Charting the Course: A Comprehensive Guide to Road Map Business Plans
Related Articles: Charting the Course: A Comprehensive Guide to Road Map Business Plans
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Charting the Course: A Comprehensive Guide to Road Map Business Plans. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Charting the Course: A Comprehensive Guide to Road Map Business Plans

In the dynamic world of business, navigating the path to success requires more than just a destination. It demands a meticulously crafted roadmap, a strategic blueprint that outlines the journey, the milestones, and the resources needed to reach the desired goal. This is where the concept of a road map business plan comes into play, serving as a vital tool for organizations of all sizes.
Defining the Road Map Business Plan
A road map business plan is not simply a static document; it is a dynamic and evolving framework that outlines the strategic direction of a business over a specific time frame. It encompasses a clear vision of the future, identifies key objectives, and lays out the steps necessary to achieve them. Unlike traditional business plans that focus on financial projections and market analysis, road maps prioritize a visual representation of the journey, breaking down complex goals into manageable tasks and timelines.
The Importance of Road Map Business Plans
The benefits of a well-crafted road map business plan are numerous and far-reaching. They offer:
- Clarity and Direction: By defining the desired end state and mapping out the path to get there, road maps provide a clear sense of direction, ensuring that all team members are aligned on the same goals and objectives.
- Strategic Alignment: Road maps serve as a unifying force, aligning all departments and functions within the organization towards a common vision. They foster collaboration and minimize internal conflicts by providing a shared understanding of priorities and responsibilities.
- Prioritization and Resource Allocation: Road maps facilitate the prioritization of initiatives and the allocation of resources based on their impact and alignment with strategic objectives. This ensures that efforts are focused on the most critical tasks, maximizing efficiency and productivity.
- Measurable Progress: Road maps typically include clear milestones and deadlines, allowing for the tracking of progress and the identification of areas requiring adjustments or course corrections. This data-driven approach enables organizations to stay on track and adapt to changing circumstances.
- Increased Accountability: The transparency and accountability inherent in road maps encourage team members to take ownership of their responsibilities and contribute actively towards achieving shared goals. This fosters a culture of responsibility and drives collective success.
- Enhanced Communication: Road maps provide a visual and easily digestible representation of the strategic plan, facilitating clear communication with stakeholders, including investors, partners, and employees. This transparency builds trust and fosters a shared understanding of the organization’s direction.
- Improved Decision-Making: By providing a comprehensive overview of the strategic landscape, road maps empower leaders to make informed decisions based on data and insights, reducing the risk of impulsive or misguided choices.
Key Components of a Road Map Business Plan
A robust road map business plan typically includes the following key components:
- Vision and Mission: A clear articulation of the organization’s long-term aspirations and its purpose in the market. This serves as the guiding principle for all strategic decisions.
- Objectives and Key Results (OKRs): Specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound objectives that outline the desired outcomes for the roadmap period. These objectives should be aligned with the overall vision and mission.
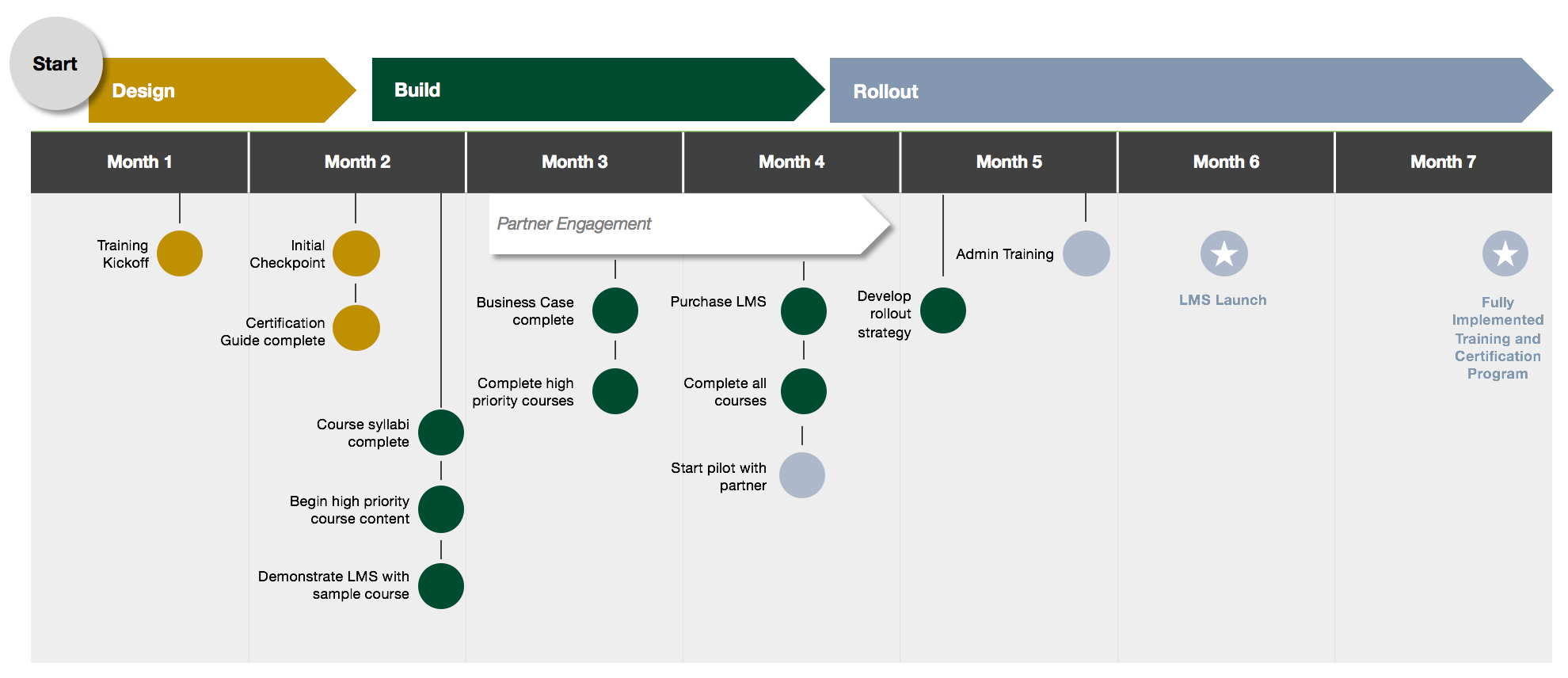
- Milestones and Deadlines: Key milestones that mark significant progress towards achieving the objectives, along with specific deadlines for completion. This provides a structured framework for tracking progress and ensuring timely execution.
- Action Items and Responsibilities: Detailed tasks and activities that need to be completed to reach each milestone, along with the individuals or teams responsible for their execution. This ensures clear ownership and accountability.
- Resources and Budget: An assessment of the resources required to execute the plan, including financial resources, personnel, and technology. This helps to ensure that the necessary resources are available and allocated effectively.
- Risk Assessment and Mitigation: Identification of potential risks and challenges that could impact the execution of the plan, along with strategies to mitigate or minimize their impact. This proactive approach helps to ensure that the organization is prepared to address unforeseen circumstances.
- Communication and Monitoring: Strategies for communicating the roadmap to stakeholders and for monitoring progress towards achieving objectives. Regular updates and feedback loops are essential for ensuring that the plan remains relevant and effective.
Developing a Road Map Business Plan: A Step-by-Step Guide
Creating a comprehensive and effective road map business plan requires a structured and collaborative approach. Here’s a step-by-step guide to assist in the process:
- Define the Scope and Timeframe: Determine the specific time frame for the roadmap, ensuring it aligns with the organization’s strategic planning cycle. Clearly define the scope of the roadmap, focusing on specific areas or initiatives that are critical to the organization’s success.
- Establish the Vision and Mission: Articulate the organization’s long-term vision and mission, providing a clear understanding of its aspirations and purpose. This forms the foundation for all subsequent planning efforts.
- Identify Key Objectives and OKRs: Define specific and measurable objectives that represent the desired outcomes for the roadmap period. These objectives should be ambitious but achievable, and they should be aligned with the overall vision and mission.
- Conduct a SWOT Analysis: Analyze the organization’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. This comprehensive assessment helps to identify areas for improvement and potential risks that need to be addressed.
- Develop a High-Level Roadmap: Create a visual representation of the roadmap, outlining the key milestones and their estimated timelines. This provides a clear overview of the journey and helps to identify potential dependencies and critical paths.
- Define Action Items and Responsibilities: Break down each milestone into specific action items and assign responsibility for their completion. This ensures that each task has a clear owner and that everyone understands their role in the execution process.
- Estimate Resources and Budget: Determine the resources required for each action item, including financial resources, personnel, and technology. This helps to ensure that the necessary resources are available and allocated effectively.
- Conduct Risk Assessment and Mitigation: Identify potential risks and challenges that could impact the execution of the plan. Develop strategies to mitigate or minimize their impact, ensuring that the organization is prepared for unforeseen circumstances.
- Establish Communication and Monitoring Mechanisms: Define clear communication channels for sharing updates and progress reports with stakeholders. Establish mechanisms for monitoring progress towards achieving objectives and for making necessary adjustments or course corrections.
- Iterate and Refine: Road maps are not static documents; they should be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect changing circumstances and new insights. This iterative process ensures that the plan remains relevant and effective over time.
FAQs: Road Map Business Plans
1. What is the difference between a road map business plan and a traditional business plan?
A traditional business plan focuses on financial projections, market analysis, and operational details. It provides a detailed overview of the business model and its financial viability. A road map business plan, on the other hand, prioritizes a visual representation of the strategic journey, outlining key milestones, timelines, and action items. It focuses on achieving specific objectives and guiding the organization towards its desired future state.
2. Who should create a road map business plan?
Any organization that aims to achieve strategic objectives and navigate a defined path to success can benefit from a road map business plan. This includes startups, established businesses, non-profit organizations, and government agencies.
3. How often should a road map business plan be updated?
The frequency of updates depends on the organization’s context and the dynamic nature of its environment. Generally, road maps should be reviewed and updated at least annually, or more frequently if significant changes occur in the market, technology, or the organization’s strategic direction.
4. What are some common challenges in developing and implementing a road map business plan?
Common challenges include:
- Lack of alignment and buy-in: Ensuring that all stakeholders are aligned on the vision, objectives, and action items is crucial for successful implementation.
- Resource constraints: Obtaining the necessary resources, including financial resources, personnel, and technology, can be challenging.
- Unforeseen circumstances: External factors such as market shifts, technological advancements, or economic downturns can disrupt the execution of the plan.
- Lack of accountability: Establishing clear responsibilities and ensuring accountability for the execution of action items is essential for success.
Tips for Creating Effective Road Map Business Plans
- Keep it simple and visual: Road maps should be clear, concise, and easy to understand. Use visual elements such as timelines, charts, and diagrams to enhance comprehension.
- Prioritize key objectives: Focus on a limited number of strategic objectives that are truly critical to the organization’s success.
- Involve key stakeholders: Engage stakeholders from different departments and levels within the organization to ensure buy-in and alignment.
- Be flexible and adaptable: Road maps should be dynamic and adaptable to changing circumstances. Regularly review and update the plan to reflect new insights and opportunities.
- Communicate effectively: Clearly communicate the roadmap to all stakeholders, ensuring that everyone understands the vision, objectives, and action items.
Conclusion
In the ever-evolving business landscape, a road map business plan is an indispensable tool for navigating towards success. It provides clarity, alignment, prioritization, accountability, and enhanced communication, empowering organizations to achieve their strategic objectives and thrive in the face of uncertainty. By embracing the principles and practices outlined in this guide, businesses can harness the power of road map business plans to chart a course for a brighter future.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting the Course: A Comprehensive Guide to Road Map Business Plans. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
