A Journey Through Time: Understanding the Historical and Geographical Significance of Samaria and Jerusalem
Related Articles: A Journey Through Time: Understanding the Historical and Geographical Significance of Samaria and Jerusalem
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through Time: Understanding the Historical and Geographical Significance of Samaria and Jerusalem. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through Time: Understanding the Historical and Geographical Significance of Samaria and Jerusalem
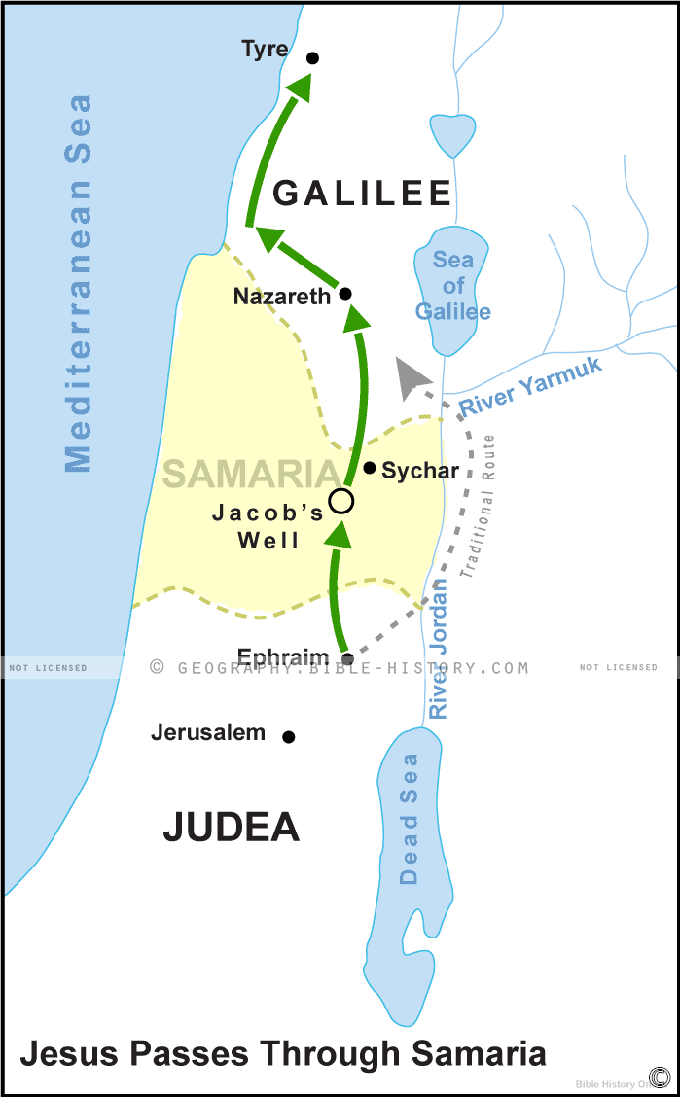
The land of Israel, a region steeped in history and religious significance, holds two prominent locations: Samaria and Jerusalem. These cities, intertwined in narratives spanning millennia, are not simply points on a map, but rather powerful symbols of cultural, religious, and political complexities. This exploration delves into the historical, geographical, and contemporary significance of Samaria and Jerusalem, illuminating their unique roles in shaping the landscape of the Middle East.
Samaria: A Land of Ancient Kingdoms and Modern Contention
Samaria, located in the northern region of the West Bank, holds a rich history dating back to the Iron Age. The region was initially inhabited by the Canaanites before becoming the heartland of the northern Israelite Kingdom. Samaria, the capital city, flourished under the rule of Omri and his successors, a period marked by significant cultural and economic development. However, its fate was sealed with the Assyrian conquest in the 8th century BCE, leading to the fall of the northern kingdom and the scattering of its people.
The region remained under foreign rule, transitioning between various empires, including the Persians, Greeks, Romans, and Byzantines. During the Roman period, Samaria was renamed Sebaste, a name derived from Augustus Caesar. This renaming reflected the Roman policy of integrating conquered territories into the empire. The city was rebuilt, and its architecture, incorporating Roman elements, stands as a testament to this era.
Jerusalem: A City of Three Faiths
Jerusalem, a city revered by Judaism, Christianity, and Islam, stands as a focal point of religious and cultural convergence. Its history stretches back to the Bronze Age, with evidence of its early development dating back to the 3rd millennium BCE. The city became the capital of the Kingdom of Judah, and its importance grew as a center of religious and political power. The First Temple, constructed by King Solomon, solidified Jerusalem’s status as the holiest site in Judaism.
The destruction of the First Temple by the Babylonians in 586 BCE marked a turning point, leading to the Babylonian Exile. However, Jerusalem was rebuilt, and the Second Temple was erected, becoming a symbol of Jewish resilience. The city was conquered by the Romans in 70 CE, resulting in the destruction of the Second Temple and the dispersal of the Jewish population. Despite this, Jerusalem remained a significant pilgrimage site for Jews.
With the rise of Christianity, Jerusalem became a focal point for the new faith. The city is believed to be the site of Jesus Christ’s crucifixion and resurrection, making it a central location for Christian pilgrimage and worship. The Holy Sepulchre, a church built over the traditional site of Jesus’ tomb, stands as a testament to this significance.
The arrival of Islam in the 7th century CE brought a new dimension to Jerusalem’s religious landscape. The city was conquered by the Umayyad Caliphate, and the Dome of the Rock, a mosque built on the Temple Mount, became a sacred site for Muslims. Jerusalem, under Muslim rule, experienced periods of both prosperity and conflict, with the city passing between various Islamic dynasties.
Contemporary Significance: A Complex Tapestry of Identity and Conflict
Samaria and Jerusalem, intertwined in history, remain at the center of contemporary geopolitical complexities. The Israeli-Palestinian conflict, a long-standing struggle for land and resources, casts a shadow over both regions. The West Bank, where Samaria is located, is a contested territory claimed by both Israel and the Palestinians. The Israeli government has established settlements in Samaria, a move that has been widely condemned by the international community as a violation of international law.
Jerusalem, a city claimed by both Israelis and Palestinians as their capital, is a focal point of the conflict. The city’s status remains unresolved, with both sides vying for control and recognition. The presence of holy sites for Judaism, Christianity, and Islam adds another layer of complexity to the conflict, highlighting the religious and political sensitivities surrounding the city.
Understanding the Map: A Key to Navigating the Past and Present
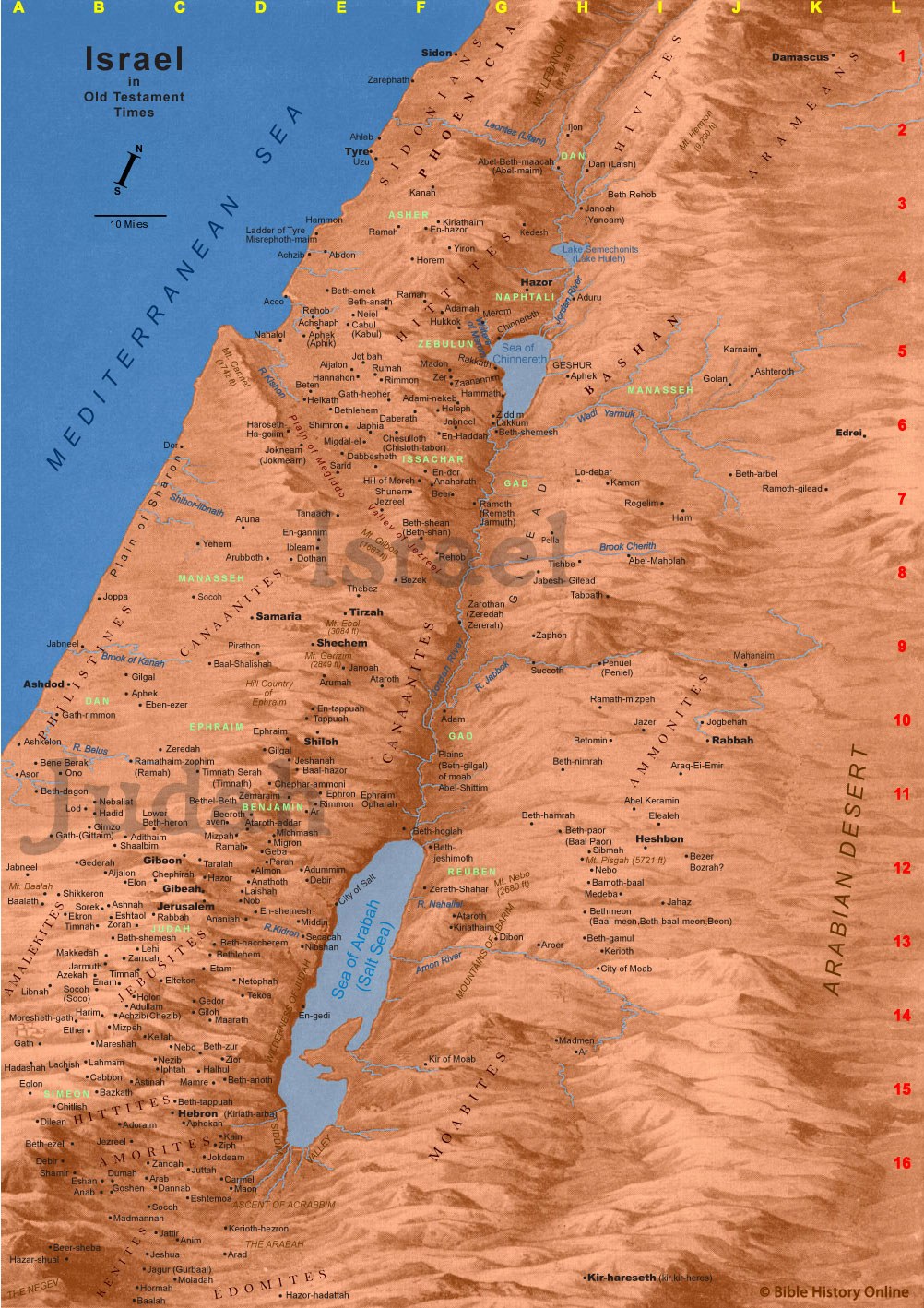
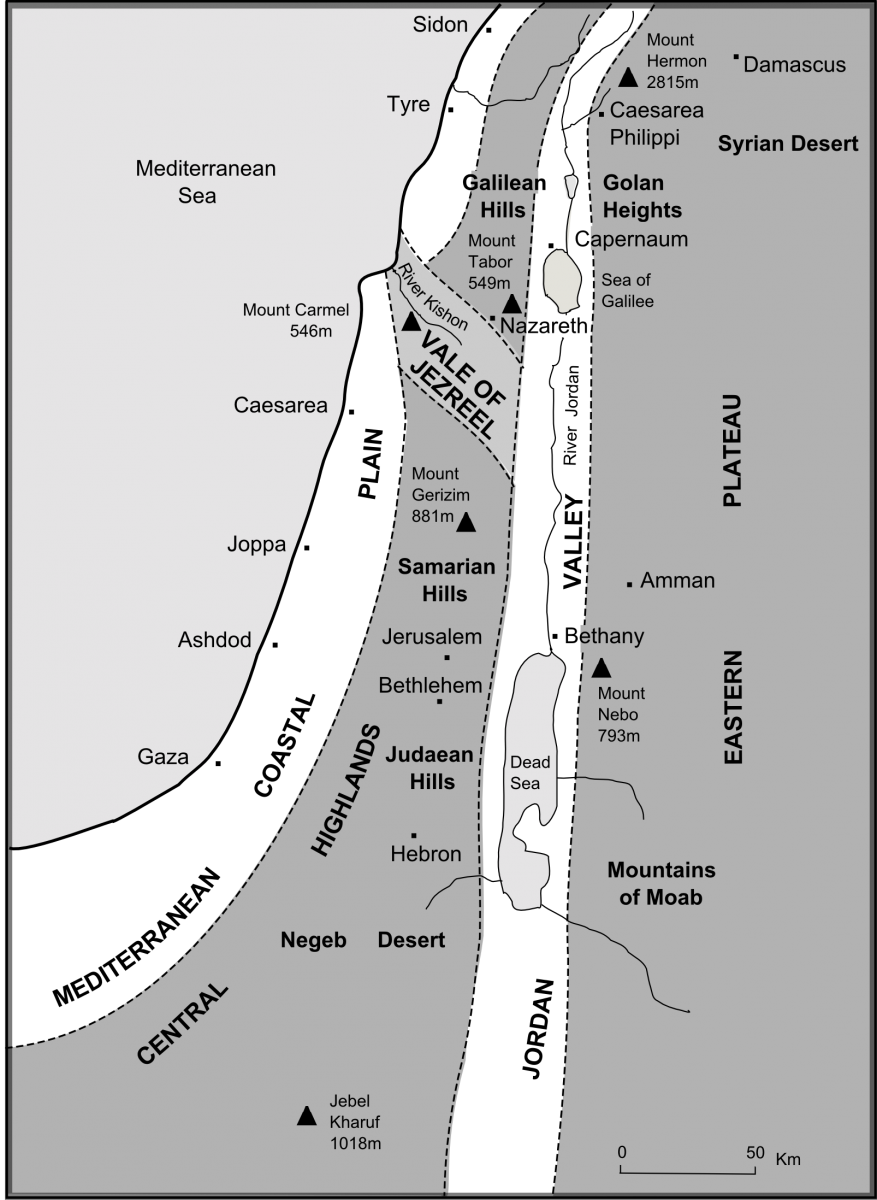
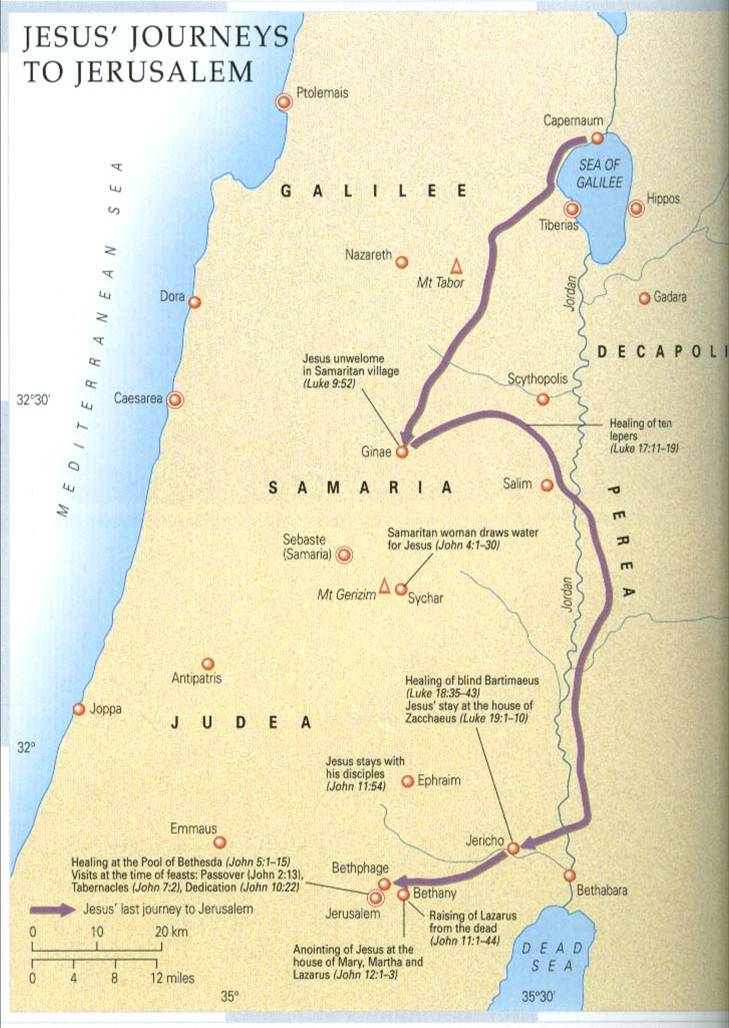
A map of Samaria and Jerusalem is not simply a geographical representation; it is a window into history, revealing the layers of civilizations that have shaped these regions. It provides a visual framework for understanding the intertwined narratives of both cities, their connections to broader historical events, and their contemporary significance. By examining the map, one can gain a deeper understanding of the following:
- Historical Connections: The map showcases the geographical proximity of Samaria and Jerusalem, highlighting their shared history and the influence of events in one region on the other. It reveals the routes of ancient empires, the movement of populations, and the flow of trade, providing a context for understanding the historical development of both cities.
- Religious Significance: The map identifies the locations of key religious sites in both Samaria and Jerusalem, providing a visual understanding of the religious importance of these regions. It highlights the presence of synagogues, churches, and mosques, emphasizing the diverse religious traditions that have converged in these areas.
- Contemporary Conflict: The map illustrates the geographical realities of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, revealing the contested territories, settlements, and border lines. It provides a visual representation of the complexities of the conflict and the challenges of finding a peaceful solution.
FAQs: Delving Deeper into the Complexities of Samaria and Jerusalem
1. What is the current status of Samaria?
Samaria, located in the northern West Bank, is currently under Israeli control. The region is home to numerous Israeli settlements, which are considered illegal under international law by many countries. The Palestinian Authority claims Samaria as part of a future Palestinian state.
2. Why is Jerusalem considered a holy city?
Jerusalem holds immense religious significance for Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. It is considered the holiest city in Judaism, housing the Temple Mount, the site of the First and Second Temples. For Christians, Jerusalem is the site of Jesus Christ’s crucifixion and resurrection, making it a central location for pilgrimage and worship. Muslims revere Jerusalem as the third holiest city in Islam, with the Dome of the Rock, located on the Temple Mount, being a sacred site.
3. What are the main challenges to peace in the region?
The Israeli-Palestinian conflict, characterized by competing claims over land and resources, poses a significant challenge to peace in the region. The issue of Jerusalem, claimed by both Israelis and Palestinians as their capital, is particularly contentious. The presence of Israeli settlements in the West Bank, considered illegal by many countries, further complicates the situation.
4. What are the prospects for a peaceful resolution?
The path to a peaceful resolution in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict is complex and fraught with challenges. Negotiations have stalled, and there is a lack of trust between the two sides. However, there are ongoing efforts to find a two-state solution, with the establishment of an independent Palestinian state alongside Israel. Achieving a lasting peace will require significant concessions from both sides and a commitment to dialogue and compromise.
Tips for Understanding Samaria and Jerusalem:
- Engage with History: Explore the historical narratives of Samaria and Jerusalem, delving into the ancient empires that ruled these regions, the religious movements that emerged, and the conflicts that shaped their development.
- Study the Map: Use a map as a tool to understand the geographical relationships between Samaria and Jerusalem, the location of key religious sites, and the complexities of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
- Seek Diverse Perspectives: Engage with a range of perspectives on the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, listening to the voices of both Israelis and Palestinians, and exploring the complexities of the situation from multiple angles.
- Support Peace Efforts: Learn about and support organizations working towards a peaceful resolution of the conflict, promoting dialogue, understanding, and cooperation between Israelis and Palestinians.
Conclusion: Navigating a Complex Landscape
Samaria and Jerusalem, two cities intertwined in history and geography, stand as powerful symbols of the Middle East’s complex tapestry of identity and conflict. Understanding their historical significance, religious importance, and contemporary challenges is essential for navigating the region’s complexities. By engaging with their narratives, studying their maps, and seeking diverse perspectives, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the profound impact these cities have had on the world and the ongoing efforts to find a path towards peace and reconciliation.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through Time: Understanding the Historical and Geographical Significance of Samaria and Jerusalem. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
