Delving into the Human Brain: A Comprehensive Guide to Brain Regions
Related Articles: Delving into the Human Brain: A Comprehensive Guide to Brain Regions
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Delving into the Human Brain: A Comprehensive Guide to Brain Regions. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Delving into the Human Brain: A Comprehensive Guide to Brain Regions
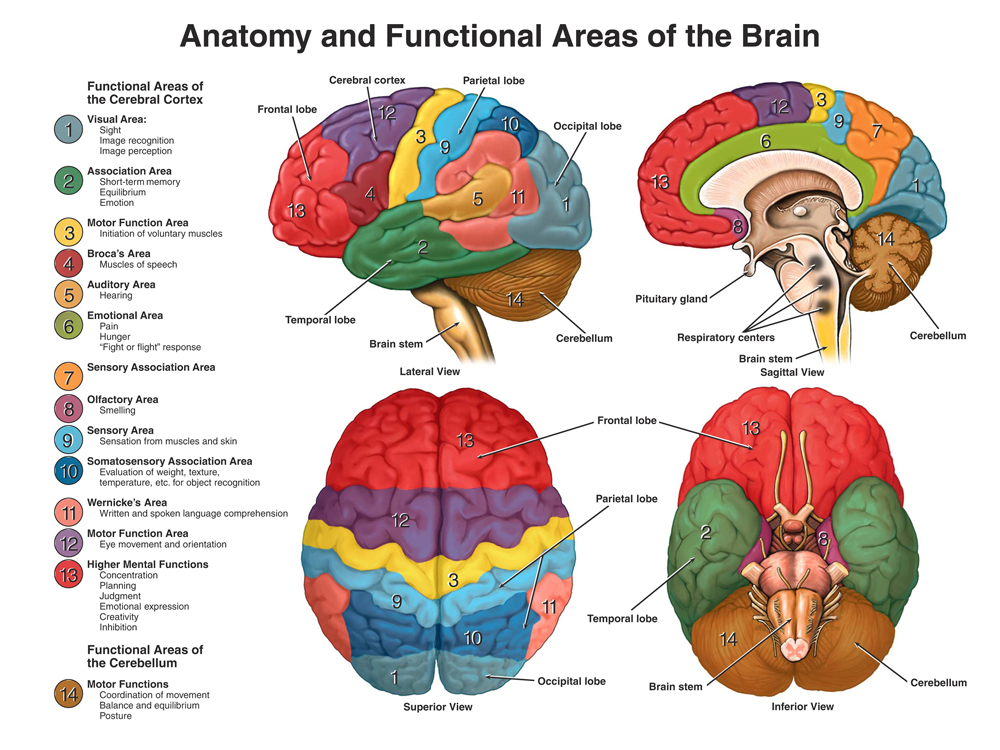
The human brain, a marvel of biological complexity, is the central command center of our being. It orchestrates everything from our thoughts and emotions to our movements and senses. Understanding the intricate network of brain regions is essential for comprehending the mechanics of our minds and the profound impact they have on our lives. This comprehensive guide explores the major brain regions, their functions, and the fascinating interplay that governs our cognitive abilities and overall well-being.
A Glimpse into the Brain’s Structure:
The brain, a soft, wrinkled organ housed within the protective skull, can be broadly divided into three major parts: the cerebrum, the cerebellum, and the brainstem.
1. The Cerebrum: The Seat of Higher Cognition
The cerebrum, the largest part of the brain, is responsible for our higher-level cognitive functions. It is divided into two hemispheres, the left and right, connected by a thick band of nerve fibers called the corpus callosum. Each hemisphere specializes in different functions, though they work together seamlessly.
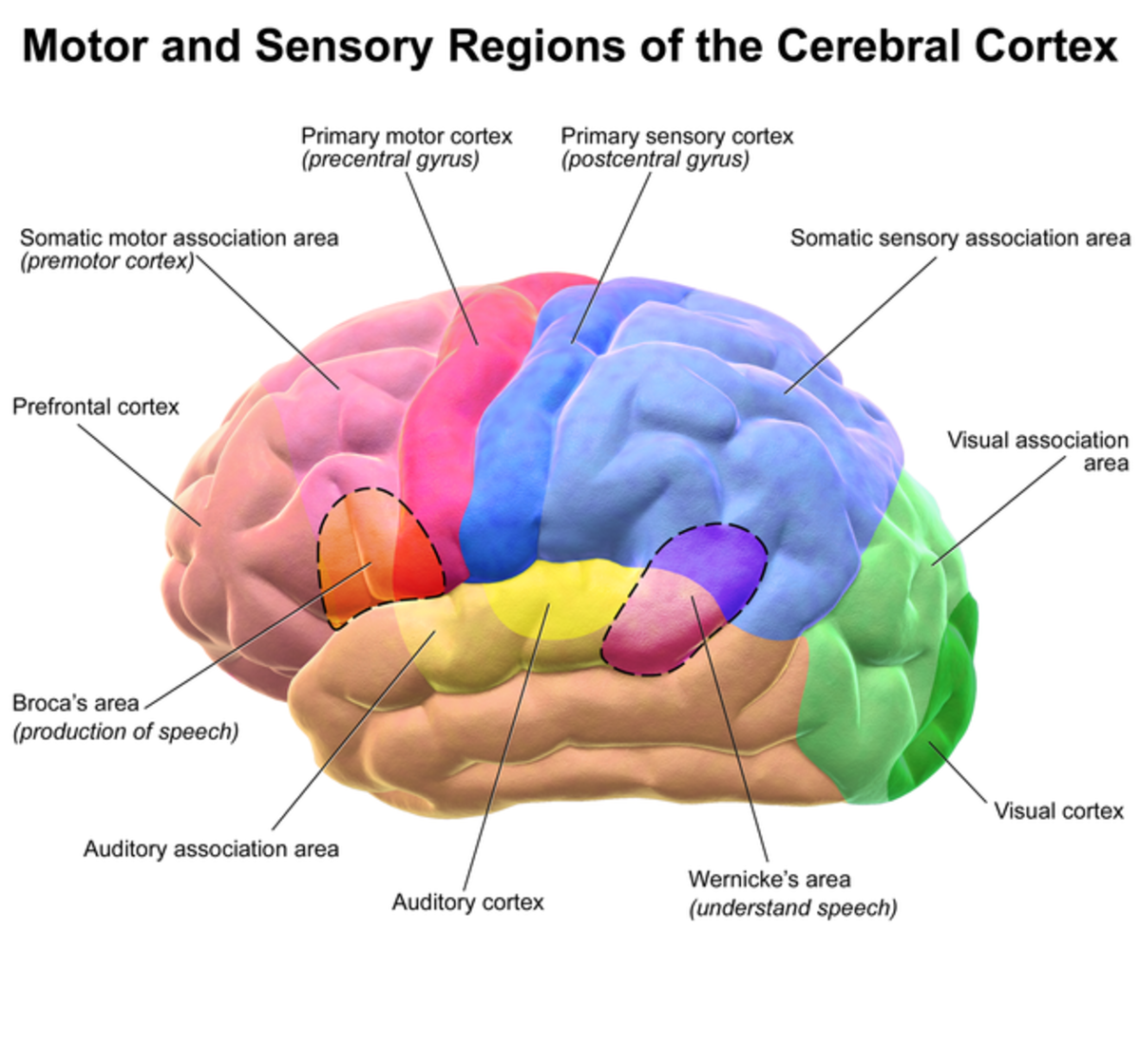
a) The Cerebral Cortex: The Outer Layer of the Cerebrum
The cerebral cortex, the outermost layer of the cerebrum, is responsible for complex cognitive processes. It is highly convoluted, increasing its surface area and allowing for greater processing power. The cortex is further divided into four lobes, each with distinct functions:
- Frontal Lobe: Located at the front of the brain, the frontal lobe is responsible for executive functions, including planning, decision-making, problem-solving, working memory, and personality. It also houses the motor cortex, which controls voluntary movements.
- Parietal Lobe: Situated behind the frontal lobe, the parietal lobe integrates sensory information, including touch, temperature, pain, and pressure. It also plays a crucial role in spatial awareness and navigation.
- Temporal Lobe: Located below the parietal lobe, the temporal lobe is responsible for processing auditory information, language comprehension, memory, and emotion. It also houses the hippocampus, a key structure for memory formation.
- Occipital Lobe: Located at the back of the brain, the occipital lobe is responsible for processing visual information, including color, shape, and motion.
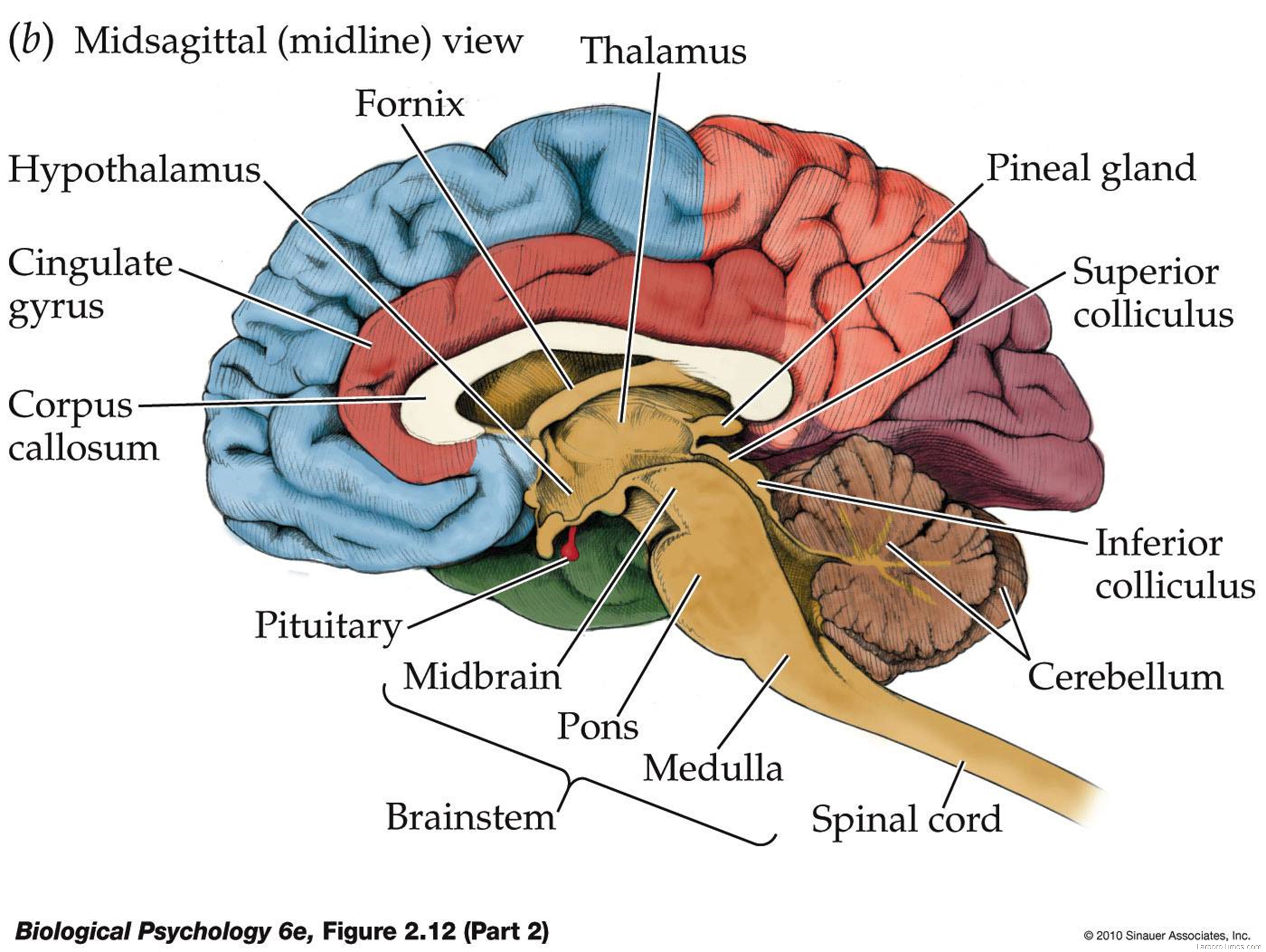
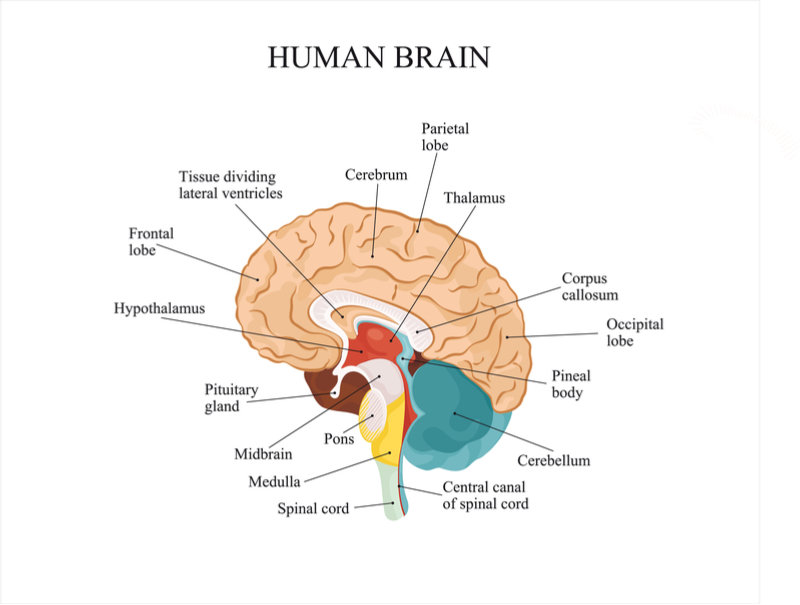
b) Subcortical Structures: Beneath the Cerebral Cortex
Beneath the cerebral cortex lies a network of subcortical structures, each playing a vital role in various brain functions:
- Thalamus: The thalamus acts as a relay center for sensory information, filtering and transmitting it to the appropriate areas of the cerebral cortex.
- Hypothalamus: The hypothalamus regulates vital bodily functions, including hunger, thirst, body temperature, and sleep-wake cycles. It also plays a role in hormone production and emotional responses.
- Amygdala: The amygdala is involved in processing emotions, particularly fear and anxiety. It also plays a role in memory formation, particularly for emotionally charged events.
- Hippocampus: The hippocampus is crucial for memory formation and retrieval, particularly for long-term memories. It also plays a role in spatial navigation.
- Basal Ganglia: The basal ganglia are involved in motor control, planning, and learning. They help coordinate smooth, voluntary movements and regulate muscle tone.
2. The Cerebellum: The Maestro of Movement and Coordination
The cerebellum, located at the back of the brain below the cerebrum, is responsible for coordinating movement, balance, and posture. It receives sensory information from the body and the cerebrum and fine-tunes motor commands, ensuring smooth and precise movements. The cerebellum also plays a role in learning and memory, particularly motor skills.
3. The Brainstem: The Lifeline of the Brain
The brainstem, connecting the cerebrum and cerebellum to the spinal cord, is essential for basic life functions. It controls breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, and sleep-wake cycles. The brainstem also relays sensory and motor information between the brain and the body.
The Importance of Understanding Brain Regions:
Mapping and understanding brain regions are crucial for several reasons:
- Medical Diagnosis and Treatment: Brain mapping aids in diagnosing neurological disorders, such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and stroke. It also helps guide surgical interventions, ensuring minimal damage to critical brain areas.
- Neurological Research: Studying brain regions allows researchers to gain insights into the mechanisms underlying cognitive processes, emotions, and behaviors. This knowledge is essential for developing new treatments for neurological disorders and improving our understanding of the human mind.
- Educational and Personal Growth: Understanding brain regions can enhance our self-awareness and provide valuable insights into how we learn, think, and interact with the world. This knowledge can be applied to improve learning strategies, enhance cognitive skills, and promote overall well-being.
FAQs on Brain Regions:
Q: What is the difference between the left and right hemispheres of the brain?
A: While both hemispheres work together, they specialize in different functions. The left hemisphere is typically dominant for language, logic, and analytical skills, while the right hemisphere excels in spatial awareness, creativity, and emotional processing.
Q: Can brain regions be damaged without causing noticeable symptoms?
A: The brain is remarkably resilient, and some damage to specific regions may go unnoticed, particularly in the early stages. However, depending on the location and extent of damage, symptoms can range from mild to severe, impacting various cognitive and physical functions.
Q: Can brain regions be trained or strengthened?
A: Neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to adapt and change, allows for some degree of training and strengthening of specific brain regions. Engaging in mentally stimulating activities, learning new skills, and practicing cognitive exercises can contribute to brain health and improve cognitive function.
Tips for Enhancing Brain Health:
- Engage in mentally stimulating activities: Puzzles, crosswords, learning new languages, and playing musical instruments can challenge your brain and promote cognitive function.
- Maintain a healthy diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids supports brain health and function.
- Exercise regularly: Physical activity improves blood flow to the brain, promoting cognitive function and reducing the risk of cognitive decline.
- Get enough sleep: Adequate sleep is essential for memory consolidation, learning, and overall brain health.
- Manage stress: Chronic stress can negatively impact brain function. Engage in relaxation techniques, such as meditation or yoga, to manage stress levels.
Conclusion:
Mapping the brain’s intricate network of regions is a continuous journey of discovery, shedding light on the complexity and wonder of the human mind. Understanding the functions of different brain regions provides invaluable insights into our cognitive abilities, emotions, and behaviors. By recognizing the importance of brain health and adopting lifestyle choices that promote optimal brain function, we can enhance our cognitive abilities, improve our well-being, and unlock the full potential of our remarkable brains.

/human-brain-regions--illustration-713784787-5973a8a8d963ac00103468ba.jpg)



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Delving into the Human Brain: A Comprehensive Guide to Brain Regions. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
