Navigating the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to the Canary Islands and their African Connection
Related Articles: Navigating the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to the Canary Islands and their African Connection
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to the Canary Islands and their African Connection. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to the Canary Islands and their African Connection

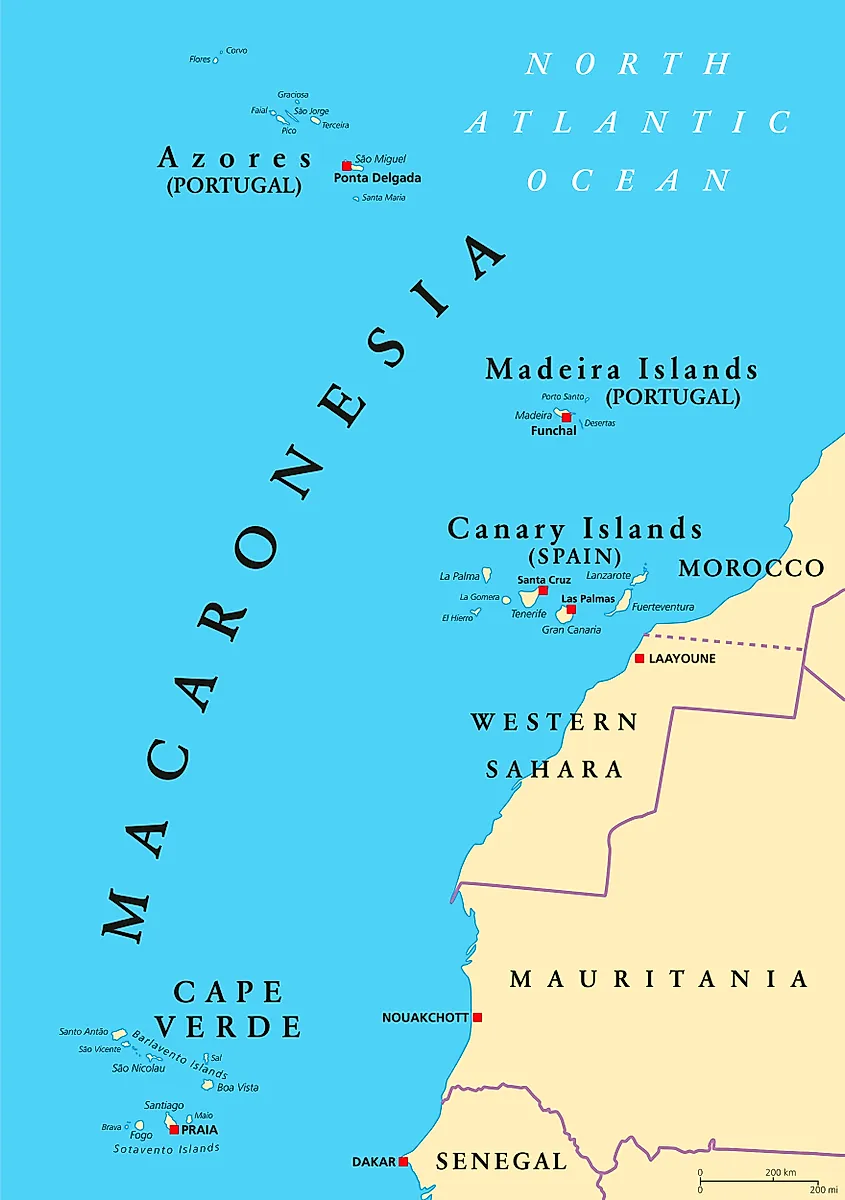
The Canary Islands, a vibrant archipelago nestled in the Atlantic Ocean, hold a unique geographical position that has profoundly shaped their history, culture, and natural environment. Often referred to as "Africa’s stepping stones," these islands, while politically part of Spain, are geographically closer to the African continent than to mainland Europe. This close proximity is not just a geographical fact; it’s a thread woven deeply into the islands’ identity, influencing everything from their flora and fauna to their cultural heritage.
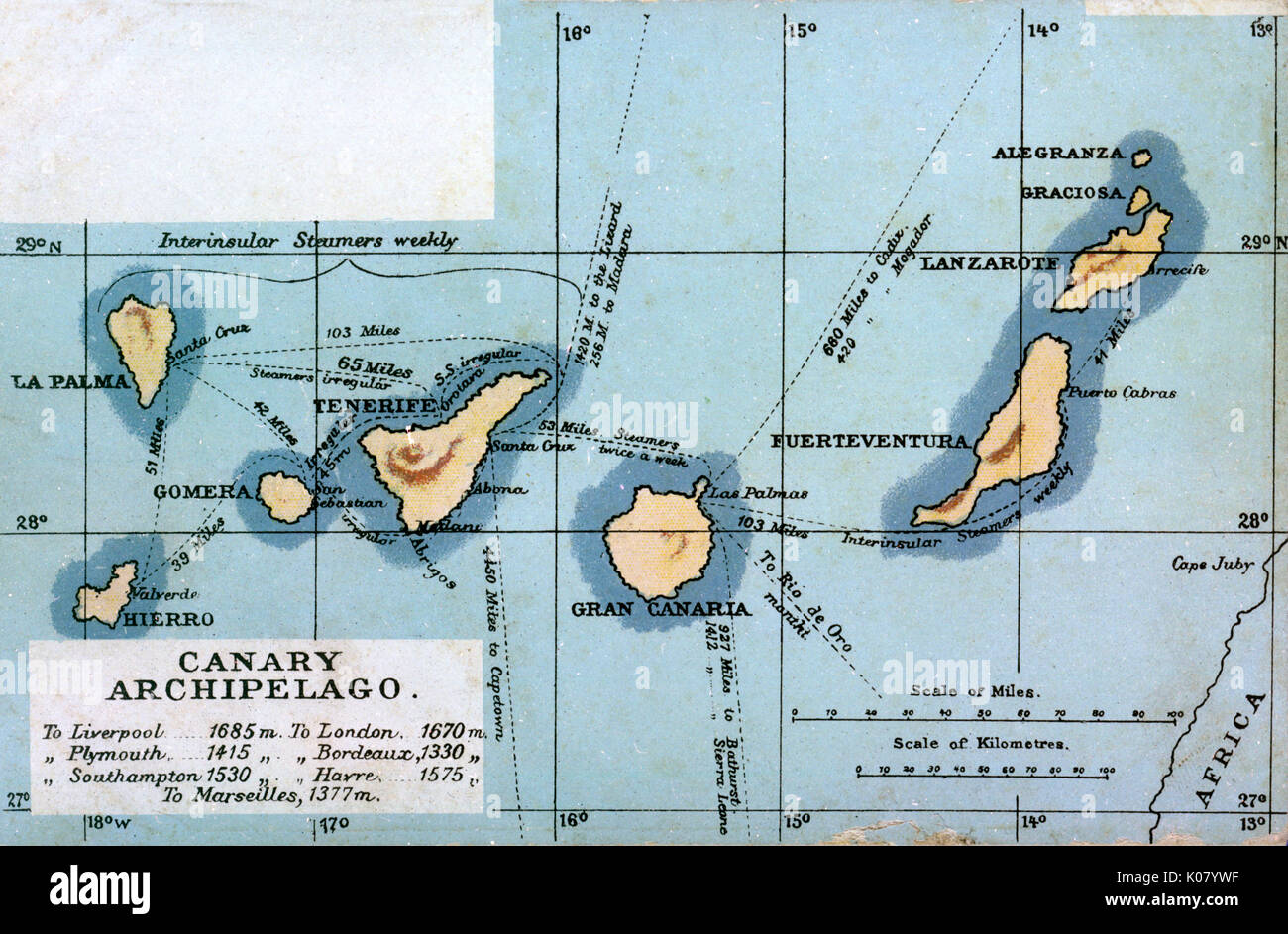
A Geographical Tapestry: Understanding the Map
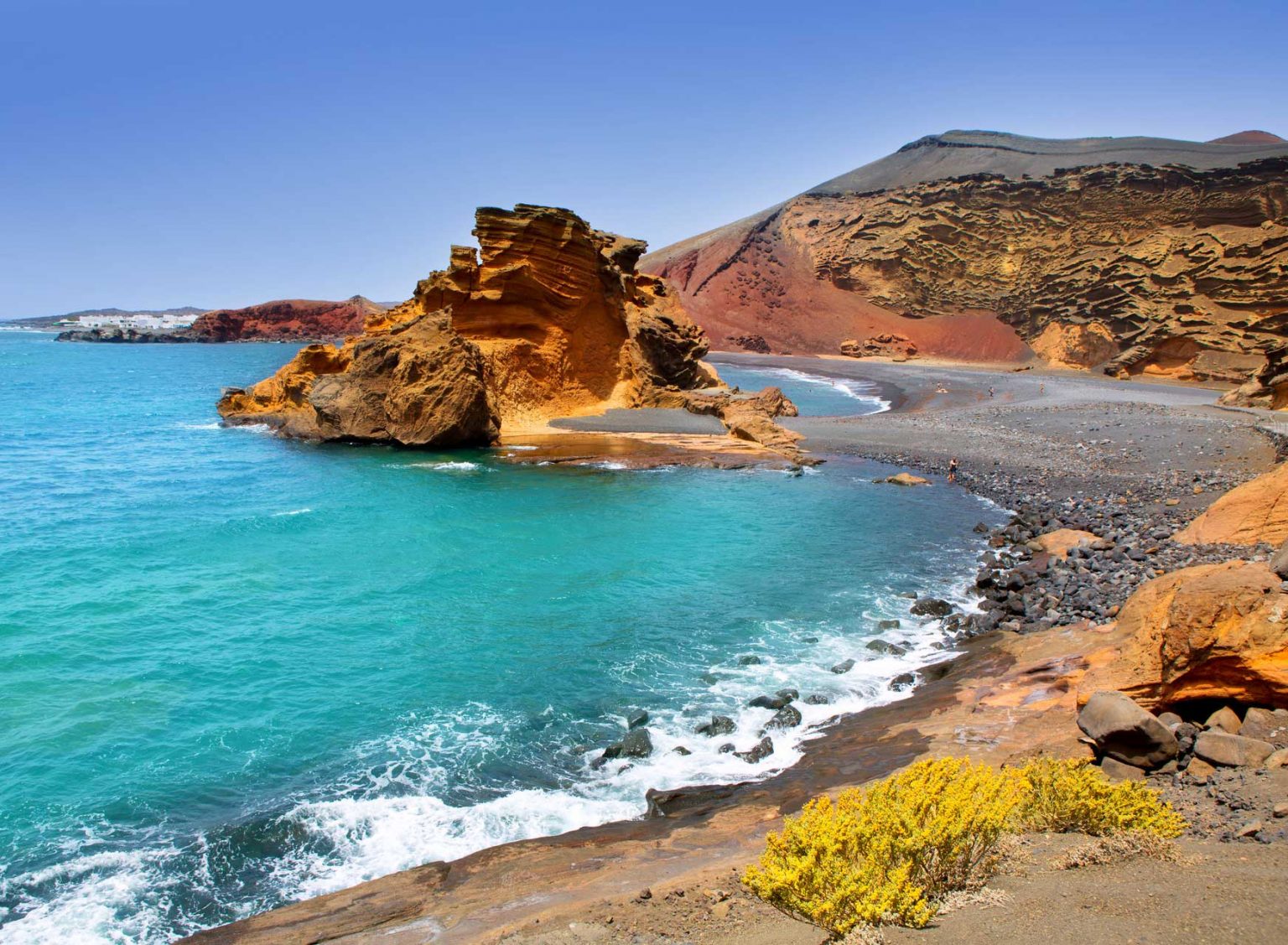
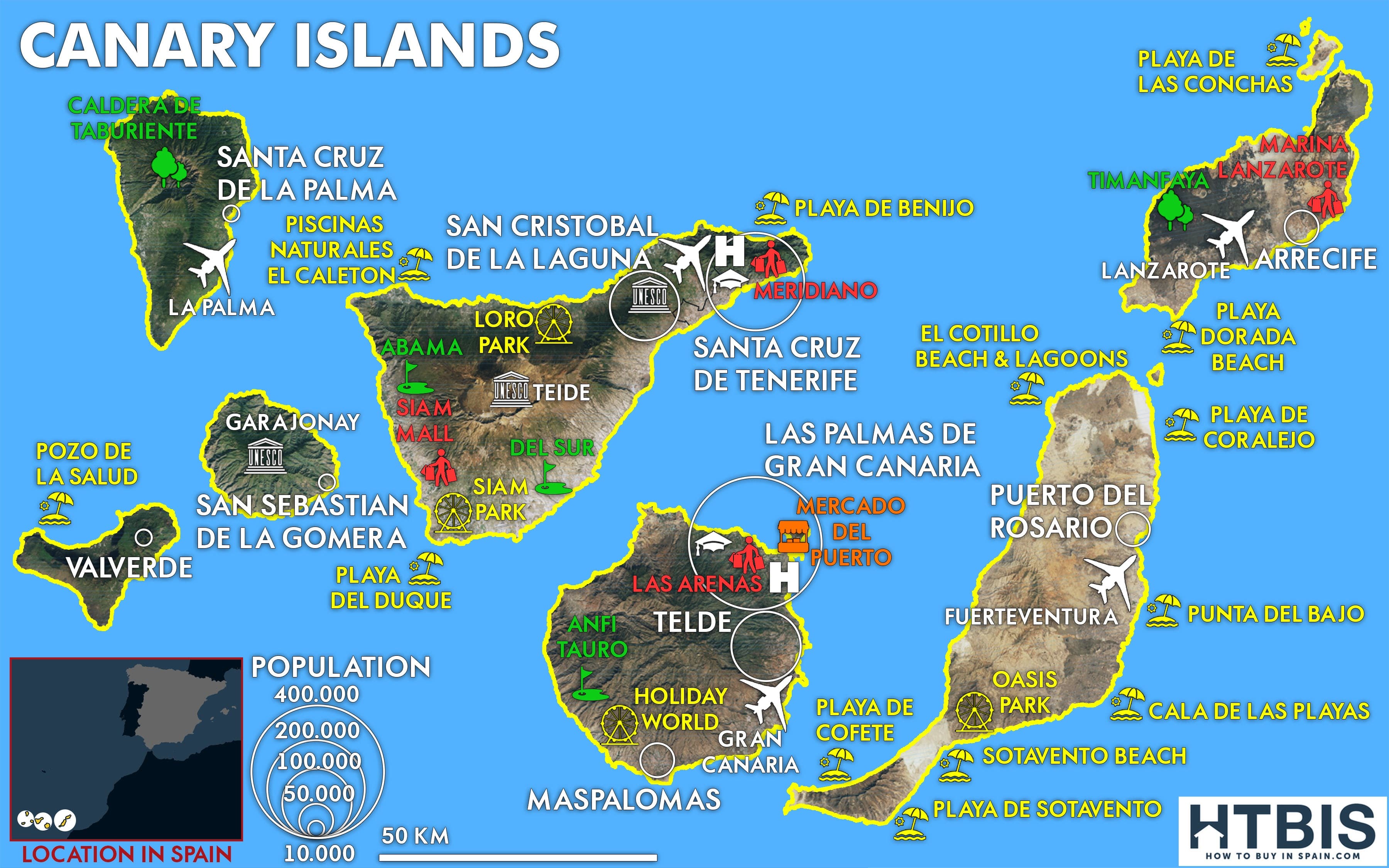
The Canary Islands, seven in total, are situated approximately 100 kilometers west of the Moroccan coast. Their volcanic origins are evident in their rugged landscapes, characterized by towering peaks, fertile valleys, and dramatic coastal cliffs.
- Tenerife: The largest and most populous island, Tenerife is dominated by Mount Teide, Spain’s highest peak and a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- Gran Canaria: Known for its diverse landscapes, Gran Canaria boasts sandy beaches, volcanic craters, and lush pine forests.
- Lanzarote: This island, with its volcanic landscape, is a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve, renowned for its unique art installations and vineyards.
- Fuerteventura: The second-largest island, Fuerteventura is known for its expansive beaches, windsurfing opportunities, and desert-like landscapes.
- La Palma: A mountainous island with a lush green interior, La Palma is a popular destination for stargazing due to its clear skies.
- La Gomera: This island is known for its dense forests, unique whistling language, and Garajonay National Park, a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- El Hierro: The smallest and most westerly island, El Hierro boasts dramatic volcanic landscapes and is a pioneer in sustainable energy.
The African Connection: A Deeply Rooted Influence
The Canary Islands’ proximity to Africa has had a profound impact on their ecological and cultural landscapes.
Ecological Intertwining:
- Flora and Fauna: The islands’ flora and fauna exhibit a distinct African influence. Many plant species found in the Canaries also thrive in North Africa, while the islands are home to unique endemic species, such as the Canary Island lizard and the Canary Island pine.
- Geological Origins: The volcanic origins of the Canary Islands are linked to the African tectonic plate. The islands’ volcanic activity is a direct result of the ongoing geological processes shaping the African continent.
- Ocean Currents: The Canary Current, a cold current flowing southward along the African coast, brings nutrient-rich waters to the islands, contributing to their rich marine biodiversity.
Cultural Intertwining:
- Historical Ties: The Canary Islands have a long history of interaction with Africa. The indigenous Guanches, who inhabited the islands before European colonization, are believed to have originated in North Africa.
- Language and Culture: The Spanish language spoken in the Canary Islands incorporates African influences, particularly in vocabulary and pronunciation. The islands’ traditional music and dance styles also reflect African roots.
- Trade and Migration: Throughout history, the Canary Islands have served as a vital trade route between Africa and Europe. This connection has led to a significant influx of African migrants to the islands, contributing to their cultural diversity.
Benefits of Understanding the Canary Islands’ African Connection:
- Enhanced Understanding of the Islands: Recognizing the African influence allows for a deeper understanding of the Canary Islands’ unique identity, cultural heritage, and natural environment.
- Appreciation of Cultural Diversity: Acknowledging the islands’ African roots promotes a greater appreciation for the diverse cultures and traditions that have shaped their identity.
- Sustainable Development: Understanding the ecological interdependence between the islands and Africa promotes responsible tourism and conservation efforts.
- Strengthening Regional Ties: Recognizing the historical and cultural ties between the Canary Islands and Africa fosters stronger relationships and collaborations between these regions.
FAQs
Q: Are the Canary Islands part of Africa?
A: While the Canary Islands are geographically closer to Africa than Europe, they are politically part of Spain.
Q: How did the Canary Islands form?
A: The Canary Islands are of volcanic origin, formed by volcanic eruptions over millions of years. The eruptions are linked to the African tectonic plate.
Q: What is the significance of the Canary Current?
A: The Canary Current is a cold current that flows southward along the African coast. It brings nutrient-rich waters to the Canary Islands, contributing to their rich marine biodiversity.
Q: What is the history of the Guanches?
A: The Guanches were the indigenous people who inhabited the Canary Islands before European colonization. They are believed to have originated in North Africa.
Q: How has the Canary Islands’ African connection influenced their culture?
A: The Canary Islands’ cultural heritage reflects a blend of Spanish and African influences. This is evident in their language, music, dance, and cuisine.
Tips for Exploring the Canary Islands’ African Connection:
- Visit the Guanches Museum in Tenerife: This museum showcases the history and culture of the indigenous Guanches, providing insights into their African roots.
- Explore the volcanic landscapes: The islands’ volcanic landscapes offer a glimpse into their geological origins and their connection to the African tectonic plate.
- Sample the local cuisine: The Canary Islands’ cuisine reflects the influence of African ingredients and cooking techniques.
- Engage with local communities: Interact with locals to learn more about their cultural heritage and their connection to Africa.
- Consider visiting the Moroccan coast: A trip to Morocco offers a firsthand experience of the cultural and geographical connections between the Canary Islands and Africa.
Conclusion
The Canary Islands, while part of Spain, are intrinsically linked to Africa. Their geographical proximity, shared geological origins, and cultural influences create a unique tapestry of history, ecology, and cultural diversity. Understanding this connection allows for a deeper appreciation of the islands’ unique identity and fosters a greater understanding of the interconnectedness of our planet. By embracing the Canary Islands’ African heritage, we can foster a richer understanding of the world and its diverse cultures, promoting respect, understanding, and sustainable development across borders.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to the Canary Islands and their African Connection. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
