Navigating the World: How Maps Locate Places
Related Articles: Navigating the World: How Maps Locate Places
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World: How Maps Locate Places. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World: How Maps Locate Places

Maps, those ubiquitous representations of the world, have played a pivotal role in human civilization for millennia. From ancient cave paintings depicting hunting grounds to sophisticated digital maps on our smartphones, maps have served as indispensable tools for navigation, exploration, and understanding our surroundings. But what exactly allows maps to pinpoint locations with such remarkable precision? This article delves into the fascinating world of mapmaking, exploring the methods and technologies that enable us to locate places with accuracy and ease.
The Foundation of Location: Latitude and Longitude
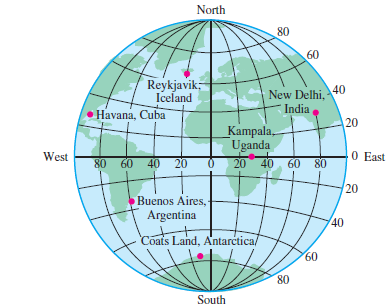
At the heart of mapmaking lies a fundamental concept: the Earth’s coordinate system. This system, based on latitude and longitude, provides a unique address for every point on the planet.
- Latitude: Imagine a series of imaginary circles drawn around the Earth, parallel to the equator. These circles represent lines of latitude, measuring distances north or south of the equator. The equator itself is designated as 0 degrees latitude, with values increasing towards the North and South Poles (90 degrees North and 90 degrees South, respectively).
- Longitude: Another set of imaginary circles, this time running from pole to pole, represent lines of longitude. These lines converge at the poles, with the prime meridian (passing through Greenwich, England) serving as the 0-degree longitude. Values increase eastward and westward from the prime meridian, reaching 180 degrees east or west.
Together, latitude and longitude create a grid system covering the entire Earth’s surface. Each location can be identified by its unique combination of latitude and longitude coordinates, forming the basis for precise location determination.
From Globe to Flat Surface: Projections and Distortion
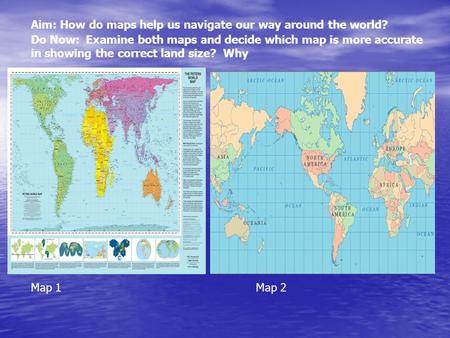
While the Earth is a sphere, maps are typically depicted on flat surfaces. This transformation, known as map projection, inevitably introduces some distortion. Different projections aim to minimize specific types of distortion, depending on the intended use of the map.
- Conformal Projections: These projections preserve angles and shapes, making them suitable for navigation and precise measurements within a limited area. However, they often distort distances and areas. Examples include the Mercator projection, commonly used for world maps.
- Equal-Area Projections: As the name suggests, these projections prioritize preserving the relative areas of landmasses. While they distort shapes, they accurately represent the proportional sizes of countries and continents. Examples include the Mollweide projection, often used for thematic maps.
- Compromise Projections: Some projections attempt to strike a balance between preserving shapes and areas. These projections generally introduce moderate distortion in both aspects, making them suitable for general-purpose maps. Examples include the Robinson projection, commonly used for world maps.
The choice of projection plays a crucial role in the accuracy and interpretation of a map. Understanding the inherent distortions of a particular projection is essential for accurate analysis and interpretation of geographical data.
Beyond the Basics: Technological Advancements
The development of modern technology has revolutionized mapmaking, enabling us to create and access highly detailed and interactive maps.
- Global Positioning System (GPS): This satellite-based navigation system utilizes a network of orbiting satellites to determine the precise location of a receiver on Earth. GPS receivers, found in smartphones, cars, and other devices, use triangulation based on signals from multiple satellites to calculate latitude, longitude, and altitude.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS software allows for the collection, storage, analysis, and visualization of geographically referenced data. This powerful tool enables the creation of sophisticated maps that integrate various layers of information, such as elevation, population density, land use, and environmental data.
- Remote Sensing: Satellite imagery and aerial photography provide high-resolution images of the Earth’s surface, capturing information that can be integrated into maps. This data is used for a wide range of applications, including urban planning, disaster response, and environmental monitoring.
- Digital Mapping Platforms: Online platforms like Google Maps, Apple Maps, and OpenStreetMap provide interactive, user-generated maps that offer real-time traffic updates, directions, and other valuable information. These platforms leverage a combination of satellite imagery, aerial photography, and user contributions to create comprehensive and dynamic maps.
The Importance of Accurate Location Data
The ability to locate places accurately is crucial for a wide range of applications, impacting our lives in numerous ways:
- Navigation: Maps guide us through unfamiliar territories, enabling us to reach our destinations safely and efficiently. Whether traveling by car, foot, or public transport, maps provide essential information for navigating roads, streets, and public spaces.
- Emergency Response: Accurate location data is vital for emergency responders, allowing them to quickly locate and assist individuals in need during disasters, accidents, or medical emergencies.
- Urban Planning: Maps are essential tools for city planners, helping them understand population distribution, infrastructure needs, and potential development areas. This data is used to optimize resource allocation, improve transportation systems, and promote sustainable urban growth.
- Environmental Monitoring: Maps play a critical role in environmental research and conservation. By analyzing spatial data, scientists can track deforestation, monitor pollution levels, and assess the impact of climate change on ecosystems.
- Business and Commerce: Location data is crucial for businesses, enabling them to target specific customer demographics, optimize delivery routes, and analyze market trends. Maps help businesses understand their customer base, identify potential growth opportunities, and make informed decisions.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between latitude and longitude?
Latitude measures the distance north or south of the equator, while longitude measures the distance east or west of the prime meridian.
2. Why are map projections necessary?
Map projections are necessary because the Earth is a sphere, and maps are typically depicted on flat surfaces. Projections allow us to represent the curved Earth on a flat plane, but they inevitably introduce some distortion.
3. What are the different types of map projections?
There are various types of map projections, each designed to minimize specific types of distortion. Conformal projections preserve angles and shapes, equal-area projections preserve areas, and compromise projections attempt to balance both aspects.
4. How does GPS work?
GPS utilizes a network of orbiting satellites to determine the precise location of a receiver on Earth. By measuring the time it takes for signals from multiple satellites to reach the receiver, GPS calculates latitude, longitude, and altitude.
5. What are the benefits of GIS?
GIS software enables the collection, storage, analysis, and visualization of geographically referenced data. This powerful tool allows for the creation of sophisticated maps that integrate various layers of information, facilitating informed decision-making in various fields.
Tips
- Understand the scale of the map: The scale of a map indicates the ratio between the distance on the map and the corresponding distance on the ground. Always pay attention to the scale to avoid misinterpretations.
- Consider the purpose of the map: Different types of maps are designed for specific purposes. Choose a map that best suits your needs, whether it’s for navigation, thematic analysis, or general reference.
- Look for reliable sources: When using digital maps, ensure they are from reputable sources. Consider using maps from established companies like Google Maps or Apple Maps, or from reputable organizations like OpenStreetMap.
- Check for updates: Digital maps are constantly updated with new information. Make sure you are using the latest version to ensure accuracy.
- Use multiple maps: Combining information from different maps can provide a more comprehensive understanding of a location.
Conclusion
Maps, from ancient depictions of the world to sophisticated digital platforms, have played a crucial role in human history and continue to shape our understanding of the world around us. By leveraging the principles of latitude and longitude, projection techniques, and advanced technologies, maps provide us with the tools to navigate, explore, and analyze our planet with unprecedented accuracy and insight. As technology continues to evolve, maps will undoubtedly play an even more significant role in our lives, empowering us to make informed decisions, connect with the world, and shape a better future.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World: How Maps Locate Places. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
