Navigating the Ptolemaic Kingdom: A Journey Through History on the Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Ptolemaic Kingdom: A Journey Through History on the Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Ptolemaic Kingdom: A Journey Through History on the Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Ptolemaic Kingdom: A Journey Through History on the Map
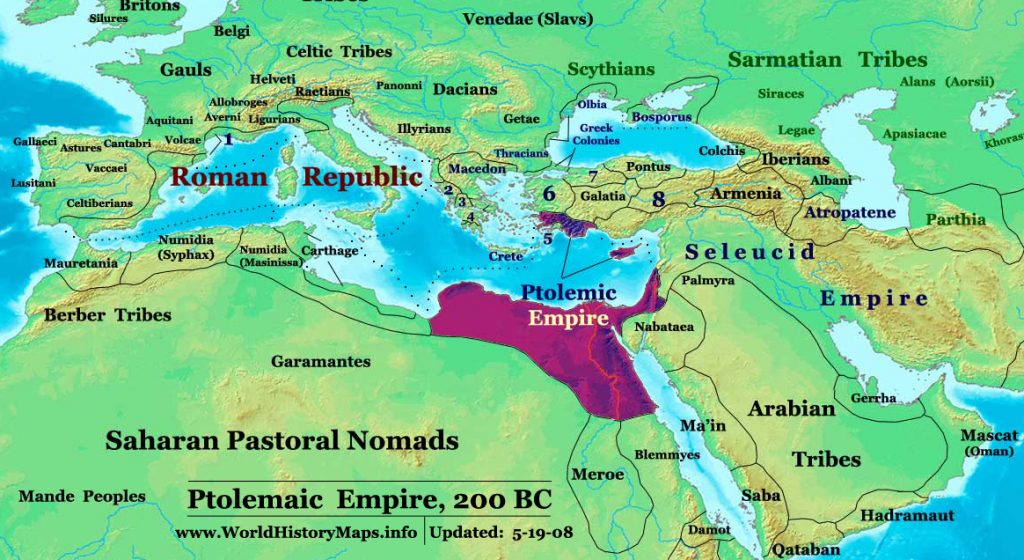
The Ptolemaic Kingdom, a Hellenistic state in ancient Egypt, flourished for nearly three centuries (305-30 BC) after the death of Alexander the Great. This period witnessed a fascinating fusion of Greek and Egyptian cultures, leaving behind a rich tapestry of history, art, and architecture. Understanding the Ptolemaic Kingdom’s geography is essential for appreciating the complexities of this era, and maps serve as invaluable tools for navigating its intricate landscape.
A Realm of Contrasts: The Ptolemaic Kingdom on the Map
The Ptolemaic Kingdom, as depicted on maps, stretched from the Mediterranean Sea in the north to the First Cataract of the Nile in the south. Its borders encompassed a diverse array of regions, each with its unique characteristics:
- The Nile Valley: The lifeblood of the kingdom, the Nile River provided fertile land for agriculture and served as a crucial waterway for transportation and trade.
- The Delta: A triangular region at the mouth of the Nile, the Delta was a fertile area with numerous cities and harbors.
- The Western Desert: This arid region was sparsely populated but held vital mineral resources and served as a buffer zone against external threats.
- The Eastern Desert: This region, with its rocky terrain and oases, offered valuable resources like gold, copper, and granite.
- The Sinai Peninsula: This strategic region, connecting Egypt to Asia, was a crucial trade route and a potential gateway for invaders.
Beyond Borders: The Ptolemaic Kingdom’s Influence
The Ptolemaic Kingdom’s map reveals not just its geographical boundaries but also its influence on the wider world.
- Trade Networks: The kingdom’s strategic location at the crossroads of trade routes fostered a vibrant economy. Maps depict its bustling ports like Alexandria, a major hub for Mediterranean trade, and Berenice, a key port for trade with India.
- Cultural Exchange: The Ptolemaic Kingdom’s map showcases the blending of Greek and Egyptian cultures. Greek cities like Alexandria, Ptolemais, and Naucratis thrived alongside ancient Egyptian cities like Memphis and Thebes, showcasing the fusion of architectural styles and artistic expressions.
- Military Expansion: The Ptolemaic Kingdom’s map demonstrates its ambition for territorial expansion. Maps highlight its attempts to control Cyrenaica, Cyprus, and parts of the Levant, reflecting its desire to secure its borders and influence in the Eastern Mediterranean.
Navigating the Map: A Journey Through Time
To fully comprehend the Ptolemaic Kingdom, it is crucial to understand how maps have evolved over time and their role in historical research.
- Ancient Maps: While ancient Egyptian maps are scarce, some surviving fragments provide valuable insights into their understanding of geography. These maps, often inscribed on papyri or stone, depict the Nile River, key cities, and geographical features.
- Greek Maps: Greek cartographers, influenced by the Egyptian tradition, created more detailed and accurate maps of the Ptolemaic Kingdom. These maps, often depicted on scrolls or engraved on stone, incorporated geographical features, cities, and important landmarks.
- Modern Maps: Modern scholars use historical sources, archaeological evidence, and geographical data to create accurate and detailed maps of the Ptolemaic Kingdom. These maps are invaluable for understanding the kingdom’s political boundaries, its trade routes, and the distribution of its population.
FAQs: Unveiling the Secrets of the Ptolemaic Kingdom
1. What were the major cities in the Ptolemaic Kingdom?
The Ptolemaic Kingdom boasted several important cities, including:
- Alexandria: The capital city, founded by Alexander the Great, was a thriving center of trade, culture, and learning.
- Memphis: The ancient capital of Egypt, Memphis remained a significant city during the Ptolemaic period.
- Thebes: Located in Upper Egypt, Thebes was a religious and cultural center, renowned for its temples and monuments.
- Ptolemais: Located in the Delta region, Ptolemais was a major port and a center for trade.
- Naucratis: An ancient Greek city in the Delta, Naucratis was a center for trade and cultural exchange.
2. How did the Ptolemaic Kingdom manage its vast territory?
The Ptolemaic Kingdom effectively managed its vast territory by:
- Administrative Divisions: The kingdom was divided into nomes (provinces), each with its own governor and administrative staff.
- Military Presence: The kingdom maintained a strong military force to protect its borders and maintain internal order.
- Taxation System: The Ptolemaic rulers implemented a system of taxation to fund their administration, military, and infrastructure projects.
3. What were the major cultural influences on the Ptolemaic Kingdom?
The Ptolemaic Kingdom experienced a fascinating fusion of Greek and Egyptian cultures, resulting in:
- Syncretism: The blending of Greek and Egyptian deities, creating new religious figures like Serapis and Isis-Hathor.
- Architecture: The construction of grand temples and palaces incorporating elements of both Greek and Egyptian architecture.
- Art: The creation of sculptures, paintings, and pottery that reflected the fusion of Greek and Egyptian artistic styles.
4. Why did the Ptolemaic Kingdom decline?
The decline of the Ptolemaic Kingdom was due to a combination of factors:
- Internal Conflicts: Power struggles within the royal family weakened the kingdom.
- External Threats: Rome’s growing power in the Mediterranean posed a significant threat to the Ptolemaic Kingdom.
- Economic Decline: The loss of trade routes and the rise of competition from other kingdoms weakened the Ptolemaic economy.
Tips for Studying the Ptolemaic Kingdom Through Maps
- Visualize the Geography: Study maps to understand the physical landscape, including the Nile River, the Delta, and the deserts.
- Identify Key Cities: Locate the major cities and understand their roles in the kingdom’s economy, politics, and culture.
- Trace Trade Routes: Follow the trade routes on maps to understand the kingdom’s economic connections with other regions.
- Analyze Political Boundaries: Examine the kingdom’s borders and how they changed over time.
- Compare Maps: Compare ancient maps with modern maps to see how our understanding of the Ptolemaic Kingdom has evolved.
Conclusion: A Legacy Enduring Through Maps
The Ptolemaic Kingdom, as revealed through maps, was a fascinating and complex civilization that left an enduring legacy. Its geographical location, cultural fusion, and political ambitions shaped the course of ancient history. Maps serve as invaluable tools for navigating this rich tapestry of history, allowing us to understand the kingdom’s geography, its people, and its lasting impact on the world. By studying the Ptolemaic Kingdom through its maps, we gain a deeper appreciation for this remarkable era and its contributions to the development of human civilization.


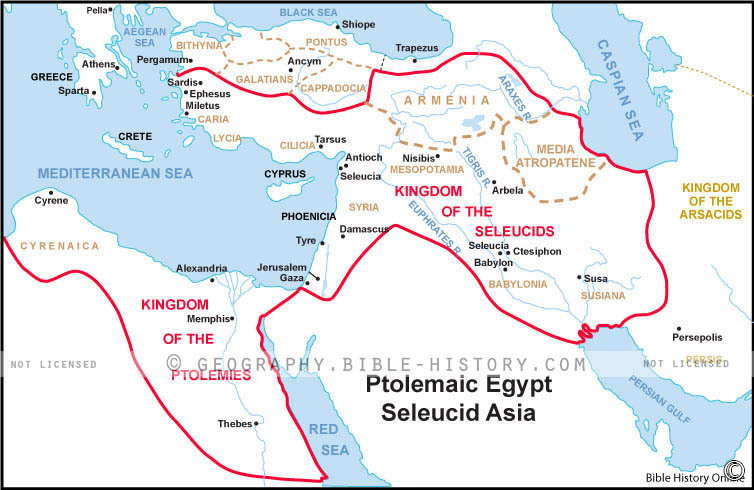



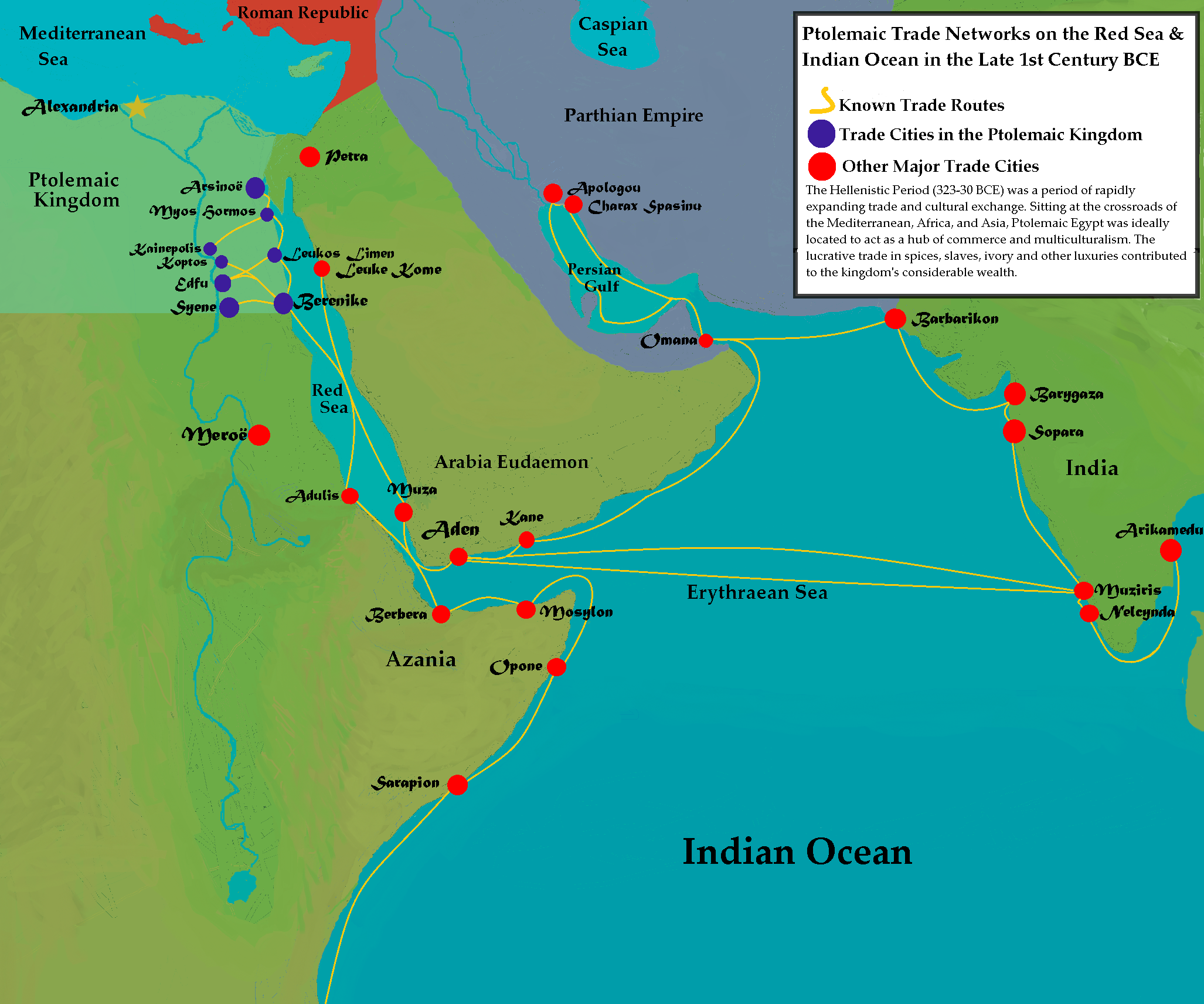

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Ptolemaic Kingdom: A Journey Through History on the Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
