s Secrets
The latitude and longitude grid’s influence extends far beyond navigation. It plays a crucial role in various scientific disciplines, including:
- Geography and Cartography: The grid forms the foundation of modern mapmaking, enabling the accurate representation of Earth’s features and the creation of various map projections.
- Geology and Geophysics: Latitude and longitude are used to pinpoint earthquake epicenters, volcanic eruptions, and other geological events, helping scientists understand the Earth’s dynamic processes.
- Climate Science: The grid facilitates the collection and analysis of climate data, allowing scientists to study weather patterns, temperature variations, and other climate-related phenomena.
- Astronomy and Space Exploration: The grid helps astronomers track celestial objects and spacecraft, providing a framework for understanding their positions and movements in the vast expanse of space.
- Environmental Studies: The grid aids in monitoring environmental changes, such as deforestation, pollution levels, and habitat loss, facilitating conservation efforts and sustainable practices.
Understanding the Grid: A Closer Look
To grasp the significance of the latitude and longitude grid, it’s essential to understand its key components:
- Degrees, Minutes, and Seconds: Each degree of latitude and longitude is further divided into 60 minutes (‘), and each minute is divided into 60 seconds ("). This system provides a highly precise way to express location.
- Hemispheres: The Earth is divided into four hemispheres: Northern, Southern, Eastern, and Western. Latitude is expressed as North (N) or South (S) of the equator, while longitude is expressed as East (E) or West (W) of the prime meridian.
- Map Projections: The latitude and longitude grid is often overlaid on various map projections, which flatten the Earth’s curved surface onto a two-dimensional plane. Different projections distort the Earth’s shape in different ways, affecting the accuracy of distance and area measurements.
Navigating the Future: The Evolution of Location Technology
While the latitude and longitude grid remains the foundation of global positioning, technology has advanced, leading to more sophisticated and user-friendly navigation tools. GPS (Global Positioning System) satellites, for instance, use the grid to determine precise locations on Earth, enabling real-time navigation and location-based services.
Furthermore, advancements in mapping software and online platforms have made it easier than ever to access and utilize the grid. Interactive maps, with their ability to zoom, pan, and display various layers of information, offer a dynamic and engaging way to explore the world and understand the power of latitude and longitude.
FAQs: Demystifying the Grid
Q: How are latitude and longitude used to navigate?
A: Latitude and longitude coordinates provide a unique address for any location on Earth. By inputting these coordinates into a GPS device, navigation system, or map application, you can determine your current position and find your way to your destination.
Q: What are the benefits of using a latitude and longitude grid?
A: The grid offers several benefits, including:
- Universality: It provides a consistent and unambiguous system for pinpointing locations across the globe.
- Accuracy: The grid allows for precise location determination, enabling accurate navigation and scientific measurements.
- Communication: The grid facilitates clear communication of location information, regardless of language or cultural differences.
- Data Analysis: The grid supports the collection, analysis, and interpretation of geographical data, aiding in various scientific disciplines.
Q: How does the latitude and longitude grid work in conjunction with map projections?
A: The grid is often overlaid on different map projections, which flatten the Earth’s surface onto a two-dimensional plane. While projections distort the Earth’s shape, the latitude and longitude grid remains a constant reference point, enabling accurate location identification and measurements within the projected map.
Q: What are some examples of how latitude and longitude are used in everyday life?
A: Latitude and longitude are used in various aspects of daily life, including:
- Navigation apps: GPS devices and navigation apps utilize the grid to determine your location and guide you to your destination.
- Online mapping platforms: Websites like Google Maps and OpenStreetMap rely on the grid to display locations, provide directions, and share geographical information.
- Weather forecasting: Meteorological services use the grid to track weather patterns, predict storms, and disseminate weather forecasts.
- Emergency services: Emergency responders use the grid to pinpoint the location of incidents, ensuring timely and efficient assistance.
Tips for Using the Latitude and Longitude Grid
- Understand the basics: Familiarize yourself with the concepts of latitude, longitude, hemispheres, and degrees, minutes, and seconds.
- Use reliable sources: Consult reputable maps, atlases, and online mapping platforms for accurate latitude and longitude information.
- Practice converting coordinates: Learn how to convert coordinates between decimal degrees and degrees, minutes, and seconds.
- Utilize online tools: Explore online tools that allow you to convert coordinates, calculate distances, and visualize locations on a map.
- Be aware of map projections: Understand that different map projections distort the Earth’s shape in different ways, potentially affecting distance and area measurements.
Conclusion: A Timeless Framework for Understanding Our World
The latitude and longitude grid, a seemingly simple yet profound invention, has revolutionized our understanding of the Earth. It provides a universal language for pinpointing locations, enabling navigation, communication, and scientific exploration. From guiding ships across vast oceans to tracking weather patterns and understanding geological processes, the grid’s influence permeates our lives. As technology continues to advance, the grid will undoubtedly continue to play a vital role in shaping our understanding of the world and our place within it.


![]()




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World: Understanding the Power of Latitude and Longitude Grids on Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
