Charting the Rise and Fall of an Empire: A Comprehensive Look at the Roman Empire Territory Map
Related Articles: Charting the Rise and Fall of an Empire: A Comprehensive Look at the Roman Empire Territory Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Charting the Rise and Fall of an Empire: A Comprehensive Look at the Roman Empire Territory Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Charting the Rise and Fall of an Empire: A Comprehensive Look at the Roman Empire Territory Map
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Charting the Rise and Fall of an Empire: A Comprehensive Look at the Roman Empire Territory Map
- 3.1 Understanding the Evolution of the Roman Empire Territory
- 3.2 The Importance of the Roman Empire Territory Map
- 3.3 FAQs about the Roman Empire Territory Map
- 3.4 Tips for Studying the Roman Empire Territory Map
- 3.5 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Charting the Rise and Fall of an Empire: A Comprehensive Look at the Roman Empire Territory Map

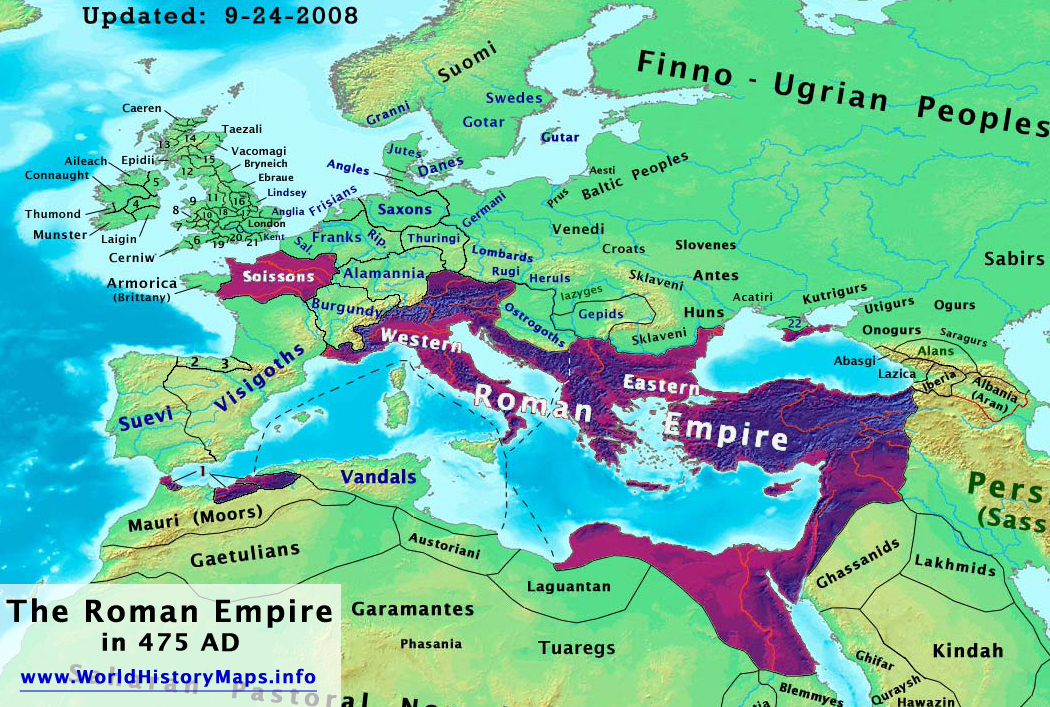
The Roman Empire, a colossal civilization that dominated the Mediterranean world for centuries, left an indelible mark on history. Its vast territorial expanse, achieved through military prowess and strategic alliances, encompassed a diverse array of cultures, landscapes, and peoples. To understand the empire’s rise and fall, its influence, and its lasting impact, examining the Roman Empire territory map is crucial. This map serves as a visual chronicle of the empire’s expansion, its administrative divisions, and its gradual contraction over time.
Understanding the Evolution of the Roman Empire Territory
The Roman Empire’s territory map is not static; it is a dynamic representation of the empire’s growth and decline. The map reflects the complex interplay of political, economic, and military factors that shaped the empire’s boundaries.
Early Beginnings and Expansion:
The Roman Empire’s origins lie in the small city-state of Rome, founded in 753 BC. Over centuries, Rome expanded its territory through a series of conquests, establishing a Republic in 509 BC. The Republic’s expansionist policies, driven by the desire for resources, land, and political power, resulted in the subjugation of neighboring territories.
The Rise of the Empire:
The Roman Republic transitioned into an empire in 27 BC with the ascension of Augustus, the first Roman emperor. Under his rule, the empire reached its peak of territorial expansion. The map during this period showcases the empire’s control over vast swathes of land, encompassing the entire Italian peninsula, the Balkans, Gaul (modern France), Hispania (modern Spain), North Africa, and parts of the Middle East.
Key Territories and Administrative Divisions:
The Roman Empire’s territory was divided into provinces, each governed by a Roman official called a proconsul or pro-praetor. This administrative structure facilitated the efficient management of the vast empire. Key provinces included:
- Italia: The heart of the empire, encompassing the Italian peninsula.
- Gallia: Covering modern France, Belgium, Switzerland, and parts of Germany.
- Hispania: Comprising modern Spain, Portugal, and Andorra.
- Africa: Stretching across North Africa, encompassing modern Tunisia, Algeria, Morocco, and parts of Libya.
- Aegyptus: The fertile Nile Valley, a vital breadbasket for the empire.
- Syria: Covering modern Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Jordan, and parts of Turkey.
The Decline and Fall:
The Roman Empire, despite its vast size and military might, eventually succumbed to internal strife, economic instability, and external pressures. The empire faced numerous challenges, including:
- Barbarian Invasions: Waves of Germanic tribes, pressured by other migrating groups, began to exert increasing pressure on the empire’s frontiers.
- Economic Decline: Inflation, trade disruptions, and a decline in agricultural productivity weakened the empire’s economic foundations.
- Political Instability: Frequent civil wars and power struggles within the imperial court weakened the central authority.
These factors contributed to the empire’s gradual fragmentation. The map reflects the empire’s shrinking territory as provinces were lost to barbarian invaders and internal rebellions.
The Eastern Roman Empire (Byzantine Empire):
In 395 AD, the Roman Empire was divided into two halves: the Western Roman Empire and the Eastern Roman Empire. The Western Roman Empire eventually collapsed in 476 AD, while the Eastern Roman Empire, also known as the Byzantine Empire, continued to thrive for another thousand years. The Byzantine Empire’s territory map, while significantly smaller than the Roman Empire at its peak, included areas of the Eastern Mediterranean, the Balkans, and parts of North Africa.
The Importance of the Roman Empire Territory Map
The Roman Empire territory map is not merely a geographical representation; it is a window into the past, offering insights into the empire’s rise, its expansion, and its eventual decline. It provides valuable information for understanding:
- The Empire’s Influence: The map reveals the vast scope of Roman influence, demonstrating the empire’s dominance over a significant portion of the known world.
- Cultural Exchange: The empire’s territorial expanse facilitated the exchange of ideas, technologies, and cultural practices between different regions, contributing to the spread of Roman culture and civilization.
- Administrative Structure: The map illustrates the empire’s administrative divisions, highlighting the complex system of governance that enabled the management of such a vast territory.
- Military Strategies: The map helps to understand the empire’s military strategies, revealing the importance of strategic locations and key fortifications.
- Economic Networks: The map highlights the empire’s trade routes and economic networks, demonstrating the interconnectedness of different regions within the empire.
- Legacy of the Empire: The map serves as a reminder of the empire’s enduring legacy, shaping the political, cultural, and linguistic landscape of Europe and the Mediterranean world.
FAQs about the Roman Empire Territory Map
Q: What was the largest extent of the Roman Empire?
A: The Roman Empire reached its largest territorial extent during the reign of Emperor Trajan (98-117 AD). At this time, the empire encompassed approximately 3.4 million square kilometers (1.3 million square miles), stretching from Britain in the north to Egypt in the south and from Spain in the west to the Euphrates River in the east.
Q: How did the Roman Empire acquire its territory?
A: The Roman Empire acquired its vast territory through a combination of conquest, alliances, and treaties. The Roman army, known for its discipline and tactical prowess, engaged in numerous wars of expansion, conquering neighboring territories and incorporating them into the empire. The empire also formed alliances with other kingdoms and tribes, expanding its influence through diplomacy and strategic partnerships.
Q: Why did the Roman Empire collapse?
A: The Roman Empire’s collapse was a complex process, resulting from a confluence of factors. Internal strife, economic decline, and external pressures from barbarian invasions all played a role. The empire’s vast size and its complex administrative structure made it increasingly difficult to govern effectively, leading to instability and eventually, fragmentation.
Q: What is the significance of the Roman Empire’s legacy?
A: The Roman Empire’s legacy is profound and multifaceted. It left behind a rich cultural heritage, including literature, art, architecture, law, and governance systems. The empire’s influence on the development of Western civilization is undeniable, shaping political structures, legal systems, and cultural values that continue to resonate today.
Tips for Studying the Roman Empire Territory Map
- Focus on Key Periods: Pay attention to the different stages of the Roman Empire’s expansion and decline, highlighting key periods of territorial growth and contraction.
- Identify Key Provinces: Understand the significance of different provinces within the empire, considering their economic importance, strategic value, and cultural diversity.
- Analyze Boundaries: Examine the empire’s boundaries, noting the natural barriers, strategic fortifications, and key points of vulnerability.
- Consider Historical Context: Understand the historical context surrounding the empire’s expansion and decline, considering the political, economic, and social factors that influenced territorial changes.
- Compare Maps: Compare different maps of the Roman Empire, highlighting the changes in territory over time and the impact of key events such as conquests, rebellions, and invasions.
Conclusion
The Roman Empire territory map is a powerful tool for understanding the empire’s rise, its expansion, and its eventual decline. It provides a visual representation of the empire’s territorial boundaries, administrative divisions, and the complex interplay of factors that shaped its history. By studying this map, we gain insights into the empire’s influence, its cultural exchange, its military strategies, and its lasting legacy. The Roman Empire, despite its eventual fall, remains a testament to the power of human ambition, the complexities of governance, and the enduring influence of a civilization that once dominated the known world.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting the Rise and Fall of an Empire: A Comprehensive Look at the Roman Empire Territory Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
