A Comprehensive Exploration of the North Dakota-Minnesota Border: Geography, History, and Shared Connections
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Exploration of the North Dakota-Minnesota Border: Geography, History, and Shared Connections
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Exploration of the North Dakota-Minnesota Border: Geography, History, and Shared Connections. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Exploration of the North Dakota-Minnesota Border: Geography, History, and Shared Connections
![Minnesota [and] North Dakota Curtis Wright Maps](https://149725886.v2.pressablecdn.com/wp-content/uploads/map_07-05-21_300dpi_14.59x11.19_inv2753-scaled.jpg)
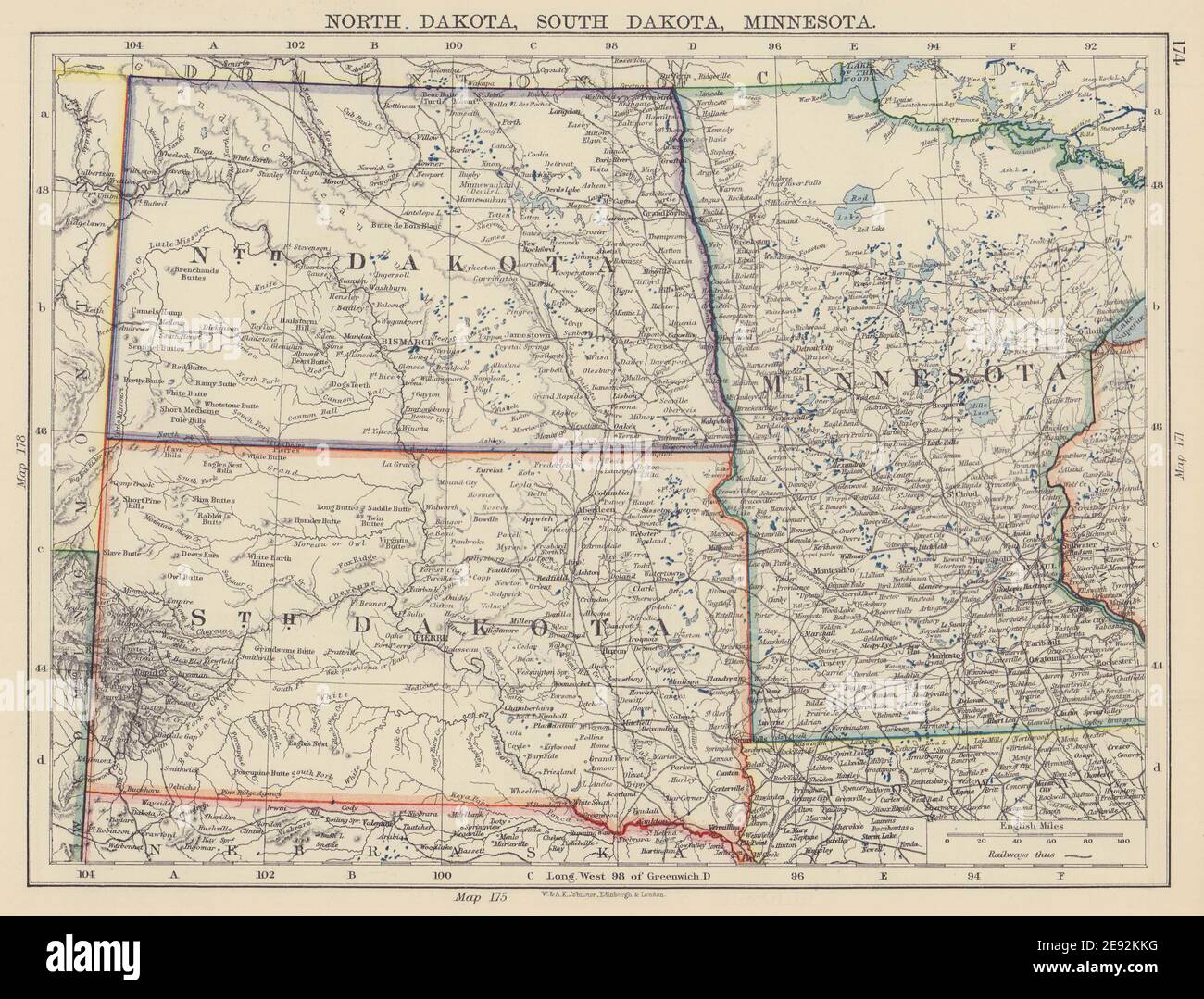
The border between North Dakota and Minnesota, a line drawn across the landscape, represents more than just a geographical division. It is a testament to the intertwined history, shared resources, and enduring cultural connections of two distinct yet closely linked states. Understanding the complexities of this border, its origins, and its impact on the region is essential to appreciating the unique character of both North Dakota and Minnesota.
A Geographical Perspective: Tracing the Border’s Path
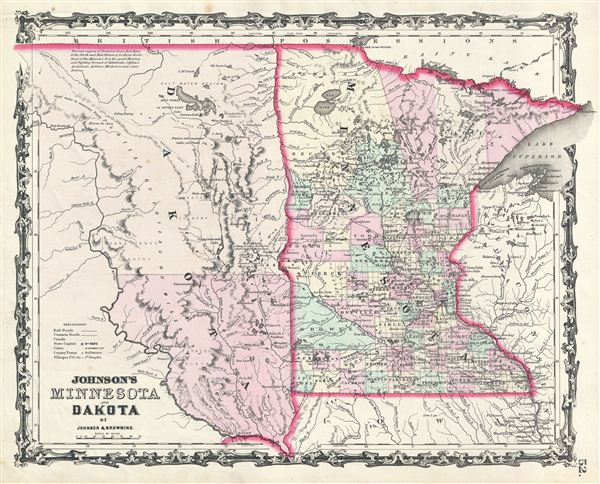
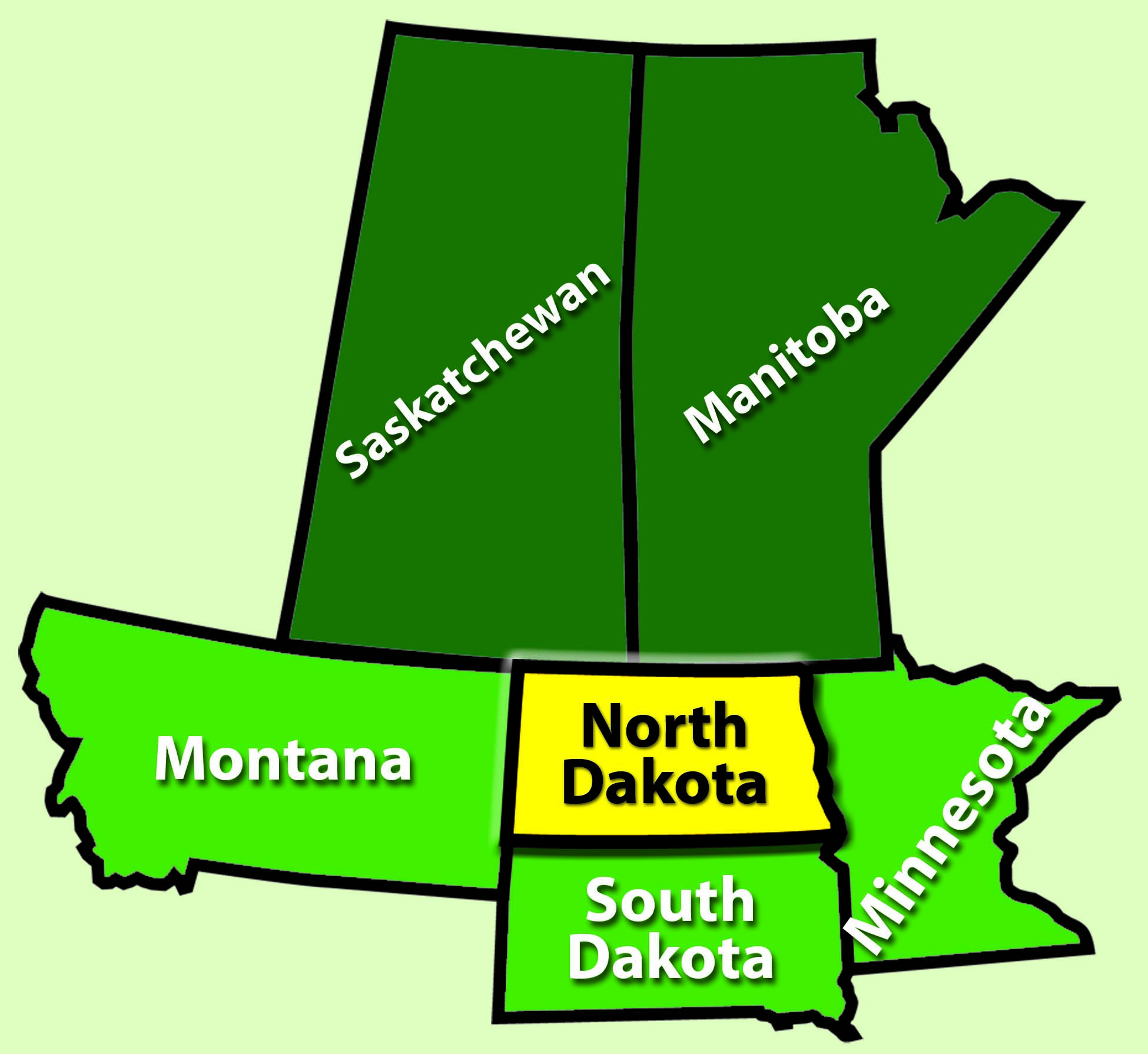
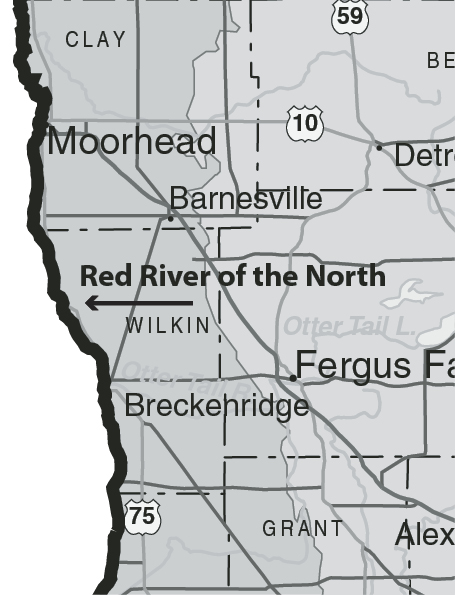
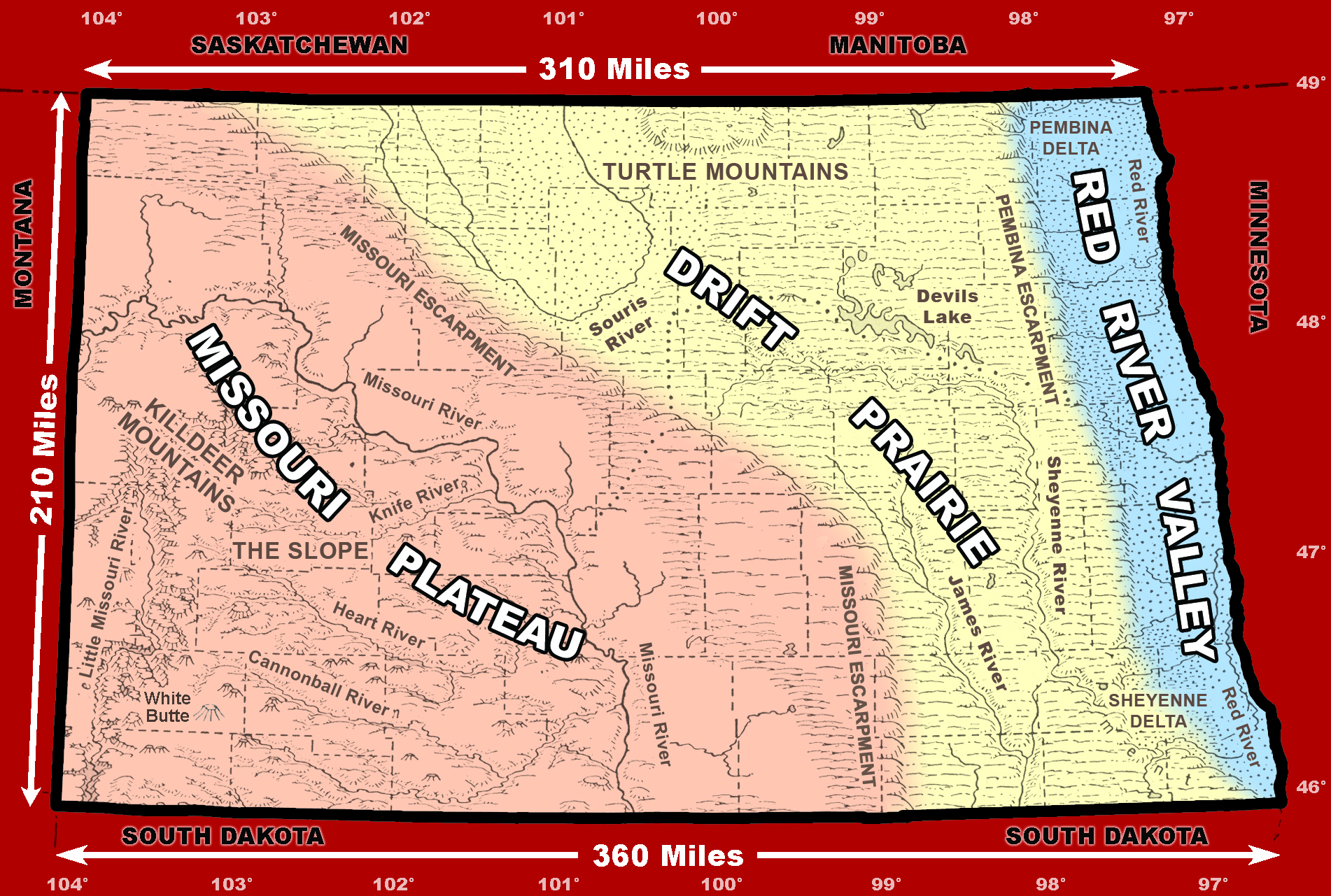
The North Dakota-Minnesota border stretches for approximately 350 miles, winding its way through diverse landscapes. Its path is defined by the Red River of the North, a meandering waterway that forms the eastern boundary of North Dakota. This river, a vital source of water and transportation throughout history, serves as a natural dividing line between the two states.
The border’s trajectory is not perfectly straight, reflecting the historical processes that shaped it. In the western portion, the border follows the 97th meridian, a line of longitude that was established as a key boundary during the westward expansion of the United States. This section of the border cuts through the prairie, marking a transition from the fertile farmlands of Minnesota to the more arid plains of North Dakota.
Historical Roots: From Exploration to Statehood
The history of the North Dakota-Minnesota border is deeply intertwined with the exploration and settlement of the region. In the 18th century, French explorers and fur traders navigated the Red River, establishing trade routes and claiming territories for their respective nations. This early exploration laid the groundwork for later settlement and the eventual establishment of state boundaries.
The formal establishment of the border can be traced back to the 1850s, when Minnesota became a territory and then a state. During this period, the Red River, already a significant waterway, was officially designated as the boundary between the two states. The 97th meridian was also incorporated as a part of the border, further solidifying the division between Minnesota and the newly established Dakota Territory (which later became North Dakota and South Dakota).
Shared Resources: The Significance of the Red River
The Red River of the North plays a pivotal role in the relationship between North Dakota and Minnesota. It serves as a crucial source of water for both states, supporting agriculture, industry, and communities along its banks. The river also provides transportation routes, facilitating trade and commerce between the two states.
The Red River’s importance has, however, also presented challenges. The river’s floodplains are prone to flooding, particularly during the spring thaw. These floods have caused significant damage and disruption to communities on both sides of the border, highlighting the need for cooperation and coordinated flood mitigation efforts.
Cultural Connections: A Tapestry of Shared Heritage
The border between North Dakota and Minnesota does not simply divide two states; it also connects two cultures. The region’s history has fostered a shared heritage, with both states exhibiting strong Scandinavian influences, evident in their architecture, traditions, and folklore.
The Red River Valley, the region encompassing the border, is characterized by a rich agricultural tradition. Farmers on both sides of the border have long shared knowledge, techniques, and resources, contributing to the region’s agricultural prosperity. This shared agricultural heritage has created a sense of community and interdependence, transcending political boundaries.
Economic Interdependence: A Border of Collaboration
The North Dakota-Minnesota border is not merely a geographical line; it is also a line of economic interdependence. The two states share vital resources, collaborate on infrastructure projects, and engage in cross-border trade. The energy sector, particularly oil production in North Dakota, has created significant economic ties with Minnesota, driving investment and employment opportunities.
The border region is also a center for agriculture, with both states contributing to the production of crops like wheat, corn, and soybeans. This shared agricultural focus fosters economic partnerships and strengthens the regional economy.
The Future of the Border: Challenges and Opportunities
The North Dakota-Minnesota border faces various challenges and opportunities in the 21st century. Climate change and its impact on water resources pose a significant concern, requiring collaborative efforts to manage the Red River’s flow and mitigate flood risks.
The border region also faces demographic shifts, with populations in rural areas experiencing decline. This trend necessitates innovative strategies to attract and retain residents, fostering economic growth and community vitality.
Despite these challenges, the border region offers opportunities for continued collaboration. The shared resources, cultural connections, and economic interdependence provide a foundation for regional development and prosperity. By working together, North Dakota and Minnesota can harness the strengths of their shared border to address challenges and seize opportunities.
FAQs about the North Dakota-Minnesota Border
1. What is the length of the North Dakota-Minnesota border?
The border between North Dakota and Minnesota is approximately 350 miles long.
2. What is the most significant geographical feature along the border?
The Red River of the North forms the eastern boundary of North Dakota and is a defining feature of the North Dakota-Minnesota border.
3. What historical events led to the establishment of the border?
The border was established through a combination of exploration, settlement, and statehood. French explorers and fur traders initially navigated the Red River, followed by settlement and the eventual establishment of Minnesota as a state and Dakota Territory.
4. What are the main shared resources between North Dakota and Minnesota?
The Red River of the North provides water resources for both states, supporting agriculture, industry, and communities. The border region also shares agricultural resources, contributing to the production of crops like wheat, corn, and soybeans.
5. What are the key cultural connections between the two states?
Both North Dakota and Minnesota share strong Scandinavian influences, evident in their architecture, traditions, and folklore. The region’s agricultural heritage has also fostered a sense of shared identity and community.
6. What are the major economic ties between North Dakota and Minnesota?
The energy sector, particularly oil production in North Dakota, has created significant economic ties with Minnesota. The border region is also a center for agriculture, with both states contributing to the production of crops.
7. What are some of the challenges facing the North Dakota-Minnesota border region?
Climate change and its impact on water resources, demographic shifts, and economic development are some of the challenges facing the border region.
8. What are some opportunities for the future of the border region?
The shared resources, cultural connections, and economic interdependence provide opportunities for regional development, collaboration, and economic growth.
Tips for Exploring the North Dakota-Minnesota Border
- Visit the Red River Valley: Explore the historical sites, agricultural landscapes, and charming towns along the Red River Valley.
- Visit the International Peace Garden: Located on the border, this garden symbolizes the peaceful relationship between the United States and Canada.
- Explore the Fort Union Trading Post National Historic Site: Located in North Dakota, this site offers insights into the fur trade era and the history of the region.
- Learn about the Scandinavian heritage: Visit museums and cultural centers to learn about the Scandinavian influences in the region.
- Attend local festivals and events: Immerse yourself in the local culture by attending festivals celebrating agriculture, history, and arts.
Conclusion
The North Dakota-Minnesota border is more than just a line on a map; it is a testament to the intertwined history, shared resources, and enduring cultural connections of two distinct yet closely linked states. Understanding the complexities of this border, its origins, and its impact on the region is essential to appreciating the unique character of both North Dakota and Minnesota. As the region faces challenges and opportunities in the 21st century, the border’s significance will only continue to grow, highlighting the importance of collaboration, shared resources, and cultural understanding.
![Minnesota [and] North Dakota Curtis Wright Maps](https://149725886.v2.pressablecdn.com/wp-content/uploads/map_07-05-21_300dpi_11.17x14.59_inv2753.1-scaled.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Exploration of the North Dakota-Minnesota Border: Geography, History, and Shared Connections. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
