Location Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing Data and Enhancing User Experience
Related Articles: Location Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing Data and Enhancing User Experience
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Location Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing Data and Enhancing User Experience. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Location Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing Data and Enhancing User Experience

Location maps, often referred to as interactive maps, are powerful tools that visually represent data tied to specific geographic locations. These maps serve as dynamic and engaging visual aids, offering a clear understanding of spatial relationships, patterns, and trends.
Understanding the Power of Location Maps
The essence of location maps lies in their ability to transform abstract data into easily digestible visuals. By overlaying data points onto a geographical backdrop, these maps offer a unique perspective, revealing insights that might remain hidden in raw datasets. This visual representation significantly enhances data comprehension and interpretation, making it a valuable tool across various industries and applications.
Types of Location Maps
Location maps come in various forms, each designed to serve specific purposes and cater to different data visualizations:
- Static Maps: These are traditional maps that depict locations and geographical features without interactive elements. They provide a basic representation of the spatial layout and are commonly used for general information or reference purposes.
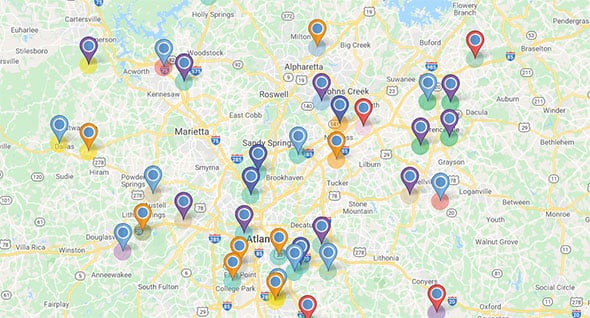
- Interactive Maps: These maps offer dynamic engagement, allowing users to explore data points, zoom in on specific areas, and access additional information by clicking or hovering over markers. Interactive maps are commonly used for data analysis, exploration, and storytelling.
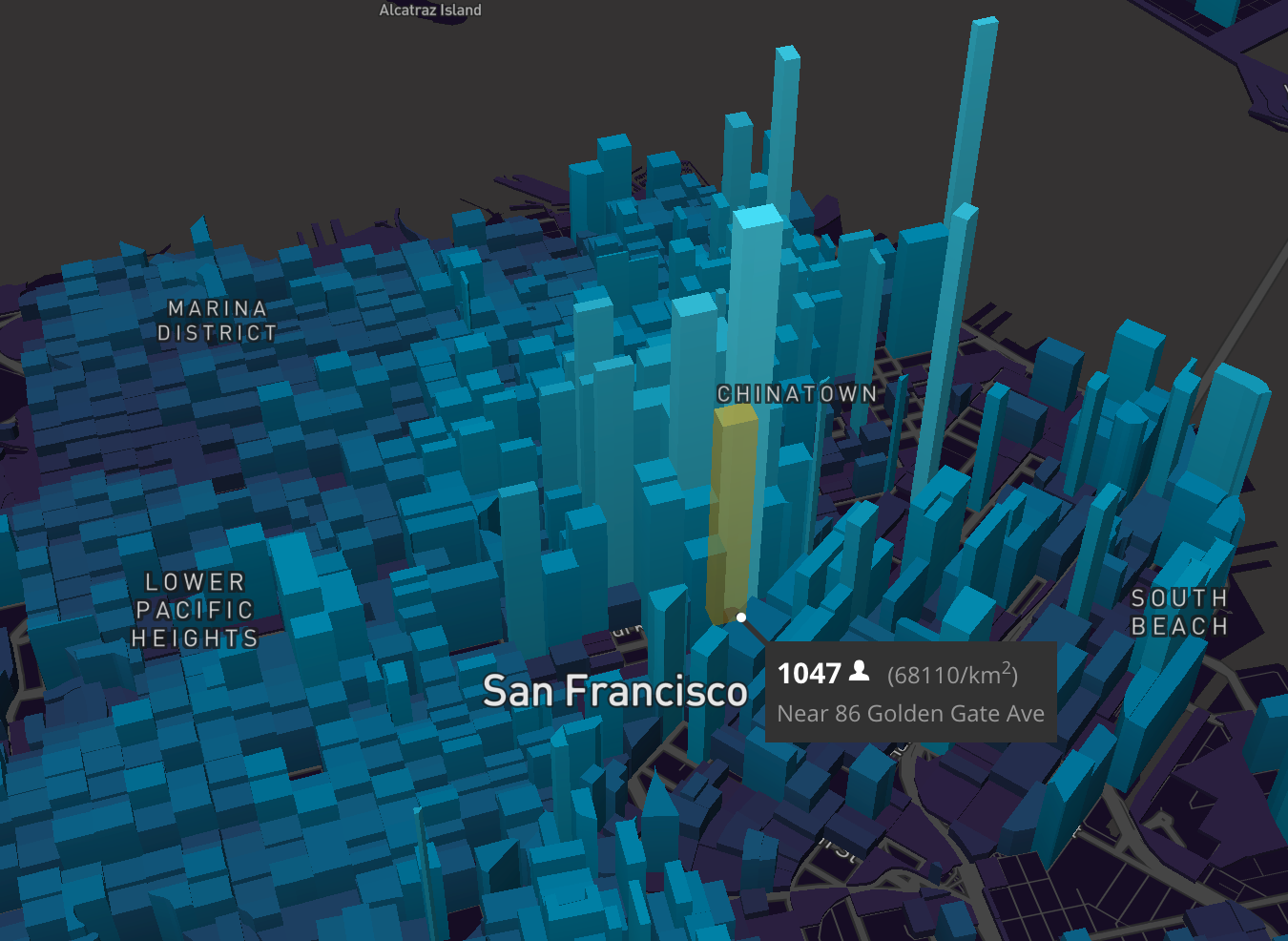
- Heat Maps: These maps use color gradients to represent data density across a geographical area. They effectively highlight areas with high concentration or activity, providing insights into patterns and trends.
- Choropleth Maps: These maps use color variations to represent data values across different geographical regions. They are particularly useful for visualizing data that varies geographically, such as population density, income levels, or disease prevalence.
- Cluster Maps: These maps group data points based on their proximity and similarity. They are useful for identifying clusters of activity or patterns within a geographical area.
Benefits of Location Maps
Location maps offer numerous advantages, making them an indispensable tool in various contexts:
- Enhanced Data Understanding: By visualizing data spatially, location maps facilitate easier comprehension of patterns, trends, and relationships that might be difficult to discern from raw data alone.
- Improved Decision-Making: Location maps provide a visual context for data, allowing users to make informed decisions based on spatial relationships and trends.
- Effective Communication: Location maps offer a clear and engaging way to communicate complex information to diverse audiences, regardless of their technical expertise.
- Increased User Engagement: Interactive location maps promote user engagement by allowing them to explore data at their own pace and interact with the information in a dynamic manner.
- Targeted Marketing and Sales: Location maps are valuable tools for businesses to identify target markets, optimize sales territories, and track customer behavior.
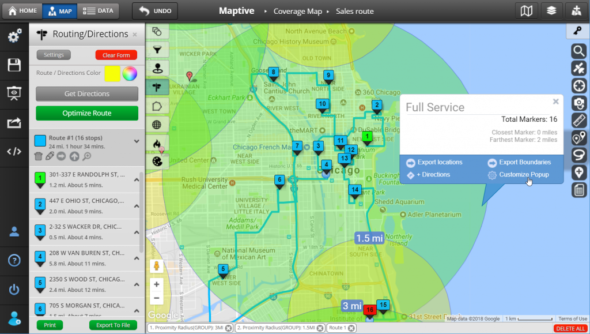
- Resource Management and Planning: Location maps can assist in planning and managing resources effectively, such as optimizing delivery routes, identifying optimal locations for facilities, and managing infrastructure projects.
- Environmental Monitoring and Analysis: Location maps play a crucial role in environmental monitoring and analysis, enabling researchers and policymakers to track changes in environmental conditions, identify pollution sources, and assess the impact of human activities.
Examples of Location Map Applications
Location maps are widely used across diverse industries and applications, demonstrating their versatility and impact:
- Real Estate: Real estate professionals utilize location maps to showcase property listings, analyze market trends, and identify potential investment opportunities.
- Retail: Retailers leverage location maps to understand customer demographics, optimize store locations, and analyze foot traffic patterns.
- Healthcare: Healthcare organizations use location maps to track disease outbreaks, analyze patient demographics, and optimize healthcare resource allocation.
- Transportation: Transportation agencies employ location maps to monitor traffic flow, plan transportation routes, and manage public transit systems.
- Tourism: Tourism organizations utilize location maps to showcase attractions, plan itineraries, and provide interactive travel guides for visitors.
- Education: Educational institutions use location maps to visualize student demographics, analyze school district performance, and plan school infrastructure projects.
- Government: Government agencies rely on location maps for disaster response planning, environmental monitoring, and urban planning initiatives.
FAQs about Location Maps
1. What are the key features of a location map?
Location maps typically include:
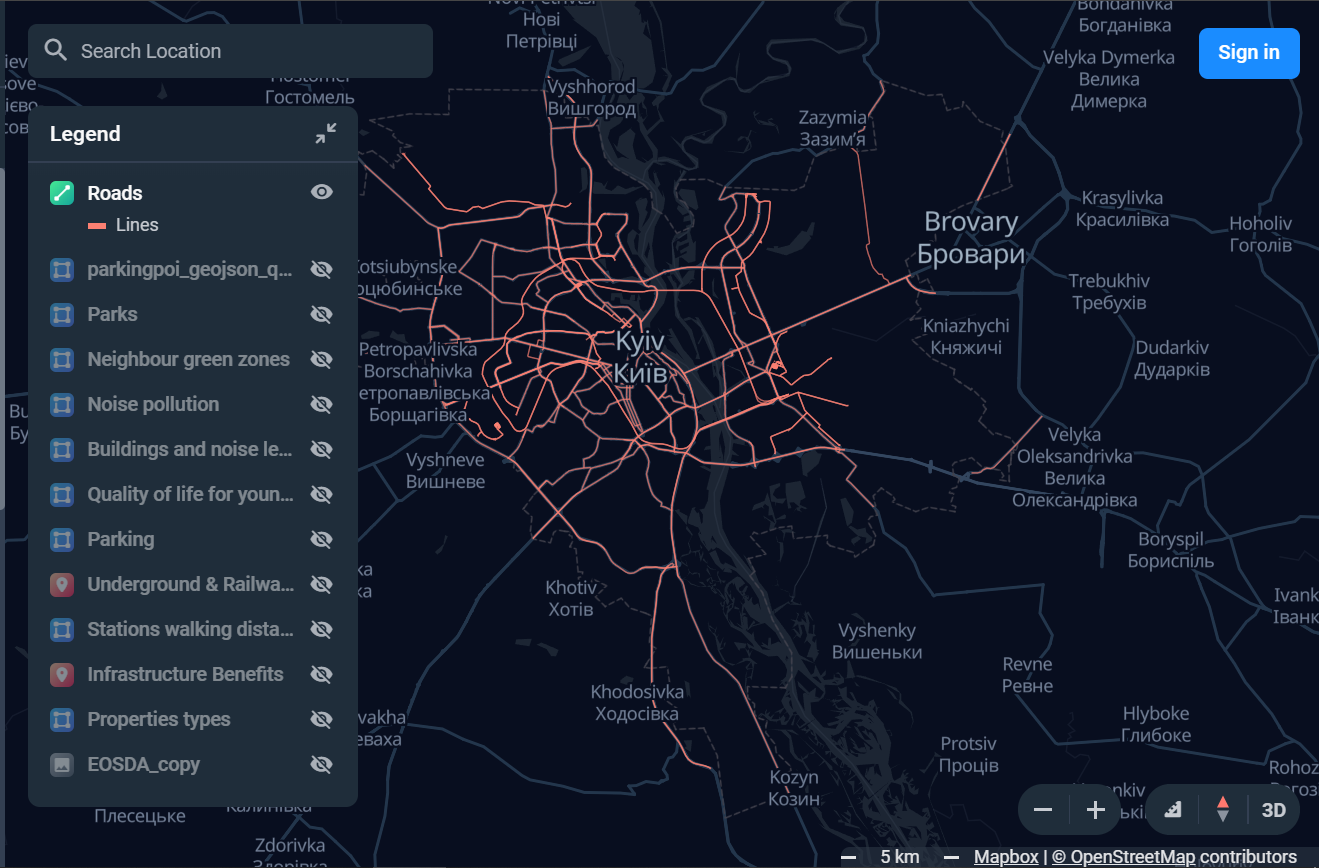
- Base Map: A background map providing geographical context, often including roads, landmarks, and administrative boundaries.
- Data Points: Markers or symbols representing specific locations or data values.
- Legends: Explanations of data points, colors, and symbols used on the map.
- Zoom and Pan Functionality: Allowing users to explore different areas and zoom in for greater detail.
- Interactive Elements: Features like pop-ups, tooltips, and filters that provide additional information upon interaction with data points.
2. How do I create a location map?
Several online tools and software platforms allow you to create location maps, such as:
- Google My Maps: A free and user-friendly platform for creating custom maps with markers, lines, and areas.
- Mapbox: A powerful platform for creating interactive maps with advanced customization options.
- ArcGIS Online: A comprehensive geospatial platform offering advanced mapping and analysis capabilities.
- Tableau: A data visualization platform with robust mapping features for creating interactive dashboards.
3. What are the best practices for creating effective location maps?
- Choose the right type of map: Select the map type that best suits the data and purpose of your visualization.
- Use clear and concise labels: Ensure data points are clearly labeled with relevant information.
- Employ color schemes thoughtfully: Use color gradients and palettes that are visually appealing and enhance data interpretation.
- Maintain a consistent style: Ensure a cohesive visual appearance throughout the map.
- Provide user-friendly navigation: Allow users to easily zoom, pan, and interact with the map.
- Include a legend: Clearly explain the meaning of data points, symbols, and color schemes.
- Test your map for accessibility: Ensure the map is accessible to users with disabilities.
4. What are the limitations of location maps?
While location maps are powerful tools, they have limitations:
- Data availability: The effectiveness of location maps depends on the availability of accurate and relevant data.
- Data bias: Location maps can reflect existing data biases, potentially skewing the interpretation of information.
- Visual complexity: Overloading maps with excessive data points can make them difficult to interpret.
- Technical limitations: Some map platforms may have limitations in terms of functionality or customization options.
Tips for Creating Effective Location Maps
- Define your target audience: Consider the level of technical expertise and information needs of your audience.
- Choose a clear and concise title: Provide a clear and descriptive title that accurately reflects the map’s purpose.
- Use a visually appealing color scheme: Employ a color scheme that is both aesthetically pleasing and enhances data interpretation.
- Highlight key data points: Use different sizes, colors, or symbols to emphasize important data points.
- Provide interactive elements: Include features like pop-ups, tooltips, and filters to enhance user engagement and provide additional information.
- Test your map thoroughly: Ensure the map functions correctly and is easy to navigate.
Conclusion
Location maps have become indispensable tools for visualizing data, enhancing user experience, and facilitating informed decision-making. By transforming raw data into engaging visuals, these maps provide a unique perspective on spatial relationships, trends, and patterns. With their increasing accessibility and versatility, location maps continue to play a crucial role in various industries, empowering users to explore data, gain valuable insights, and drive informed actions.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Location Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing Data and Enhancing User Experience. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
